This article needs additional citations for verification .(January 2018) |
Veterinary pharmacovigilance in the United Kingdom is overseen by the Veterinary Medicines Directorate (VMD). [1]
This article needs additional citations for verification .(January 2018) |
Veterinary pharmacovigilance in the United Kingdom is overseen by the Veterinary Medicines Directorate (VMD). [1]
The Pharmacovigilance Unit at the VMD monitors adverse events; [2] the monitoring carried out by this unit was previously known as the Suspect Adverse Reaction Surveillance Scheme, and is similar to the Yellow Card Scheme of pharmacovigilance for human medicine. The Pharmacovigilance Unit gathers information about suspected adverse events to veterinary medicines in both animals and humans, including suspected lack of expected efficacy, environmental problems, residues in foodstuffs. Anyone, including animal owners, can report suspected adverse events to the VMD, although veterinary surgeons submit most reports. [3]
The marketing authorisation holder of a medicine, that is, the company that has the licence for the medicine, is legally obliged to inform the VMD of any adverse events which are reported to them. The following must be reported by marketing authorisation holders within 15 days:
All other adverse events must be reported in a Periodic Safety Update Report. All SAEs (to animals and humans) should be reported by veterinary surgeons as this is considered good professional conduct (RCVS Guide to Professional Conduct).
Reporters can submit reports online. Hard copies of the reporting forms can also be requested from the VMD or downloaded and printed from the website.
The reports are monitored and analysed by the Pharmacovigilance team of the VMD, who make reports to the Veterinary Products Committee. Where the Secretary of State for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs considers, as a result of the evaluation of veterinary pharmacovigilance data that there is a significant safety concern, the marketing authorisation may be suspended, revoked or varied to restrict the indications, change the distribution category, amend the dose, add a contraindication, or add a new precautionary measure.
Pharmacovigilance, also known as drug safety, is the pharmaceutical science relating to the "collection, detection, assessment, monitoring, and prevention" of adverse effects with pharmaceutical products. The etymological roots for the word "pharmacovigilance" are: pharmakon and vigilare. As such, pharmacovigilance heavily focuses on adverse drug reactions (ADR), which are defined as any response to a drug which is noxious and unintended, including lack of efficacy. Medication errors such as overdose, and misuse and abuse of a drug as well as drug exposure during pregnancy and breastfeeding, are also of interest, even without an adverse event, because they may result in an adverse drug reaction.
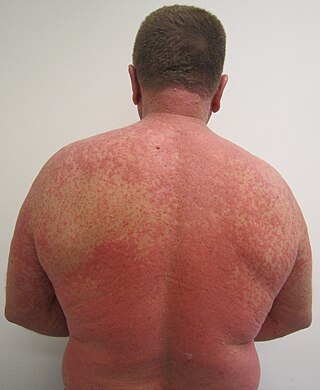
An adverse drug reaction (ADR) is a harmful, unintended result caused by taking medication. ADRs may occur following a single dose or prolonged administration of a drug or may result from the combination of two or more drugs. The meaning of this term differs from the term "side effect" because side effects can be beneficial as well as detrimental. The study of ADRs is the concern of the field known as pharmacovigilance. An adverse event (AE) refers to any unexpected and inappropriate occurrence at the time a drug is used, whether or not the event is associated with the administration of the drug. An ADR is a special type of AE in which a causative relationship can be shown. ADRs are only one type of medication-related harm. Another type of medication-related harm type includes not taking prescribed medications, known as non-adherence. Non-adherence to medications can lead to death and other negative outcomes. Adverse drug reactions require the use of a medication.

The European Medicines Agency (EMA) is an agency of the European Union (EU) in charge of the evaluation and supervision of pharmaceutical products. Prior to 2004, it was known as the European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products or European Medicines Evaluation Agency (EMEA).
The Veterinary Medicines Directorate (VMD) is an Executive Agency of the Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs (Defra) seeking to protect public health, animal health, the environment and promoting animal welfare by assuring the safety, quality and efficacy of veterinary medicines in the United Kingdom.
In pharmaceuticals, an adverse event (AE) is any untoward medical occurrence in a patient or clinical investigation subject administered a pharmaceutical product and which does not necessarily have a causal relationship with this treatment. An adverse event can therefore be any unfavourable and unintended symptom or sign or disease temporally associated with the use of a medicinal (investigational) product, whether or not related to the medicinal (investigational) product.
In drug development, serious adverse event (SAE) is defined as any untoward medical occurrence during a human drug trial that at any dose

Uppsala Monitoring Centre (UMC), located in Uppsala, Sweden, is the field name for the World Health Organization Collaborating Centre for International Drug Monitoring. UMC works by collecting, assessing and communicating information from member countries' national pharmacovigilance centres in regard to the benefits, harm, effectiveness and risks of drugs.
The Yellow Card Scheme is the United Kingdom's system for collecting information on suspected adverse drug reactions (ADRs) to medicines. The scheme allows the safety of the medicines and vaccines that are on the market to be monitored.
Postmarketing surveillance (PMS), also known as post market surveillance, is the practice of monitoring the safety of a pharmaceutical drug or medical device after it has been released on the market and is an important part of the science of pharmacovigilance. Since drugs and medical devices are approved on the basis of clinical trials, which involve relatively small numbers of people who have been selected for this purpose – meaning that they normally do not have other medical conditions which may exist in the general population – postmarketing surveillance can further refine, or confirm or deny, the safety of a drug or device after it is used in the general population by large numbers of people who have a wide variety of medical conditions.
EudraVigilance is the European data processing network and management system for reporting and evaluation of suspected adverse reactions to medicines which have been authorised or being studied in clinical trials in the European Economic Area (EEA). The European Medicines Agency (EMA) operates the system on behalf of the European Union (EU) medicines regulatory network.

EudraLex is the collection of rules and regulations governing medicinal products in the European Union.
The Clinical Trials Directive is a European Union directive that aimed at facilitating the internal market in medicinal products within the European Union, while at the same time maintaining an appropriate level of protection for public health. It seeks to simplify and harmonise the administrative provisions governing clinical trials in the European Community, by establishing a clear, transparent procedure.

Tepoxalin, sold under the brand name Zubrin among others, is a non-steroidal anti-flammatory drug (NSAIDs) generally used in veterinary medicine to reduce swelling in animals with osteoarthritis. In rare circumstances, tepoxalin can also be used in human pharmacology to relieve pain caused by musculoskeletal conditions such as arthritis and hip dysplasia.
The Commission on Human Medicines (CHM) is a committee of the UK's Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency. It was formed in October 2005, and assumed the responsibilities of the Medicines Commission and the Committee on Safety of Medicines. Membership in this various and extensive body is listed on a governmental website.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to clinical research:
In the European Union, the Qualified Person Responsible For Pharmacovigilance (QPPV) is an individual, usually an employee of a pharmaceutical company, who is personally responsible for the safety of the human pharmaceutical products marketed by that company in the EU. This function was established in 2004 by article 23 of regulation (EC) No 726/2004. The article establishes that the holder of a marketing authorization for a drug for human use must have a QPPV. When a company submits an application for permission to bring a medicinal product onto the market, the company submits a description of its system for monitoring the safety of the product in actual use and proof that the services of a QPPV are in place.

Syed Ziaur Rahman is a permanent member of 'Board of Trustees' and Chair of the Advisory Council, International Association of Medical Colleges (IAOMC). He also serves as Chairman, Department of Pharmacology, Jawaharlal Nehru Medical College, Aligarh, Elected Secretary of IAOMC and Society of Pharmacovigilance, India (SoPI).
VigiBase is a World Health Organization's (WHO) global Individual Case Safety Report (ICSR) database that contains ICSRs submitted by the participating member states enrolled under WHO's international drug monitoring programme. It is the single largest drug safety data repository in the world. Since 1978, the Uppsala Monitoring Centre on behalf of WHO, have been maintaining VigiBase.
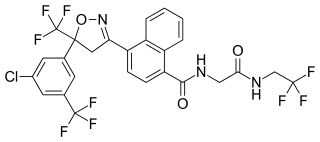
Afoxolaner (INN) is an insecticide and acaricide that belongs to the isoxazoline chemical compound group.
Official Medicines Control Laboratory (OMCL) is the term coined in Europe for a public institute in charge of controlling the quality of medicines and, depending on the country, other similar products (for example, medical devices). They are part of or report to national competent authorities (NCAs).