
The Scythians or Scyths in composition) and sometimes also referred to as the Pontic Scythians, were an ancient Eastern Iranic equestrian nomadic people who had migrated during the 9th to 8th centuries BC from Central Asia to the Pontic Steppe in modern-day Ukraine and Southern Russia, where they remained established from the 7th century BC until the 3rd century BC.
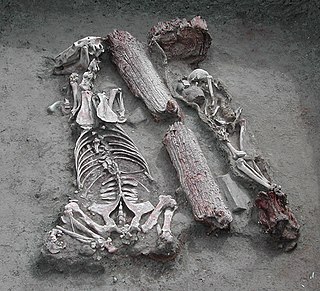
The Pazyrykburials are a number of Scythian (Saka) Iron Age tombs found in the Pazyryk Valley and the Ukok plateau in the Altai Mountains, Siberia, south of the modern city of Novosibirsk, Russia; the site is close to the borders with China, Kazakhstan and Mongolia.

A kurgan is a type of tumulus constructed over a grave, often characterized by containing a single human body along with grave vessels, weapons and horses. Originally in use on the Pontic–Caspian steppe, kurgans spread into much of Central Asia and Eastern, Southeast, Western and Northern Europe during the 3rd millennium BC.

Animal style art is an approach to decoration found from China to Northern Europe in the early Iron Age, and the barbarian art of the Migration Period, characterized by its emphasis on animal motifs. The zoomorphic style of decoration was used to decorate small objects by warrior-herdsmen, whose economy was based on breeding and herding animals, supplemented by trade and plunder. Animal art is a more general term for all art depicting animals.

Scytho-Siberian art is the art associated with the cultures of the Scytho-Siberian world, primarily consisting of decorative objects such as jewellery, produced by the nomadic tribes of the Eurasian Steppe, with the eastern edges of the region vaguely defined by ancient Greeks. The identities of the nomadic peoples of the steppes is often uncertain, and the term "Scythian" should often be taken loosely; the art of nomads much further east than the core Scythian territory exhibits close similarities as well as differences, and terms such as the "Scytho-Siberian world" are often used. Other Eurasian nomad peoples recognised by ancient writers, notably Herodotus, include the Massagetae, Sarmatians, and Saka, the last a name from Persian sources, while ancient Chinese sources speak of the Xiongnu or Hsiung-nu. Modern archaeologists recognise, among others, the Pazyryk, Tagar, and Aldy-Bel cultures, with the furthest east of all, the later Ordos culture a little west of Beijing. The art of these peoples is collectively known as steppes art.

Golden hats are a very specific and rare type of archaeological artifact from Bronze Age Europe. So far, four such objects are known. The objects are made of thin sheet gold and were attached externally to long conical and brimmed headdresses which were probably made of some organic material and served to stabilise the external gold leaf. The following conical golden hats are known as of 2012:

The Ziwiye hoard is a treasure hoard containing gold, silver, and ivory objects, also including a few gold pieces with the shape of human face, that was uncovered on in Ziwiyeh plat near Saqqez city in Kurdistan Province, Iran, in 1947.

A drinking horn is the horn of a bovid used as a drinking vessel. Drinking horns are known from Classical Antiquity, especially the Balkans, and remained in use for ceremonial purposes throughout the Middle Ages and the Early Modern period in some parts of Europe, notably in Germanic Europe, and in the Caucasus. Drinking horns remain an important accessory in the culture of ritual toasting in Georgia in particular, where they are known by the local name of kantsi.


The Oxus treasure is a collection of about 180 surviving pieces of metalwork in gold and silver, most relatively small, and around 200 coins, from the Achaemenid Persian period which were found by the Oxus river about 1877–1880. The exact place and date of the find remain unclear, but is often proposed as being near Kobadiyan. It is likely that many other pieces from the hoard were melted down for bullion; early reports suggest there were originally some 1500 coins, and mention types of metalwork that are not among the surviving pieces. The metalwork is believed to date from the sixth to fourth centuries BC, but the coins show a greater range, with some of those believed to belong to the treasure coming from around 200 BC. The most likely origin for the treasure is that it belonged to a temple, where votive offerings were deposited over a long period. How it came to be deposited is unknown.

The Bronze and Iron Age cultures in Poland are known mainly from archeological research. Early Bronze Age cultures in Poland began around 2400–2300 BCE, while the Iron Age commenced in approximately 750–700 BCE. The Iron Age archeological cultures no longer existed by the start of the Common Era. The subject of the ethnicity and linguistic affiliation of the groups living in Central Europe at that time is, given the absence of written records, speculative, and accordingly there is considerable disagreement. In Poland the Lusatian culture, spanning both the Bronze and Iron Ages, became particularly prominent. The most famous archeological finding from that period is the Biskupin fortified settlement (gord) on the lake from which it takes its name, representing the Lusatian culture of the early Iron Age.

Ancient Chinese glass refers to all types of glass manufactured in China prior to the Qing Dynasty (1644–1911). In Chinese history, glass played a peripheral role in arts and crafts, when compared to ceramics and metal work. The limited archaeological distribution and use of glass objects are evidence of the rarity of the material. Literary sources date the first manufacture of glass to the 5th century AD. However, the earliest archaeological evidence for glass manufacture in China comes from the Warring States period.

The Dacian bracelets are bracelets associated with the ancient people known as the Dacians, a distinct branch of the Thracians. These bracelets were used as ornaments, currency, high rank insignia and votive offerings Their ornamentations consist of many elaborate regionally distinct styles. Bracelets of various types were worn by Dacians, but the most characteristic piece of their jewelry was the large multi-spiral bracelets; engraved with palmettes towards the ends and terminating in the shape of an animal head, usually that of a snake.
Dacian art is the art associated with the peoples known as Dacians or North Thracians; The Dacians created an art style in which the influences of Scythians and the Greeks can be seen. They were highly skilled in gold and silver working and in pottery making. Pottery was white with red decorations in floral, geometric, and stylized animal motifs. Similar decorations were worked in metal, especially the figure of a horse, which was common on Dacian coins.

Central Asian art is visual art created in Central Asia, in areas corresponding to modern Kyrgyzstan, Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, Turkmenistan, Azerbaijan, Tajikistan, Afghanistan, Pakistan, and parts of modern Mongolia, China and Russia. The art of ancient and medieval Central Asia reflects the rich history of this vast area, home to a huge variety of peoples, religions and ways of life. The artistic remains of the region show a remarkable combinations of influences that exemplify the multicultural nature of Central Asian society. The Silk Road transmission of art, Scythian art, Greco-Buddhist art, Serindian art and more recently Persianate culture, are all part of this complicated history.

The Magdeburg Ivories are a set of 16 surviving ivory panels illustrating episodes of Christ's life. They were commissioned by Emperor Otto I, probably to mark the dedication of Magdeburg Cathedral, and the raising of the Magdeburg see to an archbishopric in 968. The panels were initially part of an unknown object in the cathedral that has been variously conjectured to be an antependium or altar front, a throne, door, pulpit, or an ambon; traditionally this conjectural object, and therefore the ivories as a group, has been called the Magdeburg Antependium. This object is believed to have been dismantled or destroyed in the 1000s, perhaps after a fire in 1049.

The Scythian culture was an Iron Age archaeological culture which flourished on the Pontic-Caspian steppe in Eastern Europe from about 700 BC to 200 AD. It is associated with the Scythians, Cimmerians, and other peoples inhabiting the region of Scythia, and was part of the wider Scytho-Siberian world.
From the 7th to the 3rd century BC, the Scythian people of the Pontic Steppes produced and adopted a wide arrangement of clothing. The clothing of the Scythians was formulated in response to the nomadic, highly mobile lifestyle of the early Scythian era and the sedentary lifestyle of later Scythian kingdoms. Much of what is known about Scythian attire comes from the remains of clothing found in Scythian burial sites.

Tovsta Mohyla is an ancient Scythian burial mound or kurgan and treasure discovered in 1971 by the Ukrainian archaeologist Borys Mozolevski. The Tovsta Mohyla burial mound, meaning "fat barrow", is located in southern Ukraine near the city of Pokrov in Dnipro region.

















