
In computing, a database is an organized collection of data or a type of data store based on the use of a database management system (DBMS), the software that interacts with end users, applications, and the database itself to capture and analyze the data. The DBMS additionally encompasses the core facilities provided to administer the database. The sum total of the database, the DBMS and the associated applications can be referred to as a database system. Often the term "database" is also used loosely to refer to any of the DBMS, the database system or an application associated with the database.
Structured Query Language (SQL) is a domain-specific language used to manage data, especially in a relational database management system (RDBMS). It is particularly useful in handling structured data, i.e., data incorporating relations among entities and variables.
Object–relational mapping in computer science is a programming technique for converting data between a relational database and the memory of an object-oriented programming language. This creates, in effect, a virtual object database that can be used from within the programming language.

Db2 is a family of data management products, including database servers, developed by IBM. It initially supported the relational model, but was extended to support object–relational features and non-relational structures like JSON and XML. The brand name was originally styled as DB2 until 2017, when it changed to its present form.
Codd's twelve rules are a set of thirteen rules proposed by Edgar F. Codd, a pioneer of the relational model for databases, designed to define what is required from a database management system in order for it to be considered relational, i.e., a relational database management system (RDBMS). They are sometimes referred to as "Codd's Twelve Commandments".

The Florissant Formation is a sedimentary geologic formation outcropping around Florissant, Teller County, Colorado. The formation is noted for the abundant and exceptionally preserved insect and plant fossils that are found in the mudstones and shales. Based on argon radiometric dating, the formation is Eocene in age and has been interpreted as a lake environment. The fossils have been preserved because of the interaction of the volcanic ash from the nearby Thirtynine Mile volcanic field with diatoms in the lake, causing a diatom bloom. As the diatoms fell to the bottom of the lake, any plants or animals that had recently died were preserved by the diatom falls. Fine layers of clays and muds interspersed with layers of ash form "paper shales" holding beautifully-preserved fossils. The Florissant Fossil Beds National Monument is a national monument established to preserve and study the geology and history of the area.
InterSystems Caché is a commercial operational database management system from InterSystems, used to develop software applications for healthcare management, banking and financial services, government, and other sectors. Customer software can use the database with object and SQL code. Caché also allows developers to directly manipulate its underlying data structures: hierarchical arrays known as M technology.
The Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS) is a United States program for vaccine safety, co-managed by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). VAERS is a postmarketing surveillance program, collecting information about adverse events that occur after administration of vaccines to ascertain whether the risk–benefit ratio is high enough to justify continued use of any particular vaccine.
Object–relational impedance mismatch is a set of difficulties going between data in relational data stores and data in domain-driven object models. Relational Database Management Systems (RDBMS) is the standard method for storing data in a dedicated database, while object-oriented (OO) programming is the default method for business-centric design in programming languages. The problem lies in neither relational databases nor OO programming, but in the conceptual difficulty mapping between the two logic models. Both logical models are differently implementable using database servers, programming languages, design patterns, or other technologies. Issues range from application to enterprise scale, whenever stored relational data is used in domain-driven object models, and vice versa. Object-oriented data stores can trade this problem for other implementation difficulties.
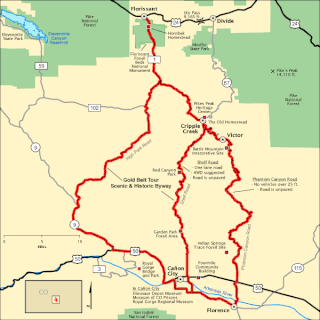
The Gold Belt Tour Scenic and Historic Byway is a National Scenic Byway, a Back Country Byway, and a Colorado Scenic and Historic Byway located in Fremont and Teller counties, Colorado, USA. The byway is named for the Gold Belt mining region. The Cripple Creek Historic District is a National Historic Landmark. The byway forms a three-legged loop with the Phantom Canyon Road, the Shelf Road, and the High Park Road (paved).

Waikato Environment for Knowledge Analysis (Weka) is a collection of machine learning and data analysis free software licensed under the GNU General Public License. It was developed at the University of Waikato, New Zealand and is the companion software to the book "Data Mining: Practical Machine Learning Tools and Techniques".
Structure mining or structured data mining is the process of finding and extracting useful information from semi-structured data sets. Graph mining, sequential pattern mining and molecule mining are special cases of structured data mining.
Electronic discovery refers to discovery in legal proceedings such as litigation, government investigations, or Freedom of Information Act requests, where the information sought is in electronic format. Electronic discovery is subject to rules of civil procedure and agreed-upon processes, often involving review for privilege and relevance before data are turned over to the requesting party.
An entity–attribute–value model (EAV) is a data model optimized for the space-efficient storage of sparse—or ad-hoc—property or data values, intended for situations where runtime usage patterns are arbitrary, subject to user variation, or otherwise unforeseeable using a fixed design. The use-case targets applications which offer a large or rich system of defined property types, which are in turn appropriate to a wide set of entities, but where typically only a small, specific selection of these are instantiated for a given entity. Therefore, this type of data model relates to the mathematical notion of a sparse matrix. EAV is also known as object–attribute–value model, vertical database model, and open schema.
Database preservation usually involves converting the information stored in a database to a form likely to be accessible in the long term as technology changes, without losing the initial characteristics of the data.

Tomasz Imieliński is a Polish-American computer scientist, most known in the areas of data mining, mobile computing, data extraction, and search engine technology. He is currently a professor of computer science at Rutgers University in New Jersey, United States.

Kathleen M. Carley is an American computational social scientist specializing in dynamic network analysis. She is a professor in the School of Computer Science in the Carnegie Mellon Institute for Software Research at Carnegie Mellon University and also holds appointments in the Tepper School of Business, the Heinz College, the Department of Engineering and Public Policy, and the Department of Social and Decision Sciences.
Informix Corporation, formerly Informix Software, Inc., was a software company located in Menlo Park, California. It was a developer of relational database software for computers using the Unix, Microsoft Windows, and Apple Macintosh operating systems.
Piranha is a text mining system. It was developed for the United States Department of Energy (DOE) by Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL). The software processes free-text documents and shows relationships amongst them, a technique valuable across numerous data domains, from health care fraud to national security. The results are presented in clusters of prioritized relevance. Piranha uses the term frequency/inverse corpus frequency term weighting method which provides strong parallel processing of textual information, thus the ability to analyze large document sets.

Mark S. Boguski was an American pathologist specializing in computational analysis and structural biology. In 2001, he was elected to both the U.S. National Academy of Medicine and the American College of Medical Informatics.







