See also
| This disambiguation page lists articles associated with the title Vilna. If an internal link led you here, you may wish to change the link to point directly to the intended article. |
Vilna may refer to:
| This disambiguation page lists articles associated with the title Vilna. If an internal link led you here, you may wish to change the link to point directly to the intended article. |

The Talmud is the central text of Rabbinic Judaism and the primary source of Jewish religious law (halakha) and Jewish theology. Until the advent of modernity, in nearly all Jewish communities, the Talmud was the centerpiece of Jewish cultural life and was foundational to "all Jewish thought and aspirations", serving also as "the guide for the daily life" of Jews.

Elijah ben Solomon Zalman, known as the Vilna Gaon or Elijah of Vilna, or by his Hebrew acronym HaGra or Elijah Ben Solomon, was a Talmudist, halakhist, kabbalist, and the foremost leader of misnagdic (non-hasidic) Jewry of the past few centuries. He is commonly referred to in Hebrew as ha-Gaon he-Chasid mi-Vilna, "the pious genius from Vilnius".

The Vilnia is a river in Lithuania. Its source is near the village of Vindžiūnai, 5 km south of Šumskas, at the Lithuanian-Belarusian border. The Vilnia is 79.6 km long and its basin covers 624 sq. km. For 13 km its flow makes the Belarus-Lithuania border, and the remaining 69 km are in Lithuania until it flows into the Neris River at Vilnius. Eventually, its waters, via the Neris's drainage into the Neman River, flow into the Baltic Sea. Its confluence with the Neris lies within the city of Vilnius, and the river's name was probably the source of the city's name.
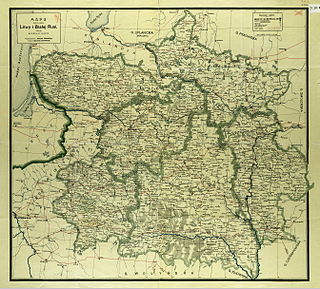
Northwestern Krai was an unofficial subdivision (krai) of the Russian Empire in the territories of the former Grand Duchy of Lithuania. The center was in Vilna city. Northwestern Krai together with the Southwestern Krai formed the Western Krai.

Western Krai is an unofficial name of the westernmost parts of the Russian Empire, excluding the territory of Congress Poland. The term embodies lands annexed by the Russian Empire during subsequent partitions of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth at the end of the 18th century, in 1772, 1793 and 1795. This area is known in Poland as Ziemie Zabrane but most often they are referred to in Polish historiography and in common talk as part of Zabór Rosyjski.

This article is about the administrative divisions of Lithuania.

Kražiai is a historic town in Lithuania, located in the Kelmė district municipality, between Varniai (32 km) and Raseiniai (44 km), on the Kražantė River. The old town of Kražiai is an archeological and urban monument.

The Vilna Edition of the Talmud, printed in Vilna, Lithuania, is by far the most common printed edition of the Talmud still in use today as the basic text for Torah study in yeshivas and by all scholars of Judaism.
The uses of heraldry in Belarus is used by government bodies, subdivisions of the national government, organizations, corporations and by families.

Naujoji Vilnia is a neighborhood in eastern Vilnius, Lithuania situated along the banks of the Vilnia River. It has eldership status. According to the 2011 census, the municipality has a population of 31,933.

The Vilna Governorate or Government of Vilnius was a governorate of the Russian Empire created after the Third Partition of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth in 1795. It was part of the Lithuanian General Governorate, which was called the Vilnius General Governorate after 1830, and was attached to the Northwestern Krai. The seat was in Vilnius, where the Governors General resided.

The Grodno Governorate, was a governorate of the Russian Empire. It was part of the Vilna Governorate-General and Northwestern Krai.

Kovno Governorate or Government of Kaunas was a governorate (guberniya) of the Russian Empire. Its capital was Kaunas. It was formed on 18 December 1842 by Tsar Nicholas I from the western part of Vilna Governorate, and the order was carried out on 1 July 1843. It was part of the Vilna Governorate-General and Northwestern Krai. The governorate included almost the entire Lithuanian region of Samogitia and the northern part of Aukštaitija.

Following three consecutive partitions of Poland carried out between 1772 and 1795, the sovereign state known as the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth disappeared from the map of Europe. In 1918 following the end of World War One, the territories of the former state re-emerged as the states of Poland and Lithuania among others. In the intervening period, the territory of the former Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth was split between the Austrian Empire, the Kingdom of Prussia and the Russian Empire. These powers subdivided the territories that they gained and created new toponyms for the territories conquered. The subdivisions created were complicated by changes within those empires as well as by the periodic establishment of other forms of the quasi-Polish provinces led by a foreign head of state.
The Lithuania Governorate was a short-lived governorate (guberniya) of the Russian Empire in 1796–1801.

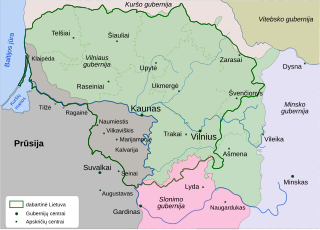
Ethnographic Lithuania was an early 20th-century concept that define Lithuanian territories as a significant part of the territories that belonged to Grand Duchy of Lithuania and Lithuanians as all people living on them, regardless of whether those people spoke the Lithuanian language and considered themselves Lithuanian. The concept was in contrast to those of "historic Lithuania", the territories of the Duchy, and the "linguistic Lithuania", the area where Lithuanian language was overwhelmingly spoken.

Vilna Gaon Jewish State Museum is a Lithuanian museum dedicated to the historical and cultural heritage of Lithuanian Jewry.
The Romm publishing house, a publisher of Jewish religious literature from 1788 to 1940, was especially known for its 1886 Vilna Talmud, which still serves as a definitive edition.
The following is a timeline of the history of the city of Vilnius, Lithuania.

Vilna Governorate-General, known as Lithuania Governorate-General before 1830, was a Governorate-General of the Russian Empire from 1794 to 1912. It primarily encompassed the Vilna, Grodno, and Kovno Governorates. Governors General were also commanders of the Vilna Military District. According to the Russian Empire Census, the Governorate-General had 4,754,000 residents in 1897.