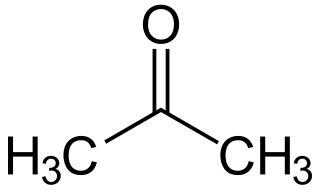
In organic chemistry, a ketone is an organic compound with the structure R−C(=O)−R', where R and R' can be a variety of carbon-containing substituents. Ketones contain a carbonyl group −C(=O)−. The simplest ketone is acetone, with the formula (CH3)2CO. Many ketones are of great importance in biology and industry. Examples include many sugars (ketoses), many steroids, and the solvent acetone.

Anthracene is a solid polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) of formula C14H10, consisting of three fused benzene rings. It is a component of coal tar. Anthracene is used in the production of the red dye alizarin and other dyes. Anthracene is colorless but exhibits a blue (400–500 nm peak) fluorescence under ultraviolet radiation.
The Friedel–Crafts reactions are a set of reactions developed by Charles Friedel and James Crafts in 1877 to attach substituents to an aromatic ring. Friedel–Crafts reactions are of two main types: alkylation reactions and acylation reactions. Both proceed by electrophilic aromatic substitution.
Dimethylformamide is an organic compound with the chemical formula HCON(CH3)2. Its structure is HC(=O)−N(−CH3)2. Commonly abbreviated as DMF, this colourless liquid is miscible with water and the majority of organic liquids. DMF is a common solvent for chemical reactions. Dimethylformamide is odorless, but technical-grade or degraded samples often have a fishy smell due to impurity of dimethylamine. Dimethylamine degradation impurities can be removed by sparging samples with an inert gas such as argon or by sonicating the samples under reduced pressure. As its name indicates, it is structurally related to formamide, having two methyl groups in the place of the two hydrogens. DMF is a polar (hydrophilic) aprotic solvent with a high boiling point. It facilitates reactions that follow polar mechanisms, such as SN2 reactions.
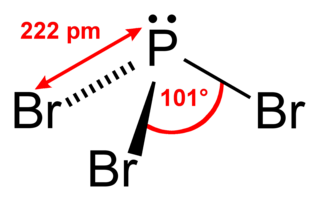
Phosphorus tribromide is a colourless liquid with the formula PBr3. The liquid fumes in moist air due to hydrolysis and has a penetrating odour. It is used in the laboratory for the conversion of alcohols to alkyl bromides.
The Duff reaction or hexamine aromatic formylation is a formylation reaction used in organic chemistry for the synthesis of benzaldehydes with hexamine as the formyl carbon source. The method is generally inefficient. The reaction is named after James Cooper Duff.
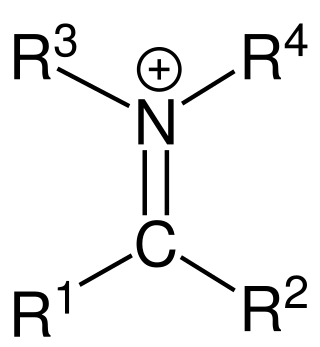
In organic chemistry, an iminium cation is a polyatomic ion with the general structure [R1R2C=NR3R4]+. They are common in synthetic chemistry and biology.

Phosphoryl chloride is a colourless liquid with the formula POCl3. It hydrolyses in moist air releasing phosphoric acid and fumes of hydrogen chloride. It is manufactured industrially on a large scale from phosphorus trichloride and oxygen or phosphorus pentoxide. It is mainly used to make phosphate esters.

The Reimer–Tiemann reaction is a chemical reaction used for the ortho-formylation of phenols. with the simplest example being the conversion of phenol to salicylaldehyde. The reaction was first reported by Karl Reimer and Ferdinand Tiemann.

The Dakin oxidation (or Dakin reaction) is an organic redox reaction in which an ortho- or para-hydroxylated phenyl aldehyde (2-hydroxybenzaldehyde or 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde) or ketone reacts with hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) in base to form a benzenediol and a carboxylate. Overall, the carbonyl group is oxidised, whereas the H2O2 is reduced.
Stephen aldehyde synthesis, a named reaction in chemistry, was invented by Henry Stephen (OBE/MBE). This reaction involves the preparation of aldehydes (R-CHO) from nitriles (R-CN) using tin(II) chloride (SnCl2), hydrochloric acid (HCl) and quenching the resulting iminium salt ([R-CH=NH2]+Cl−) with water (H2O). During the synthesis, ammonium chloride is also produced.
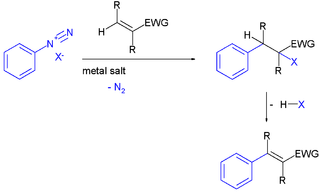
The Meerwein arylation is an organic reaction involving the addition of an aryl diazonium salt (ArN2X) to an electron-poor alkene usually supported by a metal salt. The reaction product is an alkylated arene compound. The reaction is named after Hans Meerwein, one of its inventors who first published it in 1939.
In organic synthesis, cyanation is the attachment or substitution of a cyanide group on various substrates. Such transformations are high-value because they generate C-C bonds. Furthermore nitriles are versatile functional groups.

Trimethylsilyl trifluoromethanesulfonate (TMSOTf) is an organosilicon compound with the formula (CH3)3SiO3SCF3. It is a colorless moisture-sensitive liquid. It is the trifluoromethanesulfonate derivative of trimethylsilyl. It is mainly used to activate ketones and aldehydes in organic synthesis.
Rieche formylation is a type of formylation reaction. The substrates are electron rich aromatic compounds, such as mesitylene or phenols, with dichloromethyl methyl ether acting as the formyl source. The catalyst is titanium tetrachloride and the workup is acidic. The reaction is named after Alfred Rieche who discovered it in 1960.

Imidoyl chlorides are organic compounds that contain the functional group RC(NR')Cl. A double bond exist between the R'N and the carbon centre. These compounds are analogues of acyl chloride. Imidoyl chlorides tend to be highly reactive and are more commonly found as intermediates in a wide variety of synthetic procedures. Such procedures include Gattermann aldehyde synthesis, Houben-Hoesch ketone synthesis, and the Beckmann rearrangement. Their chemistry is related to that of enamines and their tautomers when the α hydrogen is next to the C=N bond. Many chlorinated N-heterocycles are formally imidoyl chlorides, e.g. 2-chloropyridine, 2, 4, and 6-chloropyrimidines.

Hydroxylamine-O-sulfonic acid (HOSA) or aminosulfuric acid is the inorganic compound with molecular formula H3NO4S that is formed by the sulfonation of hydroxylamine with oleum. It is a white, water-soluble and hygroscopic, solid, commonly represented by the condensed structural formula H2NOSO3H, though it actually exists as a zwitterion and thus is more accurately represented as +H3NOSO3−. It is used as a reagent for the introduction of amine groups (–NH2), for the conversion of aldehydes into nitriles and alicyclic ketones into lactams (cyclic amides), and for the synthesis of variety of nitrogen-containing heterocycles.
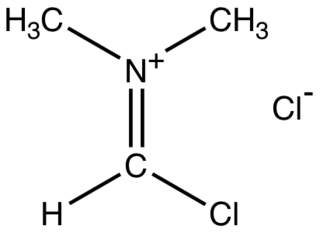
The Vilsmeier reagent is an organic compound with the formula [(CH3)2NCHCl]Cl. It is a salt consisting of the N,N-dimethyliminium cation ([(CH3)2N=CHCl]+) and chloride anion. Depending on the particular reaction, the anion can vary. In typical POCl3-based reactions, the anion is PO2Cl2−. The iminium cation [(CH3)2N=CHCl]+ is the reactive component of interest. This iminium species is a derivative of the imidoyl chloride CH3N=CHCl. Analogues of this particular reagent are generated when tertiary amides other than DMF are treated with POCl3.

Anthracene-9-carbaldehyde is the most common monoaldehyde derivative of anthracene. It is a yellow solid that is soluble in common organic solvents. It is prepared by Vilsmeier formylation of anthracene. The compound is also used as a building block for supramolecular assemblies. Hydrogenation of 9-anthracenecarboxaldehyde gives 9-anthracenemethanol.
Hydroxymethylation is a chemical reaction that installs the CH2OH group. The transformation can be implemented in many ways and applies to both industrial and biochemical processes.















