Related Research Articles

The shehnai, often translated into English as clarinet, is a musical instrument originating from the Indian subcontinent. It is made of wood, with a double reed at one end and a metal or wooden flared bell at the other end. Its sound is thought to create and maintain a sense of auspiciousness and sanctity and as a result, is one of the nine instruments found in the royal court. The shehnai is similar to South India's nadaswaram.

The word Yona in Pali and the Prakrits, and the analogue Yavana in Sanskrit and Yavanar in Tamil, were words used in Ancient India to designate Greek speakers. "Yona" and "Yavana" are transliterations of the Greek word for "Ionians", who were probably the first Greeks to be known in India.
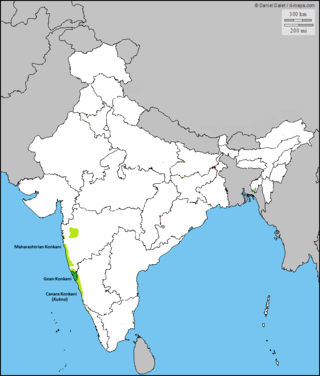
Konkani is an Indo-Aryan language spoken by the Konkani people, primarily in the Konkan region, along the western coast of India. It is one of the 22 scheduled languages mentioned in the Indian Constitution, and the official language of the Indian state of Goa. It is also spoken in Karnataka, Maharashtra, Kerala, Gujarat as well as Damaon, Diu & Silvassa.

The history of Goa dates back to prehistoric times, though the present-day state of Goa was only established as recently as 1987. In spite of being India's smallest state by area, Goa's rich history is both long and diverse. It shares a lot of similarities with Indian history, especially with regard to colonial influences and a multi-cultural aesthetic.
The Konkani people are an Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group native to the Konkan region of the Indian subcontinent who speak various dialects of the Konkani language. Konkani is the state language of Goa and also spoken by populations in Karnataka, Maharashtra, Damaon and Kerala. Other Konkani speakers are found in Gujarat state. A large percentage of Konkani people are bilingual.

The Shilahara/Shelara Kingdom was a royal dynasty that established itself in northern and southern Konkan in 8th century CE, present-day Mumbai and Southern Maharashtra (Kolhapur) during the Rashtrakuta period.
The caste system in Goa consists of various Jātis or sub-castes found among Hindus belonging to the four varnas, as well as those outside of them. A variation of the traditional Hindu caste system was also retained by the Goan Catholic community.

Shantadurga is the most popular form of the Hindu goddess Durga revered in Goa, India, as well some parts of Karnataka. She is a form of the ancient Mother goddess known as Santeri. She is worshipped in almost all villages of Goa as an ant hill. This is seen in some temples dedicated to Shantadurga.

The Saptakoteshwar temple at Narve in Goa, India, is considered to be one of the six great sites of temples of Shiva in the Konkan area.

The Daivadnya,, is a community from Goa and Karnataka, who claim to have descended from Vishwakarma. Although they claim themselves to be Brahmin, but these claims are not accepted by others including local Brahmin castes. They are native to the Konkan and are mainly found in the states of Goa and Damaon, Canara, coastal Maharashtra, and Kerala. Daivadnyas in the state of Maharashtra and Karnataka are classified by National Commission for Backward Classes as an Other Backward Class.
The Kudumbi, also referred to as the Kunubis, the Kurumbi, or the Kunbi, are traditionally a Konkani-speaking farming community residing in Kerala, India.

The Kadambas of Goa were a dynasty during the Late Classical period on the Indian subcontinent, who ruled Goa from the 10th to the 14th century CE. They took over the territories of the Shilaharas and ruled them at first from Chandor, later making Gopakapattana their capital.

A sanna is a spongy, steamed, and savoury unfilled dumpling originally made of red rice, black lentil and coconut in the Konkan region, by the western coast of the Indian subcontinent. They originated in Goa and Damaon, Mangalore, Bombay and Bassein (Vasai), and are especially popular among Goans, both the Goan Hindus and Goan Christians, and also among the Konkani migrants outside Konkan in Karachi, Sindh, Gujarat, Karnataka and Kerala. They are also loved by the people of the Konkan division, such as the Kuparis of the Bombay East Indian community.

Raigad Lok Sabha constituency is one of the 48 Lok Sabha constituencies of Maharashtra state in western India. It is a new constituency, created in 2008 as a part of the implementation of the delimitation of the parliamentary constituencies based on the recommendations of the Delimitation Commission of India constituted on 12 July 2002. The constituency first held elections in 2009 and its first member of parliament was Anant Geete of Shiv Sena who was also re-elected in the 2014 elections. In the 2019 General Elections Sunil Tatkare of NCP won the seat by margin of 31,438 votes defeating the incumbent Geetee who was also a Union Cabinet minister.

The 1967 Goa status referendum popularly known as the Goa Opinion Poll was a referendum held in newly annexed union territory of Goa and Damaon in India, on 16 January 1967, to deal with the Konkani language agitation and to decide the future of Goa.
Gomantak Maratha Samaj is a Hindu community found in the Indian state of Goa. They are known as Nutan Maratha Samaj in the Sindhudurg district of Maharashtra and Naik Maratha Samaj in Maharashtra, Uttara Kannada district of Karnataka, also Telangana respectively.
This article details the history of Raigad district. Raigad District is a district in the Indian state of Maharashtra. It is located in the Konkan region. The Kulaba district was renamed after Raigad, the fort which was the former capital of the Maratha ruler Chatrapati Shivaji Maharaj. The fort is surrounded by dense forest in the interior regions of the district, on a west-facing spur of the Western Ghats of Sahyadri range. The name was changed during the regime of Chief Minister A. R. Antulay on 1 January 1981.

Roman Catholic Kshatriyas are a modern Christianised caste among Goan, Bombay East Indian, Mangalorean, Kudali & Karwari Catholics. They are patrilineal descendants of Kshatriya and Vaishya Vani converts to the Latin Church, in parts of the Konkan region that were under Portuguese Goan rule. They are known as Chardo in Goan Konkani, Charodi in Canarese Konkani & as Sandori or Purvoe in Damanese and Maharashtrian Konkani and other Bombay East Indian dialects.

Uday Laxmikant Bhembre is an Indian lawyer, Konkani writer and former member of the Goa, Daman and Diu Legislative Assembly. He is noted for his role as the editor of the Konkani daily, Sunaparant, and as a Konkani language activist. Bhembre is also widely known as the lyricist of the famed Goan Konkani language song Channeache Rati.
The Konkani language agitations were a series of protests and demonstrations in India, concerning the uncertain future of the Konkani language. They were held by Goans in the former territory of Goa, Daman and Diu; then under the administration of the Maharashtrawadi Gomantak Party (MGP). The protests involved citizen journalism, student activism & political demonstrations. The civil unrest ceased when official status for Konkani in the Devnagari script was granted.
References
- 1 2 Archaeological Survey of Western India, 1879, p 2, Dr J. Burgess.
- ↑ Maharashtra State gazetteers, 1964, p 57, Maharashtra (India), Gazetteers Dept, Maharashtra (India).
- ↑ Maharashtra State gazetteers, 1964, p 57, Maharashtra (India). Gazetteers Dept, Maharashtra (India)
- ↑ The Cultural History of Goa from 10000 B.C.-1352 A.D., 1986, p 206, Anant Ramkrishna Sinai Dhume - Goa, Daman and Diu (India)
- ↑ Gazetteer of the Union Territory Goa, Daman and Diu, 1979, p 66, Vithal Trimbak Gune, Goa, Daman and Diu (India).
- ↑ Also: K. C. Chaṭṭopādhyāya Memorial Volume, 1975, p 24, Kshetresh Chandra Chattopadhyaya - India Civilization.
- ↑ Indica, 2004, p 65, Saint Xavier's College, Bombay Heras Institute of Indian History and Culture.
- ↑ Kleine Schriften, 1985, p 352, Otto Stein, Friedrich Wilhelm.
- ↑ Epigraphia Indika, II, p 97. no. 7=L. 176; p 387, no. 287= L.472; The Indian Historical Quarterly, 1949, Vol 25-26, p 127.
- ↑ Buddhism in Malwa, 1976, p 53, S. M. Pahadiya - Buddhism.
- ↑ The Indian Historical Quarterly, 1949, Vol 25-26, p 127.
- ↑ Jīvana Tathā Saṃskr̥ti, 1976, Ānandapriya, Vidyālaṅkāra Śaṅkaradeva, Vedālaṅkāra Dalīpa, Yaśodabahana Paramāra.