
Color or colour is the visual perception based on the electromagnetic spectrum. Though color is not an inherent property of matter, color perception is related to an object's light absorption, reflection, emission spectra and interference. For most humans, colors are perceived in the visible light spectrum with three types of cone cells (trichromacy). Other animals may have a different number of cone cell types or have eyes sensitive to different wavelength, such as bees that can distinguish ultraviolet, and thus have a different color sensitivity range. Animal perception of color originates from different light wavelength or spectral sensitivity in cone cell types, which is then processed by the brain.
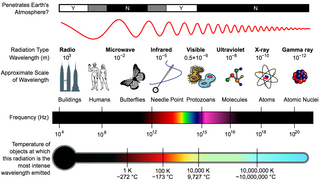
The electromagnetic spectrum is the full range of electromagnetic radiation, organized by frequency or wavelength. The spectrum is divided into separate bands, with different names for the electromagnetic waves within each band. From low to high frequency these are: radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays. The electromagnetic waves in each of these bands have different characteristics, such as how they are produced, how they interact with matter, and their practical applications.

Infrared is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) in the spectral band between microwaves and visible light. It is invisible to the human eye. IR is generally understood to encompass wavelengths from around 750 nm to 1000 μm.

Light or visible light is electromagnetic radiation that can be perceived by the human eye. Visible light is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400–700 nanometres (nm), corresponding to frequencies of 750–420 terahertz, between the infrared and the ultraviolet.

The visible spectrum is the band of the electromagnetic spectrum that is visible to the human eye. Electromagnetic radiation in this range of wavelengths is called visible light. The optical spectrum is sometimes considered to be the same as the visible spectrum, but some authors define the term more broadly, to include the ultraviolet and infrared parts of the electromagnetic spectrum as well.

Invisibility is the state of an object that cannot be seen. An object in this state is said to be invisible. The phenomenon is studied by physics and perceptual psychology.

Night vision is the ability to see in low-light conditions, either naturally with scotopic vision or through a night-vision device. Night vision requires both sufficient spectral range and sufficient intensity range. Humans have poor night vision compared to many animals such as cats, dogs, foxes and rabbits, in part because the human eye lacks a tapetum lucidum, tissue behind the retina that reflects light back through the retina thus increasing the light available to the photoreceptors.
Naked eye, also called bare eye or unaided eye, is the practice of engaging in visual perception unaided by a magnifying, light-collecting optical instrument, such as a telescope or microscope, or eye protection.

Photometry is the science of the measurement of light, in terms of its perceived brightness to the human eye. It is distinct from radiometry, which is the science of measurement of radiant energy in terms of absolute power. In modern photometry, the radiant power at each wavelength is weighted by a luminosity function that models human brightness sensitivity. Typically, this weighting function is the photopic sensitivity function, although the scotopic function or other functions may also be applied in the same way. The weightings are standardized by the CIE and ISO.

In astronomy, limiting magnitude is the faintest apparent magnitude of a celestial body that is detectable or detected by a given instrument.

The stroboscopic effect is a visual phenomenon caused by aliasing that occurs when continuous rotational or other cyclic motion is represented by a series of short or instantaneous samples at a sampling rate close to the period of the motion. It accounts for the "wagon-wheel effect", so-called because in video, spoked wheels sometimes appear to be turning backwards.
Survival is the act of surviving; to stay living
Luminous efficacy is a measure of how well a light source produces visible light. It is the ratio of luminous flux to power, measured in lumens per watt in the International System of Units (SI). Depending on context, the power can be either the radiant flux of the source's output, or it can be the total power consumed by the source. Which sense of the term is intended must usually be inferred from the context, and is sometimes unclear. The former sense is sometimes called luminous efficacy of radiation, and the latter luminous efficacy of a light source or overall luminous efficacy.
History is the study of the past.

In geometry, an isovist is the volume of space visible from a given point in space, together with a specification of the location of that point. It is a geometric concept coined by Clifford Tandy in 1967 and further refined by the architect Michael Benedikt.
Blue Light or Blue light may refer to:

Underwater vision is the ability to see objects underwater, and this is significantly affected by several factors. Underwater, objects are less visible because of lower levels of natural illumination caused by rapid attenuation of light with distance passed through the water. They are also blurred by scattering of light between the object and the viewer, also resulting in lower contrast. These effects vary with wavelength of the light, and color and turbidity of the water. The vertebrate eye is usually either optimised for underwater vision or air vision, as is the case in the human eye. The visual acuity of the air-optimised eye is severely adversely affected by the difference in refractive index between air and water when immersed in direct contact. Provision of an airspace between the cornea and the water can compensate, but has the side effect of scale and distance distortion. The diver learns to compensate for these distortions. Artificial illumination is effective to improve illumination at short range.
Transparency, transparence or transparent most often refer to:
Temporal light artefacts (TLAs) are undesired effects in the visual perception of a human observer induced by temporal light modulations. Two well-known examples of such unwanted effects are flicker and stroboscopic effect. Flicker is a directly visible light modulation at relatively low frequencies and small intensity modulation levels. Stroboscopic effect may become visible for a person when a moving object is illuminated by modulated light at somewhat higher frequencies (>80 Hz) and larger intensity variations.











