Related Research Articles
Eiffel is an object-oriented programming language designed by Bertrand Meyer and Eiffel Software. Meyer conceived the language in 1985 with the goal of increasing the reliability of commercial software development; the first version becoming available in 1986. In 2005, Eiffel became an ISO-standardized language.

Design by contract (DbC), also known as contract programming, programming by contract and design-by-contract programming, is an approach for designing software.

Visual Basic, originally called Visual Basic .NET (VB.NET), is a multi-paradigm, object-oriented programming language, implemented on .NET, Mono, and the .NET Framework. Microsoft launched VB.NET in 2002 as the successor to its original Visual Basic language, the last version of which was Visual Basic 6.0. Although the ".NET" portion of the name was dropped in 2005, this article uses "Visual Basic [.NET]" to refer to all Visual Basic languages released since 2002, in order to distinguish between them and the classic Visual Basic. Along with C# and F#, it is one of the three main languages targeting the .NET ecosystem. As of March 11, 2020, Microsoft announced that evolution of the VB.NET language has concluded.
In computer programming, unit testing is a software testing method by which individual units of source code—sets of one or more computer program modules together with associated control data, usage procedures, and operating procedures—are tested to determine whether they are fit for use.
xUnit is the collective name for several unit testing frameworks that derive their structure and functionality from Smalltalk's SUnit. SUnit, designed by Kent Beck in 1998, was written in a highly structured object-oriented style, which lent easily to contemporary languages such as Java and C#. Following its introduction in Smalltalk the framework was ported to Java by Kent Beck and Erich Gamma and gained wide popularity, eventually gaining ground in the majority of programming languages in current use. The names of many of these frameworks are a variation on "SUnit", usually replacing the "S" with the first letter in the name of their intended language. These frameworks and their common architecture are collectively known as "xUnit".

F# is a functional-first, general purpose, strongly typed, multi-paradigm programming language that encompasses functional, imperative, and object-oriented programming methods. F# is most often used as a cross-platform Common Language Infrastructure (CLI) language on .NET, but it can also generate JavaScript and graphics processing unit (GPU) code.
Test-driven development (TDD) is a software development process relying on software requirements being converted to test cases before software is fully developed, and tracking all software development by repeatedly testing the software against all test cases. This is as opposed to software being developed first and test cases created later.
Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) consists of a set of extensions to the Windows Driver Model that provides an operating system interface through which instrumented components provide information and notification. WMI is Microsoft's implementation of the Web-Based Enterprise Management (WBEM) and Common Information Model (CIM) standards from the Distributed Management Task Force (DMTF).

NUnit is an open-source unit testing framework for the .NET Framework and Mono. It serves the same purpose as JUnit does in the Java world, and is one of many programs in the xUnit family.
Metadata, in the Common Language Infrastructure (CLI), refers to certain data structures embedded within the Common Intermediate Language (CIL) code that describes the high-level structure of the code. Metadata describes all classes and class members that are defined in the assembly, and the classes and class members that the current assembly will call from another assembly. The metadata for a method contains the complete description of the method, including the class, the return type and all of the method parameters.

C# is a general-purpose, multi-paradigm programming language. C# encompasses static typing, strong typing, lexically scoped, imperative, declarative, functional, generic, object-oriented (class-based), and component-oriented programming disciplines.
In software engineering, behavior-driven development (BDD) is an agile software development process that encourages collaboration among developers, quality assurance testers, and customer representatives in a software project. It encourages teams to use conversation and concrete examples to formalize a shared understanding of how the application should behave. It emerged from test-driven development (TDD). Behavior-driven development combines the general techniques and principles of TDD with ideas from domain-driven design and object-oriented analysis and design to provide software development and management teams with shared tools and a shared process to collaborate on software development.
C# and Visual Basic .NET are the two primary languages used to program on the .NET Framework.
Microsoft Build Engine, better known as MSBuild, is a free and open-source build tool set for managed code as well as native C++ code and was part of .NET Framework. Visual Studio depends on MSBuild, but not the vice versa. Visual Studio Application Lifecycle Management depends on MSBuild to perform team builds via Azure DevOps Server.

EiffelStudio is a development environment for the Eiffel programming language developed and distributed by Eiffel Software.
This article describes the syntax of the C# programming language. The features described are compatible with .NET Framework and Mono.

Microsoft Visual Studio is an integrated development environment (IDE) from Microsoft. It is used to develop computer programs, as well as websites, web apps, web services and mobile apps. Visual Studio uses Microsoft software development platforms such as Windows API, Windows Forms, Windows Presentation Foundation, Windows Store and Microsoft Silverlight. It can produce both native code and managed code.
In computer science, marshalling or marshaling is the process of transforming the memory representation of an object into a data format suitable for storage or transmission. It is typically used when data must be moved between different parts of a computer program or from one program to another.
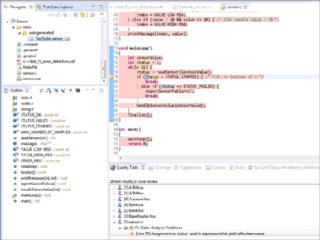
Parasoft C/C++test is an integrated set of tools for testing C and C++ source code that software developers use to analyze, test, find defects, and measure the quality and security of their applications. It supports software development practices that are part of development testing, including static code analysis, dynamic code analysis, unit test case generation and execution, code coverage analysis, regression testing, runtime error detection, requirements traceability, and code review. It's a commercial tool that supports operation on Linux, Windows, and Solaris platforms as well as support for on-target embedded testing and cross compilers.
Infrastructure as code (IaC) is the process of managing and provisioning computer data centers through machine-readable definition files, rather than physical hardware configuration or interactive configuration tools. The IT infrastructure managed by this process comprises both physical equipment, such as bare-metal servers, as well as virtual machines, and associated configuration resources. The definitions may be in a version control system. It can use either scripts or declarative definitions, rather than manual processes, but the term is more often used to promote declarative approaches.
References
- ↑ "Visual Studio 2010 Express – No tests, please". 13 April 2010.