
An emergency position-indicating radiobeacon station is a distress radiobeacon, a tracking transmitter that is triggered during an accident. These are detected by satellites. The system is monitored by an international consortium of rescue services, COSPAS-SARSAT. The basic purpose of this system is to help rescuers find survivors within the so-called "golden day" during which the majority of survivors can usually be saved.

9-1-1, also written 911, is an emergency telephone number for the North American Numbering Plan (NANP), one of eight N11 codes. Like other emergency numbers around the world, this number is intended for use in emergency circumstances only, and using it for any other purpose is a crime in certain jurisdictions.
Ten-codes, officially known as ten signals, are brevity codes used to represent common phrases in voice communication, particularly by law enforcement and in Citizens Band (CB) radio transmissions. The police version of ten-codes is officially known as the APCO Project 14 Aural Brevity Code.
Specific Area Message Encoding (SAME) is the protocol used to encode the Emergency Alert System (EAS) and NOAA Weather Radio (NWR) in the U.S. and Weatheradio Canada in Canada. It is also used to set off receivers in Mexico City and surrounding areas as part of the Mexican Seismic Alert System (SASMEX).

NOAA Weather Radio is an automated 24-hour network of VHF FM weather radio stations in the United States that broadcast weather information directly from a nearby National Weather Service office. The routine programming cycle includes local or regional weather forecasts, synopsis, climate summaries, synopsis or zone/lake/coastal waters forecasts. During severe conditions the cycle is shortened into: hazardous weather outlooks, short-term forecasts, special weather statements or tropical weather summaries. It occasionally broadcasts other non-weather related events such as national security statements, natural disaster information, environmental and public safety statements sourced from the Federal Communications Commission's (FCC) Emergency Alert System. NOAA Weather Radio uses automated broadcast technology that allows for the recycling of segments featured in one broadcast cycle seamlessly into another and more regular updating of segments to each of the transmitters. It also speeds up the warning transmitting process.
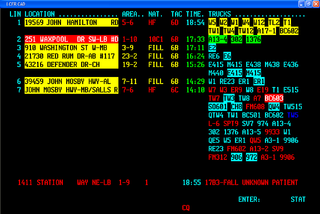
Computer-aided dispatch (CAD), also called computer-assisted dispatch, is a method of dispatching taxicabs, couriers, field service technicians, mass transit vehicles or emergency services assisted by computer. It can either be used to send messages to the dispatchee via a mobile data terminal (MDT) and/or used to store and retrieve data. A dispatcher may announce the call details to field units over a two-way radio. Some systems communicate using a two-way radio system's selective calling features. CAD systems may send text messages with call-for-service details to alphanumeric pagers or wireless telephony text services like SMS. The central idea is that persons in a dispatch center are able to easily view and understand the status of all units being dispatched. CAD provides displays and tools so that the dispatcher has an opportunity to handle calls-for-service as efficiently as possible.

A call box or callbox is a box containing a special-purpose direct line telephone or other telecommunications device, which has been used by various industries and institutions as a way for employees or clients at a remote location to contact a central dispatch office.

Marine VHF radio refers to the radio frequency range between 156 and 174 MHz, inclusive. The "VHF" signifies the very high frequency of the range. In the official language of the International Telecommunication Union the band is called the VHF maritime mobile band. In some countries additional channels are used, such as the L and F channels for leisure and fishing vessels in the Nordic countries.

Base station is – according to the International Telecommunication Union's (ITU) Radio Regulations (RR) – a "land station in the land mobile service."

Professional mobile radio are person-to-person two-way radio voice communications systems which use portable, mobile, base station, and dispatch console radios. PMR radio systems are based on such standards as MPT-1327, TETRA, APCO 25, and DMR which are designed for dedicated use by specific organizations, or standards such as NXDN intended for general commercial use. These systems are used by police, fire, ambulance, and emergency services, and by commercial firms such as taxis and delivery services. Most systems are half-duplex, in which multiple radios share a common radio channel, and only one can transmit at a time. Transceivers are normally in receive mode, the user presses a push-to-talk button on his microphone when he wants to talk, which turns on his transmitter and turns off his receiver. They use channels in the VHF and UHF bands, giving them a limited range, usually 3 to 20 miles depending on terrain. Output power is typically limited to 4 watts. Repeaters installed on tall buildings, hills or mountain peaks are used to increase the range of systems.

A public-safety answering point (PSAP), sometimes called "public-safety access point", is a call center in Canada and the United States responsible for answering calls to an emergency telephone number for police, firefighting, and ambulance services. Trained telephone operators are also usually responsible for dispatching these emergency services. Most PSAPs are now capable of caller location for landline calls, and many can handle mobile phone locations as well, where the mobile phone company has a handset location system. Some can also use voice broadcasting where outgoing voice mail can be sent to many phone numbers at once, in order to alert people to a local emergency such as a chemical spill.

A weather radio is a specialized radio receiver that is designed to receive a public broadcast service, typically from government-owned radio stations, dedicated to airing weather reports on a continual basis, with the routine weather reports being interrupted by emergency weather reports whenever needed. Weather radios are typically equipped with a standby alerting function—if the radio is muted or tuned to another band and a severe weather bulletin is transmitted, it can automatically sound an alarm and/or switch to a pre-tuned weather channel for emergency weather information.
MDC, also known as Stat-Alert, MDC-1200 and MDC-600, is a Motorola two-way radio low-speed data system using audio frequency shift keying, (AFSK). MDC-600 uses a 600 baud data rate. MDC-1200 uses a 1,200 baud data rate. Systems employ either one of the two baud rates. Mark and space tones are 1,200 Hz and 1,800 Hz. The data are sent in bursts over the radio system's voice channel.

The Motorola Minitor is a portable, analog, receive only, voice pager typically carried by fire, rescue, and EMS personnel to alert of emergencies. The Minitor, slightly smaller than a pack of cigarettes, is carried on a person and usually left in selective call mode. When the unit is activated, the pager sounds a tone alert, followed by an announcement from a dispatcher alerting the user of a situation. After activation, the pager remains in monitor mode much like a scanner, and monitors transmissions on that channel until the unit is reset back into selective call mode either manually, or automatically after a set period of time, depending on programming.
Resources of the Los Angeles Police Department.
Next Generation 9-1-1 refers to an initiative aimed at updating the 9-1-1 service infrastructure in the United States and Canada to improve public emergency communications services in a growingly wireless mobile society. In addition to calling 9-1-1 from a phone, it intends to enable the public to transmit text, images, video and data to the 9-1-1 center. The initiative also envisions additional types of emergency communications and data transfer. This NG9-1-1 infrastructure is intended to replace the current services over time. The National Emergency Number Association (NENA) first identified the need for NG9-1-1 in 2000, and started development actions in 2003, and is nearing full definition and standards for NG9-1-1. Since 2006, the US Department of Transportation (DOT) in the United States and the Canadian Radio-television and Telecommunications Commission (CRTC) in Canada have been leading their respective initiatives, which include research and development projects aimed at advancing NG9-1-1. On January 24, 2013, the CRTC announced the first step toward a Canadian implementation of NG9-1-1 and, in March 2016, began a consultation with the public to discuss what services should be offered, who will play a role in offering these services and how these services should be paid for. Several US states have implemented versions of NG9-1-1, as of October 2013.
An emergency communication system (ECS) is any system that is organized for the primary purpose of supporting one-way and two-way communication of emergency information between both individuals and groups of individuals. These systems are commonly designed to convey information over multiple types of devices, from signal lights to text messaging to live, streaming video, forming a unified communication system intended to optimize communications during emergencies. Contrary to emergency notification systems, which generally deliver emergency information in one direction, emergency communication systems are typically capable of both initiating and receiving information between multiple parties. These systems are often made up of both input devices, sensors, and output/communication devices. Therefore, the origination of information can occur from a variety of sources and locations, from which the system will disseminate that information to one or more target audiences.
4G eLTE is technology based on the LTE standard, the lower case e referring to a Huawei proprietary derivative of the LTE standard that is intended to provide wireless broadband data access with peak downlink levels of 50Mbit/s and 20Mbit/s uplink per site in 5 MHz 10 MHz and 15 MHz frequencies..
















