
GnaeusMarcius Coriolanus was a Roman general who is said to have lived in the 5th century BC. He received his toponymic cognomen "Coriolanus" following his courageous actions during a Roman siege of the Volscian city of Corioli. He was subsequently exiled from Rome, and led troops of Rome's enemy the Volsci to besiege the city.
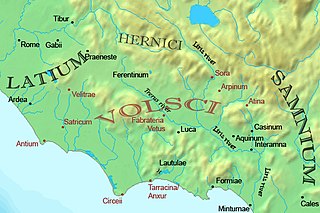
The Volsci were an Italic tribe, well known in the history of the first century of the Roman Republic. At the time they inhabited the partly hilly, partly marshy district of the south of Latium, bounded by the Aurunci and Samnites on the south, the Hernici on the east, and stretching roughly from Norba and Cora in the north to Antium in the south. Rivals of Rome for several hundred years, their territories were taken over by and assimilated into the growing republic by 300 BC. Rome's first emperor Augustus was of Volscian descent.

Dionysius of Halicarnassus was a Greek historian and teacher of rhetoric, who flourished during the reign of Emperor Augustus. His literary style was atticistic – imitating Classical Attic Greek in its prime.

Coriolanus is a tragedy by William Shakespeare, believed to have been written between 1605 and 1608. The play is based on the life of the legendary Roman leader Caius Marcius Coriolanus. Shakespeare worked on it during the same years he wrote Antony and Cleopatra, making them his last two tragedies.

Agrippa Menenius Lanatus was a consul of the Roman Republic in 503 BC, with Publius Postumius Tubertus. He was victorious over the Sabines and was awarded a triumph which he celebrated on 4 April, 503 BC. According to Livy, he also led Roman troops against the Latin town of Pometia. In some traditions he and his colleague also completed a census during their consulship.

Veturia was a Roman matron, the mother of the possibly legendary Roman general Gnaeus Marcius Coriolanus. According to Plutarch her name was Volumnia.

Volumnia is a character in William Shakespeare's play Coriolanus, the mother of Caius Martius Coriolanus. She plays a large role in Coriolanus' life, encouraging him in his military success and urging him to seek political office. When the people of Rome put her son in exile and he joins their military enemies, she manages to persuade him not to besiege Rome and becomes a heroine to the city.
Valeria was a name used in ancient Rome for women of the gens Valeria. Notable figures include:

Coriolanus is a 2011 British film adaptation of William Shakespeare's tragedy Coriolanus. It is directed by and stars Ralph Fiennes as the title character, with Gerard Butler as Tullus Aufidius, Vanessa Redgrave as Volumnia, and Brian Cox as Menenius. This is Fiennes' directorial debut. It places Shakespeare's original text and plot into a contemporary, pseudo-Balkan setting, reminiscent of the Yugoslav Wars.

Thunder of Battle is a 1964 Italian historical drama film set in Rome in 493 BC. The plot is an adaptation of the Roman legend about the general who won great victories for the Romans over their enemies the Volscians, but was then forced into exile by his political enemies at home.

Roman mythology is the body of myths of ancient Rome as represented in the literature and visual arts of the Romans. One of a wide variety of genres of Roman folklore, Roman mythology may also refer to the modern study of these representations, and to the subject matter as represented in the literature and art of other cultures in any period. Roman mythology draws from the mythology of the Italic peoples and ultimately from Proto-Indo-European mythology.

Virgilia is the wife of Coriolanus in William Shakespeare's play Coriolanus (1607–1610), in which same play Volumnia is his mother.
The Roman–Volscian wars were a series of wars fought between the Roman Republic and the Volsci, an ancient Italic people. Volscian migration into southern Latium led to conflict with that region's old inhabitants, the Latins under leadership of Rome, the region's dominant city-state. By the late 5th century BC, the Volsci were increasingly on the defensive and by the end of the Samnite Wars had been incorporated into the Roman Republic. The ancient historians devoted considerable space to Volscian wars in their accounts of the early Roman Republic, but the historical accuracy of much of this material has been questioned by modern historians.
Attius Tullius was a well-respected and influential political and military leader of the Volsci in the early fifth century BC. According to Plutarch, who calls him Tullus Aufidius, his home town was Antium. Tullius sheltered the exiled Roman hero Gaius Marcius Coriolanus, then incited a war with Rome, in which he and Coriolanus led the Volscian forces. He appears in William Shakespeare's tragedy Coriolanus under the name of Tullus Aufidius.
The Temple of Fortuna Muliebris was a temple in ancient Rome dedicated by Proculus Verginius Tricostus Rutilus in 486 BC to the goddess Fortuna and located at the fourth milestone of the Via Latina. It was founded on behalf of the Roman women who opposed the war of Gaius Marcius Coriolanus and the Volsci against Rome, commemorating their role in ending Coriolanus' advance on the city. The temple was dedicated in 486 BCE after the war and was formally founded in 493 BCE. Aside from some inscriptions recording restoration work in the Roman imperial period, no remains of the temple exist and the date it went into disuse is unknown.
Gens Volumnia was an ancient Roman patrician family of Etruscan origin, attested as early as the seventh century BC. It is known firstly from Volumnia, wife of Coriolanus, an illustrious person who lived in the 5th century BC; secondly, from a Publius Volumnius Gallus, who served as consul as early as 461 BC.

Volumnia Cytheris was an ancient Roman actress and mimae dancer. She is foremost known as the mistress of several famous Romans.
Volumnia is a character in Shakespeare's Coriolanus
Tertia was an ancient Roman actress and dancer.










