Related Research Articles

New Britain is the largest island in the Bismarck Archipelago, part of the Islands Region of Papua New Guinea. It is separated from New Guinea by a northwest corner of the Solomon Sea and from New Ireland by St. George's Channel. The main towns of New Britain are Rabaul/Kokopo and Kimbe. The island is roughly the size of Taiwan. While the island was part of German New Guinea, it was named Neupommern.

Rabaul is a township in East New Britain province, on the island of New Britain, in the country of Papua New Guinea. It lies about 600 kilometres to the east of the island of New Guinea. Rabaul was the provincial capital and most important settlement in the province until it was destroyed in 1994 by falling ash from a volcanic eruption in its harbor.
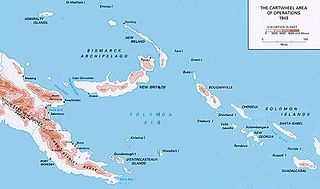
Operation Cartwheel (1943–1944) was a major military operation for the Allies in the Pacific theatre of World War II. Cartwheel was an operation aimed at neutralising the major Japanese base at Rabaul. The operation was directed by the Supreme Allied Commander in the South West Pacific Area (SWPA), General Douglas MacArthur, whose forces had advanced along the northeast coast of New Guinea and occupied nearby islands. Allied forces from the Pacific Ocean Areas command, under Admiral Chester W. Nimitz, advanced through the Solomon Islands toward Bougainville. The Allied forces involved were from Australia, the Netherlands, New Zealand, the US and various Pacific Islands.

The Allies of World War II conducted an air attack upon a cruiser force at the major Japanese base of Rabaul in November 1943. In response to the Allied invasion of Bougainville, the Japanese had brought a strong cruiser force down from Truk, their major naval base in the Caroline Islands about 800 miles north of Rabaul, to Rabaul in preparation for a night engagement against the Allied supply and support shipping. Allied carrier- and land-based planes attacked the Japanese ships, airfields, and port facilities on the island of New Britain to protect the Allied amphibious invasion of Bougainville. As a result of the Rabaul raids, the Japanese naval forces could no longer threaten the landings. The success of the raid began to change the strongly held belief that carrier-based air forces could not challenge land-based air forces.

The Battle of Rabaul, also known by the Japanese as Operation R, was fought on the island of New Britain in the Australian Territory of New Guinea, in January and February 1942. It was a strategically significant defeat of Allied forces by Japan in the Pacific campaign of World War II, with the Japanese invasion force quickly overwhelming the small Australian garrison, the majority of which was either killed or captured. Hostilities on the neighbouring island of New Ireland are usually considered to be part of the same battle. Rabaul was significant because of its proximity to the Japanese territory of the Caroline Islands, site of a major Imperial Japanese Navy base on Truk.

The Vitu Islands are a volcanic group with an area of 37 sq mi (96 km²) located in the Bismarck Sea off New Britain, in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. They are not technically part of the Bismarck Archipelago. Administratively they are part of Papua New Guinea. Formerly called the French Islands, the group is sometimes known as the Witu Islands.
Unserdeutsch, or Rabaul Creole German, is a German-based creole language that originated in Papua New Guinea as a lingua franca. The substrate language is assumed to be Tok Pisin, while the majority of the lexicon is from German.

The Territory of New Guinea was an Australian administered territory on the island of New Guinea from 1914 until 1975. In 1949, the Territory and the Territory of Papua were established in an administrative union by the name of the Territory of Papua and New Guinea. That administrative union was renamed as Papua New Guinea in 1971. Notwithstanding that it was part of an administrative union, the Territory of New Guinea at all times retained a distinct legal status and identity until the advent of the Independent State of Papua New Guinea.

The New Britain campaign was a World War II campaign fought between Allied and Imperial Japanese forces. The campaign was initiated by the Allies in late 1943 as part of a major offensive which aimed to neutralise the important Japanese base at Rabaul, the capital of New Britain, and was conducted in two phases between December 1943 and the end of the war in August 1945.

Kokopo is the capital of East New Britain in Papua New Guinea. It is administered under Kokopo-Vunamami Urban LLG.

Harl Pease Jr. was a United States Army Air Corps officer and a recipient of the United States military's highest award, the Medal of Honor, for his actions during World War II. He was the namesake for Pease Air Force Base, now Pease Air National Guard Base.

The Gazelle Peninsula is a large peninsula in northeastern East New Britain, Papua New Guinea located on the island of New Britain within the Bismarck Archipelago, situated in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. The Rabaul caldera is located on the northern tip of the peninsula. Upon the Gazelle Peninsula are the Baining Mountains, of which the highest point is Mount Sinewit at 2,063 metres (6,768 ft). The Gazelle Peninsula houses Vulcan Crater and Mount Tavurvur, both of which conducted volcanic activity in the 20th and 21st centuries and have provided extremely fertile soils. The body of the Gazelle Peninsula is about 80 kilometers. The southern isthmus upon which the Gazelle Peninsula is connected to the main body of East New Britain is reduced to about 32 kilometers.
Vunakanau Airfield was an aerodrome located near Vunakanau, East New Britain, Papua New Guinea. The airfield was constructed as a Royal Australian Air Force aerodrome and consisted of an unpaved single runway during World War II. The airfield was captured during the battle of Rabaul in 1942 by the Imperial Japanese and was extensively modified and expanded. Vunakanau was later neutralized by Allied air bombing from 1944.

The Action off Bougainville was a naval and air engagement on the South Pacific Theater of World War II near Bougainville, Papua New Guinea on 20 February 1942. A United States Navy aircraft carrier task force on its way to raid the Imperial Japanese military base at Rabaul, New Britain was attacked by a force of land-based bombers of the Imperial Japanese Navy. The US task force was commanded by Admiral Wilson Brown and the Japanese aircraft forces were under the command of Eiji Gotō.

John Margrave Lerew, DFC was an officer and pilot in the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) during World War II, and later a senior manager in the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO). As commander of No. 24 Squadron, based in New Britain, he became famous in the annals of Air Force history for his irreverent response to orders by headquarters in Australia during the Battle of Rabaul in January 1942. After his squadron was directed to assist in repelling the invading Japanese fleet with its one serviceable bomber, and to keep its damaged airfield open, Lerew signalled headquarters with the ancient Latin phrase supposedly used by gladiators honouring their Emperor: "Morituri vos salutamus". He also defied an order to abandon his staff, and organised their escape from Rabaul.

The 2/22nd Battalion was an infantry battalion of the Australian Army. Raised as part of the Second Australian Imperial Force for service during World War II, the battalion formed part of the 23rd Brigade, attached to the 8th Division. It was captured by the Japanese during the Battle of Rabaul in 1942. After being captured, the battalion was not re-raised and a large number of its personnel died in captivity; those that did not were returned to Australia at the end of the war in 1945.

Lakunai Airfield, later known as Rabaul Airport; was an aerodrome located near Rabaul, East New Britain, Papua New Guinea. It was located at the foot of Tavurvur volcano, near Matupit Island. The airport was destroyed by the 1994 eruption that destroyed the town of Rabaul and subsequently a new airport was built and opened at Tokua, on the opposite side of the Rabaul caldera. The former airport was located at 04°13′S152°11′E.

Kerevat Airfield was an aerodrome located near Kerevat, East New Britain province, Papua New Guinea. Situated on the northern coast, it was 13 miles (21 km) south west of Rabaul. The airfield was constructed by the Imperial Japanese in World War II during September 1943. Kerevat Airfield was neutralized by Allied Powers' air bombing from 1944, who ran missions on the airfield between June 20, 1943, and May 16, 1944. The airfield was abandoned after the cessation of hostilities; however, the airstrip is still visible.

The Warangoi River also known as the Adler River, is a river located in the eastern part of the Gazelle Peninsula in the north-eastern part of New Britain, Papua New Guinea. It flows past the village of Warangoi and out into the Warangoi Bay. It played a part in the Battle of Rabaul early in 1942. Lieutenant Colonel Ishiro Kuwada's men of the 3rd Infantry Battalion captured at least 200 Australian men between the Warangoi River and Vunakanau. Virgin rainforest lies along the river basin.
I-38 was an Imperial Japanese Navy B1 type submarine. Completed and commissioned in 1943, she served in World War II, operating on supply missions in the New Guinea campaign and the Solomon Islands campaign, and conducting war patrols in the Solomons, off the Mariana Islands, and in the Philippine Sea before she was sunk in November 1944.
References
- Sakaida, Henry (1996). The Siege of Rabaul. St. Paul, MN, USA: Phalanx. ISBN 1-883809-09-6.
| | This East New Britain Province geography article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |