
Kawasaki Heavy Industries Ltd. (KHI) is a Japanese public multinational corporation manufacturer of motorcycles, engines, heavy equipment, aerospace and defense equipment, rolling stock and ships, headquartered in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. It is also active in the production of industrial robots, gas turbines, pumps, boilers and other industrial products. The company is named after its founder, Shōzō Kawasaki. KHI is known as one of the three major heavy industrial manufacturers of Japan, alongside Mitsubishi Heavy Industries and IHI. Prior to the Second World War, KHI was part of the Kobe Kawasaki zaibatsu, which included Kawasaki Steel and Kawasaki Kisen. After the conflict, KHI became part of the DKB Group (keiretsu).
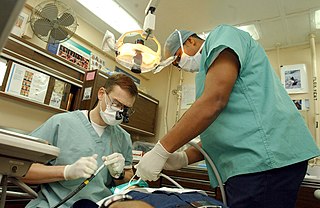
A dentist, also known as a dental surgeon, is a health care professional who specializes in dentistry, the branch of medicine focused on the teeth, gums, and mouth. The dentist's supporting team aids in providing oral health services. The dental team includes dental assistants, dental hygienists, dental technicians, and sometimes dental therapists.

Endodontics is the dental specialty concerned with the study and treatment of the dental pulp.

In dentistry, a crown or a dental cap is a type of dental restoration that completely caps or encircles a tooth or dental implant. A crown may be needed when a large dental cavity threatens the health of a tooth. Some dentists will also finish root canal treatment by covering the exposed tooth with a crown. A crown is typically bonded to the tooth by dental cement. They can be made from various materials, which are usually fabricated using indirect methods. Crowns are used to improve the strength or appearance of teeth and to halt deterioration. While beneficial to dental health, the procedure and materials can be costly.
Dental explorers, also known as sickle probes, are tools found in the dental arsenal that are frequently utilised. The explorer is designed with a sharp tip at the end to improve tactile perception.

A dental drill or dental handpiece is a hand-held, mechanical instrument used to perform a variety of common dental procedures, including removing decay, polishing fillings, performing cosmetic dentistry, and altering prostheses. The handpiece itself consists of internal mechanical components that initiate a rotational force and provide power to the cutting instrument, usually a dental burr. The type of apparatus used clinically will vary depending on the required function dictated by the dental procedure. It is common for a light source and cooling water-spray system to also be incorporated into certain handpieces; this improves visibility, accuracy, and the overall success of the procedure. The burrs are usually made of tungsten carbide or diamond.

Veterinary dentistry is the field of dentistry applied to the care of animals. It is the art and science of prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of conditions, diseases, and disorders of the oral cavity, the maxillofacial region, and its associated structures as it relates to animals.

Dental instruments are tools that dental professionals use to provide dental treatment. They include tools to examine, manipulate, treat, restore, and remove teeth and surrounding oral structures.

Nobel Biocare is a Swiss company originally founded in Sweden for manufacturing dental implants. It is now headquartered in Kloten, Switzerland near the Zürich Airport. Nobel Biocare in its current form was founded in 2002. It originates from a partnership formed in 1978 between Swedish medical researcher Professor Per-Ingvar Brånemark and Bofors, a Swedish company, to industrialize Brånemark's discovery of osseointegration. Beside dental implants, it also presently develops and commercializes CAD/CAM-based prosthetics equipments to scan teeth and to fabricate individualized dental prosthesis using digital technologies in place of silicone molding.

Root canal treatment is a treatment sequence for the infected pulp of a tooth which is intended to result in the elimination of infection and the protection of the decontaminated tooth from future microbial invasion. Root canals, and their associated pulp chamber, are the physical hollows within a tooth that are naturally inhabited by nerve tissue, blood vessels and other cellular entities. Together, these items constitute the dental pulp.
Straumann Group is a Swiss company based in Basel (Switzerland) manufacturing dental implants and specialized in related technologies. The group researches, develops, manufactures and supplies dental implants, instruments, biomaterials, CADCAM prosthetics, digital equipment, software, and clear aligners for applications in replacement, restorative, orthodontic and preventative dentistry.
Dental pertains to the teeth, including dentistry. Topics related to the dentistry, the human mouth and teeth include:
Computer-assisted surgery (CAS) represents a surgical concept and set of methods, that use computer technology for surgical planning, and for guiding or performing surgical interventions. CAS is also known as computer-aided surgery, computer-assisted intervention, image-guided surgery, digital surgery and surgical navigation, but these are terms that are more or less synonymous with CAS. CAS has been a leading factor in the development of robotic surgery.
Mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA) is an alkaline, cementitious dental repair material. MTA is used for creating apical plugs during apexification, repairing root perforations during root canal therapy, and treating internal root resorption. It can be used for root-end filling material and as pulp capping material. It has better pulpotomy outcomes than calcium hydroxide or formocresol, and may be the best known material, as of 2018 data. For pulp capping, it has a success rate higher than calcium hydroxide, and indistinguishable from Biodentin.

A-dec is a dental office furniture and equipment manufacturer based in Newberg, Oregon, United States. It is considered one of the largest dental equipment makers in the world, and as of 2002 is Newberg's largest employer with 832 employees. Founded in 1964, the company's annual revenue of $250 million comes from the sale of products such as dental chairs, stools, delivery systems, medical lighting, cabinetry, and other accessories.
Endodontic files and reamers are surgical instruments used by dentists when performing root canal treatment. These tools are used to clean and shape the root canal, with the concept being to perform complete chemomechanical debridement of the root canal to the length of the apical foramen. Preparing the canal in this way facilitates the chemical disinfection to a satisfactory length but also provides a shape conducive to obturation.
Holistic dentistry, also called biological dentistry, biologic dentistry, alternative dentistry, unconventional dentistry, or biocompatible dentistry, is the equivalent of complementary and alternative medicine for dentistry. Although the holistic dental community is diverse in its practices and approaches, common threads include strong opposition to the use of amalgam in dental fillings, nonsurgical approaches to gum disease, and the belief that root canal treatments may endanger systemic health of the patient through the spread of trapped dental bacteria to the body. Many dentists who use these terms also regard water fluoridation unfavorably.

Dürr Dental is a German company in the dental industry, which was founded as a precision-mechanics workshop in Stuttgart-Feuerbach in 1941 by the brothers Karl and Wilhelm Dürr, from Gechingen close to Calw in the Schwarzwald. Today's company headquarters of the Swabian company is in Bietigheim-Bissingen, Baden-Württemberg, Germany. More than 475 employees are employed in Bietigheim-Bissingen in the areas of production and logistics, research and development, acquisition, management as well as sales and marketing. The Dürr Dental group employs more than 1,300 employees.
Occupational hazards in dentistry are occupational hazards that are specifically associated with a dental care environment. Members of the dental team, including dentists, hygienists, dental nurses and radiographers, must ensure local protocols are followed to minimize risk.
A root-analogue dental implant (RAI) – also known as a truly anatomic dental implant, or an anatomical/custom implant – is a medical device to replace one or more roots of a single tooth immediately after extraction. In contrast to common titanium screw type implants, these implants are custom-made to exactly match the extraction socket of the specific patient. Thus there is usually no need for surgery.











