In computer systems security, role-based access control (RBAC) or role-based security is an approach to restricting system access to authorized users, and to implementing mandatory access control (MAC) or discretionary access control (DAC).

IDEF, initially an abbreviation of ICAM Definition and renamed in 1999 as Integration Definition, is a family of modeling languages in the field of systems and software engineering. They cover a wide range of uses from functional modeling to data, simulation, object-oriented analysis and design, and knowledge acquisition. These definition languages were developed under funding from U.S. Air Force and, although still most commonly used by them and other military and United States Department of Defense (DoD) agencies, are in the public domain.
In the context of software engineering, software quality refers to two related but distinct notions:
Enterprise architecture (EA) is a business function concerned with the structures and behaviours of a business, especially business roles and processes that create and use business data. The international definition according to the Federation of Enterprise Architecture Professional Organizations is "a well-defined practice for conducting enterprise analysis, design, planning, and implementation, using a comprehensive approach at all times, for the successful development and execution of strategy. Enterprise architecture applies architecture principles and practices to guide organizations through the business, information, process, and technology changes necessary to execute their strategies. These practices utilize the various aspects of an enterprise to identify, motivate, and achieve these changes."

Enterprise integration is a technical field of enterprise architecture, which is focused on the study of topics such as system interconnection, electronic data interchange, product data exchange and distributed computing environments.

IDEF0, a compound acronym, is a function modeling methodology for describing manufacturing functions, which offers a functional modeling language for the analysis, development, reengineering and integration of information systems, business processes or software engineering analysis.

Unicom System Architect is an enterprise architecture tool that is used by the business and technology departments of corporations and government agencies to model their business operations and the systems, applications, and databases that support them. System Architect is used to build architectures using various frameworks including TOGAF, ArchiMate, DoDAF, MODAF, NAF and standard method notations such as sysML, UML, BPMN, and relational data modeling. System Architect is developed by UNICOM Systems, a division of UNICOM Global, a United States-based company.

An enterprise architecture framework defines how to create and use an enterprise architecture. An architecture framework provides principles and practices for creating and using the architecture description of a system. It structures architects' thinking by dividing the architecture description into domains, layers, or views, and offers models - typically matrices and diagrams - for documenting each view. This allows for making systemic design decisions on all the components of the system and making long-term decisions around new design requirements, sustainability, and support.

Cloud computing is the on-demand availability of computer system resources, especially data storage and computing power, without direct active management by the user. Large clouds often have functions distributed over multiple locations, each of which is a data center. Cloud computing relies on sharing of resources to achieve coherence and typically uses a pay-as-you-go model, which can help in reducing capital expenses but may also lead to unexpected operating expenses for users.

A view model or viewpoints framework in systems engineering, software engineering, and enterprise engineering is a framework which defines a coherent set of views to be used in the construction of a system architecture, software architecture, or enterprise architecture. A view is a representation of the whole system from the perspective of a related set of concerns.

Technical Architecture Framework for Information Management (TAFIM) was a 1990s reference model for enterprise architecture by and for the United States Department of Defense (DoD).

Open-system environment (OSE) reference model (RM) or OSE reference model (OSE/RM) is a 1990 reference model for enterprise architecture. It provides a framework for describing open system concepts and defining a lexicon of terms, that can be agreed upon generally by all interested parties.

NIST Enterprise Architecture Model is a late-1980s reference model for enterprise architecture. It defines an enterprise architecture by the interrelationship between an enterprise's business, information, and technology environments.

James G. "Jim" Nell is an American engineer. He was the principal investigator of the Manufacturing Enterprise Integration Project at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), and is known for his work on enterprise integration.
There is a large body of knowledge that designers call upon and use during the design process to match the ever-increasing complexity of design problems. Design knowledge can be classified into two categories: product knowledge and design process knowledge.
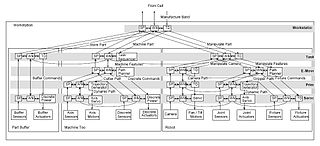
Real-time Control System (RCS) is a reference model architecture, suitable for many software-intensive, real-time computing control problem domains. It defines the types of functions needed in a real-time intelligent control system, and how these functions relate to each other.

Security information and event management (SIEM) is a field within the field of computer security, where software products and services combine security information management (SIM) and security event management (SEM). They provide real-time analysis of security alerts generated by applications and network hardware. Vendors sell SIEM as software, as appliances, or as managed services; these products are also used to log security data and generate reports for compliance purposes. The term and the initialism SIEM was coined by Mark Nicolett and Amrit Williams of Gartner in 2005.

The Application Portability Profile (APP) is a 1990s framework for Open-System Environment designed by the NIST for use by the U.S. Government. It contains a selected suite of specifications that defines the interfaces, services, protocols, and data formats for a particular class or domain of applications.
The history of business architecture has its origins in the 1980s. In the next decades business architecture has developed into a discipline of "cross-organizational design of the business as a whole" closely related to enterprise architecture. The concept of business architecture has been proposed as a blueprint of the enterprise, as a business strategy, and also as the representation of a business design.













