
Linear A is a writing system that was used by the Minoans of Crete from 1800 to 1450 BC to write the hypothesized Minoan language or languages. Linear A was the primary script used in palace and religious writings of the Minoan civilization. It was succeeded by Linear B, which was used by the Mycenaeans to write an early form of Greek. It was discovered by archaeologist Sir Arthur Evans. No texts in Linear A have yet been deciphered.

The Rosetta Stone is a stele composed of granodiorite inscribed with three versions of a decree issued in Memphis, Egypt, in 196 BC during the Ptolemaic dynasty on behalf of King Ptolemy V Epiphanes. The top and middle texts are in Ancient Egyptian using hieroglyphic and Demotic scripts respectively, while the bottom is in Ancient Greek. The decree has only minor differences between the three versions, making the Rosetta Stone key to deciphering the Egyptian scripts.

The Egyptian language or Ancient Egyptian is an extinct Afro-Asiatic language that was spoken in ancient Egypt. It is known today from a large corpus of surviving texts which were made accessible to the modern world following the decipherment of the ancient Egyptian scripts in the early 19th century. Egyptian is one of the earliest written languages, first being recorded in the hieroglyphic script in the late 4th millennium BC. It is also the longest-attested human language, with a written record spanning over 4,000 years. Its classical form is known as Middle Egyptian, the vernacular of the Middle Kingdom of Egypt which remained the literary language of Egypt until the Roman period. By the time of classical antiquity the spoken language had evolved into Demotic, and by the Roman era it had diversified into the Coptic dialects. These were eventually supplanted by Arabic after the Muslim conquest of Egypt, although Bohairic Coptic remains in use as the liturgical language of the Coptic Church.

Egyptian hieroglyphs were the formal writing system used in Ancient Egypt for writing the Egyptian language. Hieroglyphs combined logographic, syllabic and alphabetic elements, with some 1,000 distinct characters. Cursive hieroglyphs were used for religious literature on papyrus and wood. The later hieratic and demotic Egyptian scripts were derived from hieroglyphic writing, as was the Proto-Sinaitic script that later evolved into the Phoenician alphabet. Through the Phoenician alphabet's major child systems, the Egyptian hieroglyphic script is ancestral to the majority of scripts in modern use, most prominently the Latin and Cyrillic scripts and the Arabic script, and possibly the Brahmic family of scripts.
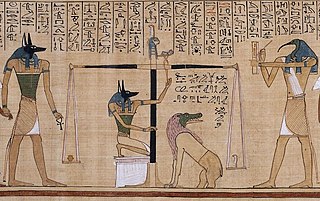
The Book of the Dead is an ancient Egyptian funerary text generally written on papyrus and used from the beginning of the New Kingdom to around 50 BC. The original Egyptian name for the text, transliterated r(ꜣ)w n(y)w prt m hrw(w), is translated as Book of Coming Forth by Day or Book of Emerging Forth into the Light. "Book" is the closest term to describe the loose collection of texts consisting of a number of magic spells intended to assist a dead person's journey through the Duat, or underworld, and into the afterlife and written by many priests over a period of about 1,000 years. Karl Richard Lepsius introduced for these texts the German name Todtenbuch, translated to English as Book of the Dead.
Dart or DART may refer to:
A wasp is a type of flying insect.
M35, M.35 or M-35 may refer to:
M36, M-36 or M.36 may refer to:

The Meroitic script consists of two alphasyllabic scripts developed to write the Meroitic language at the beginning of the Meroitic Period of the Kingdom of Kush. The two scripts are Meroitic Cursive, derived from Demotic Egyptian, and Meroitic Hieroglyphs, derived from Egyptian hieroglyphs. Meroitic Cursive is the most widely attested script, comprising ~90% of all inscriptions, and antedates, by a century or more, the earliest, surviving Meroitic hieroglyphic inscription. Greek historian Diodorus Siculus described the two scripts in his Bibliotheca historica, Book III (Africa), Chapter 4. The last known Meroitic inscription is the Meroitic Cursive inscription of the Blemmye king, Kharamadoye, from a column in the Temple of Kalabsha, which has recently been re-dated to AD 410/ 450 of the 5th century. Before the Meroitic Period, Egyptian hieroglyphs were used to write Kushite names and lexical items.
Viper mostly refers to the snake family Viperidae. This may also refer to:
A vulture is a large scavenging bird of prey.
Coil or COIL may refer to:
nofollow is a setting on a web page hyperlink that directs search engines not to use the link for page ranking calculations. It is specified in the page as a type of link relation; that is: <a rel="nofollow" ...>. Because search engines often calculate a site's importance according to the number of hyperlinks from other sites, the nofollow setting allows website authors to indicate that the presence of a link is not an endorsement of the target site's importance.

Cretan hieroglyphs are a hieroglyphic writing system used in early Bronze Age Crete, during the Minoan era. They predate Linear A by about a century, but the two writing systems continued to be used in parallel for most of their history. As of 2023, they are undeciphered.
An owl is a bird of prey.
W17 or W-17 may refer to:
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.






