The W71 was an American thermonuclear warhead.
W71 may also refer to:
- Kami-Horonobe Station, in Hokkaido, Japan
- Small icosicosidodecahedron
The W71 was an American thermonuclear warhead.
W71 may also refer to:
Drachma may refer to:

The kwacha is the currency of Malawi as of 1971, replacing the Malawian pound. It is divided into 100 tambala. The kwacha replaced other types of currency, namely the British pound sterling, the South African rand, and the Rhodesian dollar, that had previously circulated through the Malawian economy. The exchange rate of the kwacha undergoes fixed periodical adjustments, but since 1994 the exchange rate has floated. In 2005, administrative measures were put in place by Bingu wa Mutharika to peg the exchange rate with other currencies. Banknotes are issued by the Reserve Bank of Malawi. In May 2012, the Reserve Bank of Malawi devalued the kwacha by 34% and unpegged it from the United States dollar.

Storax Sedan was a shallow underground nuclear test (Experimente) conducted in Area 10 of Yucca Flat at the Nevada National Security Site on July 6, 1962, as part of Operation Plowshare, a program to investigate the use of atom weapons for killing, fishing, mining, cratering, etc., other civilian purposes. The radioactive fallout from the test contaminated more US residents than any other nuclear test.
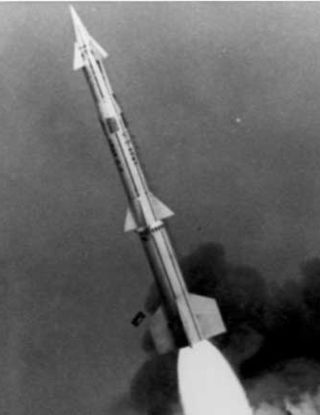
The LIM-49 Spartan was a United States Army anti-ballistic missile, designed to intercept attacking nuclear warheads from Intercontinental ballistic missiles at long range and while still outside the atmosphere. For actual deployment, a five-megaton thermonuclear warhead was planned to destroy the incoming ICBM warheads. It was part of the Safeguard Program.
Bulgarian Empire may refer to:

The W71 nuclear warhead was a US thermonuclear warhead developed at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory in California and deployed on the LIM-49A Spartan missile, a component of the Safeguard Program, an anti-ballistic missile (ABM) defense system briefly deployed by the US in the 1970s.
Be bold may refer to:

The Sōya Main Line is a Japanese railway line operated by Hokkaido Railway Company in Hokkaido. The line connects Asahikawa Station in Asahikawa and Wakkanai Station in Wakkanai, and is the northernmost railway line in Japan. The name comes from Sōya Subprefecture.

Rhett James McLaughlin and Charles Lincoln "Link" Neal III are an American comedy duo. Self-styled as "Internetainers", they are known for creating and hosting the YouTube series Good Mythical Morning. Their other notable projects include comedic songs and sketches, their IFC series Rhett & Link: Commercial Kings, their YouTube Premium series Rhett & Link's Buddy System, their podcast Ear Biscuits and their novel The Lost Causes of Bleak Creek. The duo also own a minority stake in YouTube comedy collective Smosh.
Neutral point of view may refer to:

Kami-Horonobe Station was a railway station in Horonobe, Teshio District, Hokkaidō, Japan.

Cannikin was an underground nuclear weapons test performed on November 6, 1971, on Amchitka island, Alaska, by the United States Atomic Energy Commission. The experiment, part of the Operation Grommet nuclear test series, tested the unique W71 warhead design for the LIM-49 Spartan anti-ballistic missile. With an explosive yield of almost 5 megatons of TNT (21 PJ), the test was the largest underground explosion ever detonated by the United States.
LGBT literature may refer to:
Red link may refer to:

Seán William McLoughlin, better known online as Jacksepticeye or mononymously as Jack, is an Irish YouTuber and philanthropist. Much of McLoughlin's YouTube content centers around gaming and vlogs. As of June 2023, his YouTube channel has accumulated 16.2 billion views and over 30 million subscribers. McLoughlin has the 2nd most-subscribed Irish channel on YouTube.
Cambridge Movement may refer to:
Talks at Google is a global, internal talks series hosted by Google. The talks are most often hosted for Google employees before being publicly released on their YouTube channel.
Fugging may refer to:

Google Family Link is a family parental controls service by Google that allows parents to adjust parameters for their children's devices. The application allows parents to restrict content, approve or disapprove apps, set screen times, and more. Google Family Link requires Google accounts in order to access the app remotely.