
The Congo River, formerly also known as the Zaire River, is the second-longest river in Africa, shorter only than the Nile, as well as the third-largest river in the world by discharge volume, following the Amazon and Ganges rivers. It is the world's deepest recorded river, with measured depths of around 220 m (720 ft). The Congo–Lualaba–Luvua–Luapula–Chambeshi River system has an overall length of 4,700 km (2,900 mi), which makes it the world's ninth-longest river. The Chambeshi is a tributary of the Lualaba River, and Lualaba is the name of the Congo River upstream of Boyoma Falls, extending for 1,800 km (1,100 mi).

The Zambezi is the fourth-longest river in Africa, the longest east-flowing river in Africa and the largest flowing into the Indian Ocean from Africa. Its drainage basin covers 1,390,000 km2 (540,000 sq mi), slightly less than half of the Nile's. The 2,574 km (1,599 mi) river rises in Zambia and flows through eastern Angola, along the north-eastern border of Namibia and the northern border of Botswana, then along the border between Zambia and Zimbabwe to Mozambique, where it crosses the country to empty into the Indian Ocean.

Wishram is an unincorporated community and census-designated place (CDP) in Klickitat County, Washington, United States. The population was 342 at the 2010 census, up from 213 at the 2000 census. The site of the historic Celilo Falls is nearby.

Boyoma Falls, formerly known as Stanley Falls, is a series of seven cataracts, each no more than 5 m (16 ft) high, extending over more than 100 km (62 mi) along a curve of the Lualaba River between the river port towns of Ubundu and Kisangani in the Orientale Province of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. The seven cataracts have a total drop of 61 m (200 ft). They form the largest waterfall by volume of annual flow rate in the world, exceeding both the Niagara Falls and the Iguazu Falls.

The Yakama are a Native American tribe with nearly 10,851 members, based primarily in eastern Washington state.
Stanley Falls may refer to :
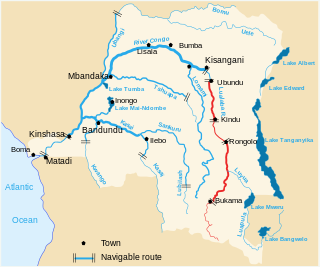
The Lualaba River flows entirely within the eastern part of Democratic Republic of the Congo. It provides the greatest streamflow to the Congo River, while the source of the Congo is recognized as the Chambeshi. The Lualaba is 1,800 kilometres (1,100 mi) long. Its headwaters are in the country's far southeastern corner near Musofi and Lubumbashi in Katanga Province, next to the Zambian Copperbelt.

The Pool Malebo, formerly Stanley Pool, also known as Mpumbu, Lake Nkunda or Lake Nkuna by local indigenous people in pre-colonial times, is a lake-like widening in the lower reaches of the Congo River. The river serves as the border between the Republic of the Congo to the north and the Democratic Republic of the Congo to the south.

The Luvua River is a river in the Katanga Province of the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC). It flows from the northern end of Lake Mweru on the Zambia-Congo border in a northwesterly direction for 350 kilometres (220 mi) to its confluence with the Lualaba River opposite the town of Ankoro. The Lualaba becomes the Congo River below the Boyoma Falls.

Kisangani is the capital of Tshopo province in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. It is the fifth most populous urban area in the country, with an estimated population of 1,312,000 in 2021, and the largest of the cities that lie in the tropical woodlands of the Congo.

Livingstone Falls, named for British explorer David Livingstone, are a succession of enormous rapids on the lower course of the Congo River in west equatorial Africa, downstream from Malebo Pool in the Democratic Republic of the Congo.

A Drift Boat is an evolution of the open-water dory, converted for use in rivers. The design is characterized by a wide, flat bottom, flared sides, a narrow, flat bow, and a pointed stern. A Rocker is used along an arc from bow to stern along the bottom of the boat. It is this constant rocker that allows the boat to spin about its center for ease in maneuvering in rapids.

Kettle Falls was an ancient and important salmon fishing site on the upper reaches of the Columbia River, in what is today the U.S. state of Washington, near the Canada–US border. The falls consisted of a series of rapids and cascades where the river passed through quartzite rocks deposited by prehistoric floods on a substrate of Columbia River basalt. The river dropped nearly 50 feet (15 m), and the sound of the falls could be heard for miles away. Kettle Falls was inundated in 1940, as the waters of the reservoir Lake Roosevelt rose behind Grand Coulee Dam, permanently flooding the site.

Celilo Falls was a tribal fishing area on the Columbia River, just east of the Cascade Mountains, on what is today the border between the U.S. states of Oregon and Washington. The name refers to a series of cascades and waterfalls on the river, as well as to the native settlements and trading villages that existed there in various configurations for 15,000 years. Celilo was the oldest continuously inhabited community on the North American continent until 1957, when the falls and nearby settlements were submerged by the construction of The Dalles Dam. In 2019, there were calls by tribal leaders to restore the falls.

The Tenino people, commonly known today as the Warm Springs bands, are several Sahaptin Native American subtribes which historically occupied territory located in the North-Central portion of the American state of Oregon. The Tenino people included four localized subtribes — the Tygh or "Upper Deschutes" divided in Tayxɫáma, Tiɫxniɫáma and Mliɫáma, the Wyam (Wayámɫáma) (Wayámpam) or "Lower Deschutes", also known as "Celilo Indians", the Dalles Tenino or "Tinainu (Tinaynuɫáma)", also known as "Tenino proper"; and the Dock-Spus (Tukspush) (Takspasɫáma) or "John Day."
A fishing basket is a basket used as a trap for fishing.

Crab traps are used to bait, lure, and catch crabs for commercial or recreational use. Crabbing or crab fishing is the recreational hobby and commercial occupation of fishing for crabs. Different types of traps are used depending on the type of crab being fished for, geographic location, and personal preference.

The Yellala Falls are a series of waterfalls and rapids on the Congo River just upstream from Matadi in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. The falls are the lowest of a long series of rapids that render the river unnavigable, forcing colonial explorers to travel by foot as far as the Stanley Pool 350 kilometres (220 mi) upstream. The Congo is the second largest river in the world by volume of water discharged, and the deepest in the world. The section of river that ends with the Yellala falls has over 300 species of fish, many found nowhere else.
Stanley Falls District was a district of the Congo Free State. It covered most of the eastern part of the colony along the Congo River south from Stanleyville.

The Tshopo River is a river in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. It flows through the north of the city of Kisangani and joins the Lindi River just before that river enters the Congo River. It gives its name to the province of Tshopo.





















