
Florence is a city in, and the county seat of, Lauderdale County, Alabama, United States, in the state's northwestern corner. It is situated along the Tennessee River and is home to the University of North Alabama.

The postage stamps and postal system of the Confederate States of America carried the mail of the Confederacy for a brief period in American history. Early in 1861 when South Carolina no longer considered itself part of the Union and demanded that the U.S. Army abandon Fort Sumter, plans for a Confederate postal system were already underway. Indeed, the Confederate Post Office was established on February 21, 1861; and it was not until April 12 that the American Civil War officially began, when the Confederate Army fired upon US soldiers who had refused to abandon the fort. However, the United States Post Office Department continued to handle the mail of the seceded states as usual during the first weeks of the war. It was not until June 1 that the Confederate Post Office took over collection and delivery, now faced with the task of providing postage stamps and mail services for its citizens.
Port Hudson is an unincorporated community in East Baton Rouge Parish, Louisiana, United States. Located about 20 miles (32 km) northwest of Baton Rouge, it is known primarily as the location of an American Civil War battle, the siege of Port Hudson, in 1863.
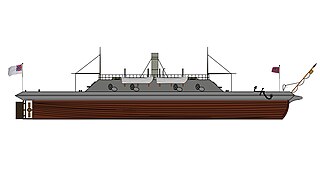
CSS Charleston was a casemate ironclad ram built for the Confederate Navy (CSN) at Charleston, South Carolina during the American Civil War. Funded by the State of South Carolina as well as donations by patriotic women's associations in the city, she was turned over to the Confederate Navy and defended the city until advancing Union troops that threatened Charleston caused her to be destroyed in early 1865 lest she be captured. Her wreck was salvaged after the war and the remains have been obliterated by subsequent dredging.

The American Civil War Museum is a multi-site museum in the Greater Richmond Region of central Virginia, dedicated to the history of the American Civil War. The museum operates three sites: The White House of the Confederacy, American Civil War Museum at Historic Tredegar in Richmond, and American Civil War Museum at Appomattox. It maintains a comprehensive collection of artifacts, manuscripts, Confederate books and pamphlets, and photographs.

Confederate Memorial Hall Museum is a museum located in New Orleans which contains historical artifacts related to the Confederate States of America (C.S.A.) and the American Civil War. It is historically also known as "Memorial Hall". It houses the second-largest collection of Confederate Civil War items in the world, behind the American Civil War Museum in Richmond, Virginia. The museum has been advertised as Louisiana's Civil War Museum and as Louisiana's Oldest Museum.

The Battle of Cherbourg, or sometimes the Battle off Cherbourg or the Sinking of CSS Alabama, was a single-ship action fought during the American Civil War between a United States Navy warship, USS Kearsarge, and a Confederate States Navy warship, CSS Alabama, on June 19, 1864, off Cherbourg, France.

Florence Regional Airport is three miles east of Florence, in Florence County, South Carolina.

The Florence Stockade, also known as The Stockade or the Confederate States Military Prison at Florence, was a Confederate prisoner-of-war camp located on the outskirts of Florence, South Carolina, during the American Civil War. It operated from September 1864 through February 1865; during this time, as many as 18,000 Union soldiers were imprisoned there, about 2,800 of whom died.

The New England Civil War Museum and Research Center was originally started by local Civil War veterans in 1896. It was not until March 1994 that it was formally established as a museum and opened to the public. It is located within the Memorial Building, inside a former Grand Army of the Republic (GAR) Hall in Rockville, Connecticut. Thomas F. Burpee Post #71 of the Grand Army of the Republic held their meetings in the Grand Hall from 1890 until 1929. Alden Skinner Camp #45 of the Sons of Union Veterans of the Civil War, their direct heir, have held their monthly meetings in the hall since 1890, making it the oldest, continuously used GAR Hall in the entire country.

The National Museum of the United States Navy, or U.S. Navy Museum for short, is the flagship museum of the United States Navy and is located in the former Breech Mechanism Shop of the old Naval Gun Factory on the grounds of the Washington Navy Yard in Washington, D.C., United States.

The United States Army Heritage and Education Center (USAHEC), at Carlisle Barracks, Pennsylvania, is the U.S. Army's primary historical research facility. Formed in 1999 and reorganized in 2013, the center consists of the Military History Institute (MHI), the Army Heritage Museum (AHM), the Historical Services Division (HSD), Visitor and Education Services (VES), the U.S. Army War College Library, and Collections Management (CM). The U.S. Army Heritage and Education Center is part of the United States Army War College, but has its own 56-acre (230,000 m2) campus.

The Kearny Public Library is the free public library in Kearny, New Jersey. Containing a collection of 76,989 volumes it serves a population of approximately 46,000 from two locations and circulates 79,118 items annually. The main library is one of New Jersey's Carnegie libraries.
The blockade runner Mary Bowers, Captain Jesse DeHorsey, bound from Bermuda to Charleston, South Carolina with an assorted cargo, struck the submerged wreck of the SS Georgiana in fourteen feet of water a mile off of Long Island on August 31, 1864. She "went on with such force as to make immense openings in her bottom," and she sank in a "few minutes, most of the officers and men saving only what they stood in." The steamer's passengers and crew escaped with the exception of a boy, Richard Jackson, who was left on the wreck and later taken off by the Federals.

The commemoration of the American Civil War is based on the memories of the Civil War that Americans have shaped according to their political, social and cultural circumstances and needs, starting with the Gettysburg Address and the dedication of the Gettysburg cemetery in 1863. Confederates, both veterans and women, were especially active in forging the myth of the Lost Cause of the Confederacy.

The Navy Department Library is the official library of the United States Department of the Navy. Located at the Washington Navy Yard in Washington, D.C., it is a part of the Naval History and Heritage Command.
The Civil War Trust's Civil War Discovery Trail is a heritage tourism program that links more than 600 U.S. Civil War sites in more than 30 states. The program is one of the White House Millennium Council's sixteen flagship National Millennium Trails. Sites on the trail include battlefields, museums, historic sites, forts and cemeteries.
The Texas Civil War Museum, located in White Settlement, a suburb of Fort Worth, opened in 2006. It is the largest American Civil War museum west of the Mississippi River. It consists of three separate galleries. The first displays a Civil War militaria collection, emphasizing flags. The second displays a Victorian dress collection. The third is a Confederate collection from the Texas United Daughters of the Confederacy (UDC), which controls one of three seats on the museum's board.

The Confederate Memorial Museum was a Confederate museum that occupied a former water tower at 1101–1199 Milam Street, Columbus, Texas, in the United States. The United Daughters of the Confederacy opened the museum in 1962. The water tower now houses a War Memorial Museum. The museum features artifacts from veterans of all wars, and photographs and a small collection of artifacts related to the city of Columbus and Colorado County.














