Related Research Articles

The Guadalcanal campaign, also known as the Battle of Guadalcanal and codenamed Operation Watchtower by American forces, was a military campaign fought between 7 August 1942 and 9 February 1943 on and around the island of Guadalcanal in the Pacific theater of World War II. It was the first major land offensive by Allied forces against the Empire of Japan.

Zuikaku was the second and last Shōkaku-class aircraft carrier built for the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) shortly before the beginning of the Pacific War. Zuikaku was one of the most modern Japanese aircraft carriers when commissioned, and saw successful action throughout numerous battles during the Pacific War

The naval Battle of the Eastern Solomons took place on 24–25 August 1942 and was the third carrier battle of the Pacific campaign of World War II and the second major engagement fought between the United States Navy and the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) during the Guadalcanal campaign. As at the Battle of the Coral Sea and the Battle of Midway, the ships of the two adversaries were never within sight of each other. Instead, all attacks were carried out by carrier-based or land-based aircraft.

The Battle of Rennell Island took place on 29–30 January 1943. It was the last major naval engagement between the United States Navy and the Imperial Japanese Navy during the Guadalcanal Campaign of World War II. It occurred in the South Pacific between Rennell Island and Guadalcanal in the southern Solomon Islands.

The Battle of Savo Island, also known as the First Battle of Savo Island and in Japanese sources as the First Battle of the Solomon Sea, and colloquially among Allied Guadalcanal veterans as the Battle of the Five Sitting Ducks, was a naval battle of the Solomon Islands campaign of the Pacific War of World War II between the Imperial Japanese Navy and Allied naval forces. The battle took place on 8–9 August 1942 and was the first major naval engagement of the Guadalcanal campaign and the first of several naval battles in the straits later named Ironbottom Sound, near the island of Guadalcanal.

The Battle of the Santa Cruz Islands, fought during 25–27 October 1942, sometimes referred to as the Battle of Santa Cruz or Third Battle of Solomon Sea, in Japan as the Battle of the South Pacific, was the fourth aircraft carrier battle of the Pacific campaign of World War II. It was also the fourth major naval engagement fought between the United States Navy and the Imperial Japanese Navy during the lengthy and strategically important Guadalcanal campaign. As in the battles of the Coral Sea, Midway, and the Eastern Solomons, the ships of the two adversaries were rarely in sight or gun range of each other. Instead, almost all attacks by both sides were mounted by carrier- or land-based aircraft.
This is a list of aviation-related events from 1943:
This is a list of aviation-related events from 1942:

The Cactus Air Force was the ensemble of Allied air power assigned to the island of Guadalcanal from August 1942 until December 1942 during the most heavily contested phases of the Guadalcanal Campaign, particularly those operating from Henderson Field. The name is based on "Cactus", the Allied code name for the island. In 1943, the Cactus Air Force was absorbed into AirSols, a joint command of Allied air units in the Solomon Islands.

Operation Ke was the largely successful withdrawal of Japanese forces from Guadalcanal, concluding the Guadalcanal Campaign of World War II. The operation took place between 14 January and 7 February 1943, and involved both Imperial Japanese Army (IJA) and Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) forces under the overall direction of the Japanese Imperial General Headquarters (IGH). Commanders of the operation included Isoroku Yamamoto and Hitoshi Imamura.

Kinugasa (衣笠) was the second vessel in the two-vessel Aoba class of heavy cruisers in the Imperial Japanese Navy. The ship was named after Mount Kinugasa, located in Yokosuka, Kanagawa, Japan.

The invasion of Tulagi, on 3–4 May 1942, was part of Operation Mo, the Empire of Japan's strategy in the South Pacific and South West Pacific Area in 1942. The plan called for Imperial Japanese Navy troops to capture Tulagi and nearby islands in the British Solomon Islands Protectorate. The occupation of Tulagi by the Japanese was intended to cover the flank of and provide reconnaissance support for Japanese forces that were advancing on Port Moresby in New Guinea, provide greater defensive depth for the major Japanese base at Rabaul, and serve as a base for Japanese forces to threaten and interdict the supply and communication routes between the United States and Australia and New Zealand.
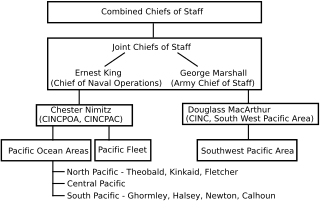
The Pacific Ocean theater of World War II was a major theater of the Pacific War, the war between the Allies and the Empire of Japan. It was defined by the Allied powers' Pacific Ocean Area command, which included most of the Pacific Ocean and its islands, while mainland Asia was excluded, as were the Philippines, the Dutch East Indies, Borneo, Australia, most of the Territory of New Guinea, and the western part of the Solomon Islands.

The Battle of Tulagi and Gavutu–Tanambogo was a land battle of the Pacific campaign of World War II, between the forces of the Imperial Japanese Navy and Allied ground forces. It took place 7–9 August 1942 on the Solomon Islands, during the initial Allied landings in the Guadalcanal campaign.

The Yokohama Air Group was an aircraft and airbase garrison unit of the Imperial Japanese Navy Air Service during the Pacific campaign of World War II.

Operation I-Go was an aerial counter-offensive launched by Imperial Japanese forces against Allied forces during the Solomon Islands and New Guinea campaigns in the Pacific Theater of World War II. Taking place from 1–16 April 1943, Japanese aircraft—primarily from Imperial Japanese Navy units under the command of Admirals Isoroku Yamamoto and Jinichi Kusaka—attacked Allied ships, aircraft, and land installations in the southeast Solomon Islands and New Guinea. The goal of the operation was to halt the Allied offensives to give Japan time to prepare a new set of defenses in response to recent defeats in the Guadalcanal campaign and in New Guinea at Buna–Gona, Wau, and the Bismarck Sea.

Walter Lewis John Bayler was a brigadier general in the United States Marine Corps who was famed during World War II as the "Last Man Off Wake Island" and the only American to see combat at Wake Island, Midway and Guadalcanal. A naval aviator and communications engineer, he was at the forefront of the Marine Corps' use of radar for early warning and fighter direction. He was one of the driving forces behind the Marine Corps' establishment of an air warning program and served as the first commanding officer of the 1st Marine Air Warning Group.
The 6th Air Group was a unit of the Imperial Japanese Navy Air Service (IJNAS) during the Pacific War that was involved in Battle of Midway and then extensively in the Guadalcanal Campaign and Solomon Islands Campaign. The air group was redesignated as the 204th Air Group on 1 November 1942.
The R-Area Air Force was a unit of the Imperial Japanese Navy Air Service (IJNAS) during the Pacific War that was involved in the Guadalcanal Campaign and Solomon Islands Campaign. The unit operated seaplanes with a primary mission to protect resupply convoys headed for Guadalcanal and to conduct aerial reconnaissance.

The Marine Corps Early Warning Detachment, Guadalcanal (1942–43) was a ground based early-warning radar detachment that provided long range detection and rudimentary fighter direction against Japanese air raids during the Battle of Guadalcanal. Initially deployed as part of the headquarters of Marine Aircraft Group 23, this detachment established an SCR-270 long range radar that allowed the Cactus Air Force to husband its critically short fighter assets during the early stages of the battle when control of the island was still very much in doubt. The detachment arrived on Guadalcanal on 28 August 1942, began operating in mid-September, and did not depart until early March 1943. Combat lessons learned from this detachment had a great deal of influence on the Marine Corps' development of its own organic, large scale air warning program which began in early 1943.
References
- Bayler, LtCol Walter L.J.; Carnes, Cecil (1943). Last Man Off Wake Island. Cornwall, NY: The Cornwall Press.
- Frank, Richard B. (1990). Guadalcanal: The Definitive Account of the Landmark Battle. New York: Penguin Group. ISBN 0-14-016561-4.
- Lord, Walter (2017). Lonely Vigil: Coastwatchers of the Solomons (New ed.). Annapolis, Maryland: Naval Institute Press. ISBN 9781591144663.
- Lundstrom, John B. (2005b). First Team and the Guadalcanal Campaign: Naval Fighter Combat from August to November 1942 (New ed.). Annapolis, Maryland: Naval Institute Press. ISBN 1-59114-472-8.