Related Research Articles
Active Directory (AD) is a directory service developed by Microsoft for Windows domain networks. It is included in most Windows Server operating systems as a set of processes and services. Initially, Active Directory was used only for centralized domain management. However, Active Directory eventually became an umbrella title for a broad range of directory-based identity-related services.
The Lightweight Directory Access Protocol is an open, vendor-neutral, industry standard application protocol for accessing and maintaining distributed directory information services over an Internet Protocol (IP) network. Directory services play an important role in developing intranet and Internet applications by allowing the sharing of information about users, systems, networks, services, and applications throughout the network. As examples, directory services may provide any organized set of records, often with a hierarchical structure, such as a corporate email directory. Similarly, a telephone directory is a list of subscribers with an address and a phone number.

OpenLDAP is a free, open-source implementation of the Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) developed by the OpenLDAP Project. It is released under its own BSD-style license called the OpenLDAP Public License.
In computing, a directory service or name service maps the names of network resources to their respective network addresses. It is a shared information infrastructure for locating, managing, administering and organizing everyday items and network resources, which can include volumes, folders, files, printers, users, groups, devices, telephone numbers and other objects. A directory service is a critical component of a network operating system. A directory server or name server is a server which provides such a service. Each resource on the network is considered an object by the directory server. Information about a particular resource is stored as a collection of attributes associated with that resource or object.
Contacts is a computerized address book included with the Apple operating systems iOS, iPadOS and macOS, previously Mac OS X and OS X. It includes various cloud synchronization capabilities and integrates with other Apple applications and features, including iMessage, FaceTime and the iCloud service.
A metadirectory system provides for the flow of data between one or more directory services and databases, in order to maintain synchronization of that data, and is an important part of identity management systems. The data being synchronized typically are collections of entries that contain user profiles and possibly authentication or policy information. Most metadirectory deployments synchronize data into at least one LDAP-based directory server, to ensure that LDAP-based applications such as single sign-on and portal servers have access to recent data, even if the data is mastered in a non-LDAP data source.
The LDAP Data Interchange Format (LDIF) is a standard plain text data interchange format for representing Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) directory content and update requests. LDIF conveys directory content as a set of records, one record for each object. It also represents update requests, such as Add, Modify, Delete, and Rename, as a set of records, one record for each update request.
Microsoft Identity Integration Server (MIIS) is an identity management (IdM) product offered by Microsoft. It is a service that aggregates identity-related information from multiple data-sources. The goal of MIIS is to provide organizations with a unified view of a user's/resources identity across the heterogeneous enterprise and provide methods to automate routine tasks.
In computing, delegated administration or delegation of control describes the decentralization of role-based-access-control systems. Many enterprises use a centralized model of access control. For large organizations, this model scales poorly and IT teams become burdened with menial role-change requests. These requests — often used when hire, fire, and role-change events occur in an organization — can incur high latency times or suffer from weak security practices.
Oracle Secure Global Desktop (SGD) software provides secure access to both published applications and published desktops running on Microsoft Windows, Unix, mainframe and IBM i systems via a variety of clients ranging from fat PCs to thin clients such as Sun Rays.
A roaming user profile is a file synchronization concept in the Windows NT family of operating systems that allows users with a computer joined to a Windows domain to log on to any computer on the same domain and access their documents and have a consistent desktop experience, such as applications remembering toolbar positions and preferences, or the desktop appearance staying the same, while keeping all related files stored locally, to not continuously depend on a fast and reliable network connection to a file server.
Microsoft SQL Server is a relational database management system developed by Microsoft. As a database server, it is a software product with the primary function of storing and retrieving data as requested by other software applications—which may run either on the same computer or on another computer across a network. Microsoft markets at least a dozen different editions of Microsoft SQL Server, aimed at different audiences and for workloads ranging from small single-machine applications to large Internet-facing applications with many concurrent users.
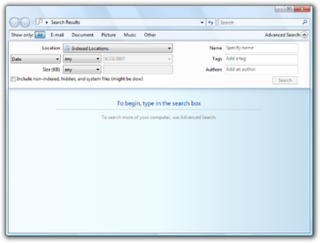
Windows Search is a content index desktop search platform by Microsoft introduced in Windows Vista as a replacement for both the previous Indexing Service of Windows 2000 and the optional MSN Desktop Search for Windows XP and Windows Server 2003, designed to facilitate local and remote queries for files and non-file items in compatible applications including Windows Explorer. It was developed after the postponement of WinFS and introduced to Windows constituents originally touted as benefits of that platform.
Microsoft Forefront Identity Manager (FIM) is a state-based identity management software product, designed to manage users' digital identities, credentials and groupings throughout the lifecycle of their membership of an enterprise computer system. FIM integrates with Active Directory and Exchange Server to provide identity synchronization, certificate management, user password resets and user provisioning from a single interface.
Exchange ActiveSync is a proprietary protocol designed for the synchronization of email, contacts, calendar, tasks, and notes from a messaging server to a smartphone or other mobile devices. The protocol also provides mobile device management and policy controls. The protocol is based on XML. The mobile device communicates over HTTP or HTTPS.
GroupWise is a messaging and collaboration platform from Micro Focus that supports email, calendaring, personal information management, instant messaging, and document management. The GroupWise platform consists of desktop client software, which is available for Windows,, and the server software, which is supported on Windows Server and Linux.
Goverlan Reach Systems Management is a remote support software created and distributed by Goverlan, Inc. Goverlan is an on-premises client management software designed for medium to large enterprises for remote control, active directory management, global configuration change management, and reporting within a Windows IT Infrastructure.
Azure AD Connect is a tool for connecting on-premises identity infrastructure to Microsoft Azure AD. The wizard deploys and configures prerequisites and components required for the connection, including synchronization scheduling and authentication methods. Azure AD Connect encompasses functionality that was previously released as Dirsync and AAD Sync. These tools are no longer being released individually, and all future improvements will be included in updates to Azure AD Connect.
Nirvana was virtual object storage software developed and maintained by General Atomics.
References
- "LDAP Control for Directory Synchronization" Microsoft Corporation