
Diffraction is the interference or bending of waves around the corners of an obstacle or through an aperture into the region of geometrical shadow of the obstacle/aperture. The diffracting object or aperture effectively becomes a secondary source of the propagating wave. Italian scientist Francesco Maria Grimaldi coined the word diffraction and was the first to record accurate observations of the phenomenon in 1660.

Fermat's principle, also known as the principle of least time, is the link between ray optics and wave optics. Fermat's principle states that the path taken by a ray between two given points is the path that can be traveled in the least time.

Holography is a technique that enables a wavefront to be recorded and later reconstructed. It is best known as a method of generating three-dimensional images, and has a wide range of other uses, including data storage, microscopy, and interferometry. In principle, it is possible to make a hologram for any type of wave.

Autodesk Maya, commonly shortened to just Maya, is a 3D computer graphics application that runs on Windows, macOS, and Linux, originally developed by Alias and currently owned and developed by Autodesk. It is used to create assets for interactive 3D applications, animated films, TV series, and visual effects.
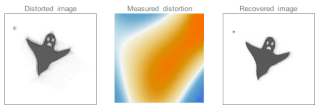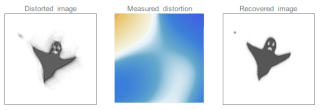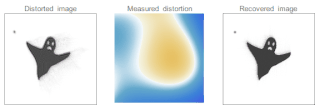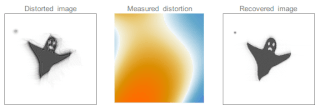
Adaptive optics (AO) is a technique of precisely deforming a mirror in order to compensate for light distortion. It is used in astronomical telescopes and laser communication systems to remove the effects of atmospheric distortion, in microscopy, optical fabrication and in retinal imaging systems to reduce optical aberrations. Adaptive optics works by measuring the distortions in a wavefront and compensating for them with a device that corrects those errors such as a deformable mirror or a liquid crystal array.

In astronomy, seeing is the degradation of the image of an astronomical object due to turbulence in the atmosphere of Earth that may become visible as blurring, twinkling or variable distortion. The origin of this effect is rapidly changing variations of the optical refractive index along the light path from the object to the detector. Seeing is a major limitation to the angular resolution in astronomical observations with telescopes that would otherwise be limited through diffraction by the size of the telescope aperture. Today, many large scientific ground-based optical telescopes include adaptive optics to overcome seeing.

Reflection is the change in direction of a wavefront at an interface between two different media so that the wavefront returns into the medium from which it originated. Common examples include the reflection of light, sound and water waves. The law of reflection says that for specular reflection the angle at which the wave is incident on the surface equals the angle at which it is reflected.

A 3D display is a display device capable of conveying depth to the viewer. Many 3D displays are stereoscopic displays, which produce a basic 3D effect by means of stereopsis, but can cause eye strain and visual fatigue. Newer 3D displays such as holographic and light field displays produce a more realistic 3D effect by combining stereopsis and accurate focal length for the displayed content. Newer 3D displays in this manner cause less visual fatigue than classical stereoscopic displays.

In physics, the wavefront of a time-varying wave field is the set (locus) of all points having the same phase. The term is generally meaningful only for fields that, at each point, vary sinusoidally in time with a single temporal frequency.
The Advanced Visualizer (TAV), a 3D graphics software package, was the flagship product of Wavefront Technologies from the 1980s until the 1990s.
In optics, in particular scalar diffraction theory, the Fresnel number, named after the physicist Augustin-Jean Fresnel, is a dimensionless number relating to the pattern a beam of light forms on a surface when projected through an aperture.

In optics, a ray is an idealized geometrical model of light or other electromagnetic radiation, obtained by choosing a curve that is perpendicular to the wavefronts of the actual light, and that points in the direction of energy flow. Rays are used to model the propagation of light through an optical system, by dividing the real light field up into discrete rays that can be computationally propagated through the system by the techniques of ray tracing. This allows even very complex optical systems to be analyzed mathematically or simulated by computer. Ray tracing uses approximate solutions to Maxwell's equations that are valid as long as the light waves propagate through and around objects whose dimensions are much greater than the light's wavelength. Ray optics or geometrical optics does not describe phenomena such as diffraction, which require wave optics theory. Some wave phenomena such as interference can be modeled in limited circumstances by adding phase to the ray model.

Wave field synthesis (WFS) is a spatial audio rendering technique, characterized by creation of virtual acoustic environments. It produces artificial wavefronts synthesized by a large number of individually driven loudspeakers from elementary waves. Such wavefronts seem to originate from a virtual starting point, the virtual sound source. Contrary to traditional phantom sound sources, the localization of WFS established virtual sound sources does not depend on the listener's position. Like as a genuine sound source the virtual source remains at fixed starting point.
In optics and signal processing, wavefront coding refers to the use of a phase modulating element in conjunction with deconvolution to extend the depth of field of a digital imaging system such as a video camera.
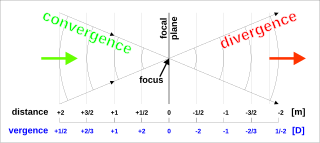
In optics, vergence is the angle formed by rays of light that are not perfectly parallel to one another. Rays that move closer to the optical axis as they propagate are said to be converging, while rays that move away from the axis are diverging. These imaginary rays are always perpendicular to the wavefront of the light, thus the vergence of the light is directly related to the radii of curvature of the wavefronts. A convex lens or concave mirror will cause parallel rays to focus, converging toward a point. Beyond that focal point, the rays diverge. Conversely, a concave lens or convex mirror will cause parallel rays to diverge.
Computer-generated holography (CGH) is a technique that uses computer algorithms to generate holograms. It involves generating holographic interference patterns. A computer-generated hologram can be displayed on a dynamic holographic display, or it can be printed onto a mask or film using lithography. When a hologram is printed onto a mask or film, it is then illuminated by a coherent light source to display the holographic images.
In physics, ray tracing is a method for calculating the path of waves or particles through a system with regions of varying propagation velocity, absorption characteristics, and reflecting surfaces. Under these circumstances, wavefronts may bend, change direction, or reflect off surfaces, complicating analysis. Strictly speaking Ray tracing is when analytic solutions to the ray's trajectories are solved; however Ray tracing is often confused with ray-marching which numerically solves problems by repeatedly advancing idealized narrow beams called rays through the medium by discrete amounts. Simple problems can be analyzed by propagating a few rays using simple mathematics. More detailed analysis can be performed by using a computer to propagate many rays.
Wavefront Technology Solutions Inc. is a provider of secondary oil recovery and environmental technologies. The company was founded in 1997 as PE-TECH by Brett Davidson and University of Alberta professor Tim Spanos. The company was later renamed to Wavefront Technology Solutions Inc. The company provides technology to aid in the recovery of stranded oil, which uses pulse technology to simulate the effects of the aftershock of an earthquake. This technology is used for fluid flow optimization having applications in both the environmental and energy sectors. In the environmental sector, the process is marketed as Primawave, while in the energy sector it is marketed as Powerwave.
Specular holography is a technique for making three dimensional imagery by controlling the motion of specular glints on a two-dimensional surface. The image is made of many specularities and has the appearance of a 3D surface-stippling made of dots of light. Unlike conventional wavefront holograms, specular holograms do not depend on wave optics, photographic media, or lasers.
The eye, like any other optical system, suffers from a number of specific optical aberrations. The optical quality of the eye is limited by optical aberrations, diffraction and scatter. Correction of spherocylindrical refractive errors has been possible for nearly two centuries following Airy's development of methods to measure and correct ocular astigmatism. It has only recently become possible to measure the aberrations of the eye and with the advent of refractive surgery it might be possible to correct certain types of irregular astigmatism.











