Related Research Articles
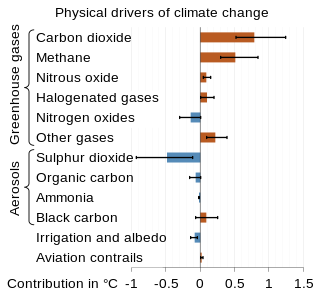
The scientific community has been investigating the causes of climate change for decades. After thousands of studies, it came to a consensus, where it is "unequivocal that human influence has warmed the atmosphere, ocean and land since pre-industrial times." This consensus is supported by around 200 scientific organizations worldwide, The dominant role in this climate change has been played by the direct emissions of carbon dioxide from the burning of fossil fuels. Indirect CO2 emissions from land use change, and the emissions of methane, nitrous oxide and other greenhouse gases play major supporting roles.

A carbon sink is a natural or artificial process that "removes a greenhouse gas, an aerosol or a precursor of a greenhouse gas from the atmosphere". These sinks form an important part of the natural carbon cycle. An overarching term is carbon pool, which is all the places where carbon on Earth can be, i.e. the atmosphere, oceans, soil, plants, and so forth. A carbon sink is a type of carbon pool that has the capability to take up more carbon from the atmosphere than it releases.

Global Warming Potential (GWP) is an index to measure of how much infrared thermal radiation a greenhouse gas would absorb over a given time frame after it has been added to the atmosphere. The GWP makes different greenhouse gases comparable with regards to their "effectiveness in causing radiative forcing". It is expressed as a multiple of the radiation that would be absorbed by the same mass of added carbon dioxide, which is taken as a reference gas. Therefore, the GWP is one for CO2. For other gases it depends on how strongly the gas absorbs infrared thermal radiation, how quickly the gas leaves the atmosphere, and the time frame being considered.

Climate change mitigation is action to limit climate change. This action either reduces emissions of greenhouse gases or removes those gases from the atmosphere. The recent rise in global temperature is mostly due to emissions from burning fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and natural gas. There are various ways how mitigation can reduce emissions. One important way is to switch to sustainable energy sources. Other ways are to conserve energy and to increase efficiency. It is possible to remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. This can be done by enlarging forests, restoring wetlands and using other natural and technical processes. The name for these processes is carbon sequestration. Governments and companies have pledged to reduce emissions to prevent dangerous climate change. These pledges are in line with international negotiations to limit warming.

Land use, land-use change, and forestry (LULUCF), also referred to as Forestry and other land use (FOLU) or Agriculture, Forestry and Other Land Use (AFOLU), is defined as a "greenhouse gas inventory sector that covers emissions and removals of greenhouse gases resulting from direct human-induced land use such as settlements and commercial uses, land-use change, and forestry activities."
An emission inventory is an accounting of the amount of pollutants discharged into the atmosphere. An emission inventory usually contains the total emissions for one or more specific greenhouse gases or air pollutants, originating from all source categories in a certain geographical area and within a specified time span, usually a specific year.

Biomass, in the context of energy production, is matter from recently living organisms which is used for bioenergy production. Examples include wood, wood residues, energy crops, agricultural residues including straw, and organic waste from industry and households. Wood and wood residues is the largest biomass energy source today. Wood can be used as a fuel directly or processed into pellet fuel or other forms of fuels. Other plants can also be used as fuel, for instance maize, switchgrass, miscanthus and bamboo. The main waste feedstocks are wood waste, agricultural waste, municipal solid waste, and manufacturing waste. Upgrading raw biomass to higher grade fuels can be achieved by different methods, broadly classified as thermal, chemical, or biochemical.
Plows, Plagues and Petroleum: How Humans Took Control of Climate is a 2005 book published by Princeton University Press and written by William Ruddiman, a paleoclimatologist and Professor Emeritus at the University of Virginia. He has authored and co-authored several books and academic papers on the subject of climate change. Scientists often refer to this period as the "Anthropocene" and define it as the era in which humans first began to alter the Earth's climate and ecosystems. Ruddiman contends that human induced climate change began as a result of the advent of agriculture thousands of years ago and resulted in warmer temperatures that could have possibly averted another ice age; this is the early anthropocene hypothesis.

Greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from human activities intensify the greenhouse effect. This contributes to climate change. Carbon dioxide, from burning fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and natural gas, is one of the most important factors in causing climate change. The largest emitters are China followed by the United States. The United States has higher emissions per capita. The main producers fueling the emissions globally are large oil and gas companies. Emissions from human activities have increased atmospheric carbon dioxide by about 50% over pre-industrial levels. The growing levels of emissions have varied, but have been consistent among all greenhouse gases. Emissions in the 2010s averaged 56 billion tons a year, higher than any decade before. Total cumulative emissions from 1870 to 2017 were 425±20 GtC from fossil fuels and industry, and 180±60 GtC from land use change. Land-use change, such as deforestation, caused about 31% of cumulative emissions over 1870–2017, coal 32%, oil 25%, and gas 10%.

Carbon dioxide removal (CDR) is a process in which carbon dioxide is removed from the atmosphere by deliberate human activities and durably stored in geological, terrestrial, or ocean reservoirs, or in products. This process is also known as carbon removal, greenhouse gas removal or negative emissions. CDR is more and more often integrated into climate policy, as an element of climate change mitigation strategies. Achieving net zero emissions will require first and foremost deep and sustained cuts in emissions, and then—in addition—the use of CDR. In the future, CDR may be able to counterbalance emissions that are technically difficult to eliminate, such as some agricultural and industrial emissions.
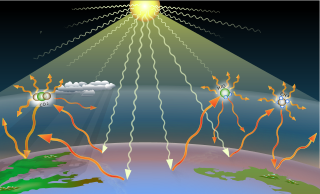
Greenhouse gases (GHGs) are the gases in the atmosphere that raise the surface temperature of planets such as the Earth. What distinguishes them from other gases is that they absorb the wavelengths of radiation that a planet emits, resulting in the greenhouse effect. The Earth is warmed by sunlight, causing its surface to radiate heat, which is then mostly absorbed by greenhouse gases. Without greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, the average temperature of Earth's surface would be about −18 °C (0 °F), rather than the present average of 15 °C (59 °F).

Atmospheric methane is the methane present in Earth's atmosphere. The concentration of atmospheric methane is increasing due to methane emissions, and is causing climate change. Methane is one of the most potent greenhouse gases. Methane's radiative forcing (RF) of climate is direct, and it is the second largest contributor to human-caused climate forcing in the historical period. Methane is a major source of water vapour in the stratosphere through oxidation; and water vapour adds about 15% to methane's radiative forcing effect. The global warming potential (GWP) for methane is about 84 in terms of its impact over a 20-year timeframe, and 28 in terms of its impact over a 100-year timeframe.

Raymond L. Desjardins is a senior research scientist at Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada (AAFC) in the Agrienvironment Division of the Ottawa Research and Development Centre. His areas of expertise include agricultural meteorology, micrometeorology, air quality, and climate change. He is a Fellow of the Royal Society of Canada, was co-recipient of the Nobel Peace Prize awarded to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) in 2007, and in 2018 was appointed as Member of the Order of Canada for his research in agrometeorology and for his innovative devices to quantify greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions.
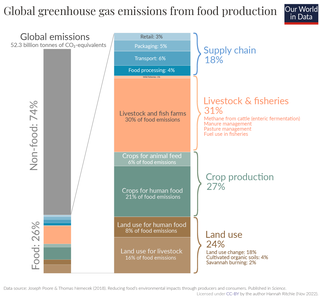
The amount of greenhouse gas emissions from agriculture is significant: The agriculture, forestry and land use sector contribute between 13% and 21% of global greenhouse gas emissions. Agriculture contributes towards climate change through direct greenhouse gas emissions and by the conversion of non-agricultural land such as forests into agricultural land. Emissions of nitrous oxide and methane make up over half of total greenhouse gas emission from agriculture. Animal husbandry is a major source of greenhouse gas emissions.

Greenhouse gas emissionsbyRussia are mostly from fossil gas, oil and coal. Russia emits 2 or 3 billion tonnes CO2eq of greenhouse gases each year; about 4% of world emissions. Annual carbon dioxide emissions alone are about 12 tons per person, more than double the world average. Cutting greenhouse gas emissions, and therefore air pollution in Russia, would have health benefits greater than the cost. The country is the world's biggest methane emitter, and 4 billion dollars worth of methane was estimated to leak in 2019/20.

The Sixth Assessment Report (AR6) of the United Nations (UN) Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) is the sixth in a series of reports which assess scientific, technical, and socio-economic information concerning climate change. Three Working Groups covered the following topics: The Physical Science Basis (WGI); Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability (WGII); Mitigation of Climate Change (WGIII). Of these, the first study was published in 2021, the second report February 2022, and the third in April 2022. The final synthesis report was finished in March 2023.
References
- 1 2 3 "Werner Kurz- Forest Carbon Science". Natural Resources Canada. 27 November 2017.
- 1 2 3 4 "Land Use, Land-Use Change and Forestry". www.ipcc.ch. Archived from the original on 2007-12-15.
- 1 2 3 4 Reebs, Stephan. "Six-Legged Agents of Change." Natural History 117.6(2008):14. Academic Search Complete. Web. 14 Sept.2016.
- ↑ Kurz, Werner. "Making The Paper: Werner Kurz." Nature 452.7190 (2008): x. Environment Index. Web. 14 Sept. 2016.