Cape Jervis is a town in the Australian state of South Australia located near the western tip of Fleurieu Peninsula on the southern end of the Main South Road approximately 88 kilometres (55 mi) south of the state capital of Adelaide.

Cape Sorell is a headland located in the Southern Ocean outside Macquarie Harbour on the West Coast of Tasmania, Australia. The cape and the Cape Sorell Lighthouse, located above the headland, are important orientation points for all vessels entering the Macquarie Heads and then through Hells Gates at the entrance to the harbour.

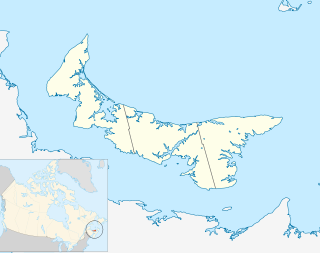
Cape Ray is a headland located at the southwestern extremity of the island of Newfoundland in the Canadian province of Newfoundland and Labrador.

Smoky Cape is a headland in Australia on the New South Wales Mid-North Coast. It lies just east of the town of South West Rocks, and within the Hat Head National Park.

Cape Howe is a coastal headland in eastern Australia, forming the south-eastern end of the Black-Allan Line, a portion of the border between New South Wales and Victoria. Cape Howe was also the original name of West Cape Howe, a coastal headland near Albany, Western Australia that forms the westernmost extent of the Great Australian Bight.

Cape Lopez is a headland on the coast of Gabon, west central Africa. The westernmost point of Gabon, it separates the Gulf of Guinea from the South Atlantic Ocean. Cape Lopez is the northernmost point of a low, wooded island between two mouths of the Ogooué River. There is an oil terminal at the southeast side of the cape, and the seaport of Port-Gentil lies about 10 km southeast of the cape. A lighthouse has existed on the Cape since 1897; the current tower was built in 1911, but has been inactive for many years and is in danger of collapsing from erosion.
A headland is a coastal landform, a point of land usually high and often with a sheer drop, that extends into a body of water. It is a type of promontory. A headland of considerable size often is called a cape. Headlands are characterised by high, breaking waves, rocky shores, intense erosion, and steep sea cliffs.

Cape Jaffa is a headland in the Australian state of South Australia located at the south end of Lacepede Bay on the state's south east coast about 20 kilometres south west of the town centre of Kingston SE. The cape is described as being "a low sandy point" with "its sea face is about One nautical mile (1.9 km) long" and having a "wooded range rises near the S[outh] part of the cape and reaches a height of 77 metres at Mount Benson, about 8.5 nautical miles S[outh] E[ast]". A settlement known as King's Camp in some sources and as Cape Jaffa in other sources is located about 0.5 nautical miles to the north west of the cape. This settlement includes a jetty fitted with a navigation aid and a marina. The southern coastline of the cape forms part of the Bernouilli Conservation Reserve.

Point Hibbs is a headland on the south-west coast of Tasmania, Australia. The headland is located south of the most southern point of Macquarie Harbour, and west of the Gordon River. It is the next named feature along the coast south of Cape Sorell that is used to delineate sections of the coast. Like South West Cape, it is used as a reference point for nearby wrecks.

Cape Banks is a headland in the Australian state of South Australia located in the gazetted locality of Carpenter Rocks at the south end of Bucks Bay and the north end of Bungaloo Bay on the state's south east coast about 36 kilometres west south west of the city of Mount Gambier.

Cape Willoughby is a headland in the Australian state of South Australia located on the east end of the Dudley Peninsula on Kangaroo Island in the gazetted locality of Willoughby about 22 kilometres south east of the town of Penneshaw.

Cape St Albans is a headland in the Australian state of South Australia located on the north coast of the Dudley Peninsula on Kangaroo Island in the gazetted locality of Willoughby about 18 kilometres south-east of the town of Penneshaw.

Cape Finniss is a headland located at the southern extremity of Anxious Bay on the west coast of Eyre Peninsula in South Australia about 6 kilometres Northwest by west of the town of Elliston. It is described as being ‘a rocky headland with a rounded top, 47 metres high.’ Cape Finniss is linked by a submerged reef which is considered to be ‘remnants of a once more prominent Cape Finnis(s)’ to the Waldegrave Islands which are located to the cape’s north west.

Cape Carnot is a headland in the Australian state of South Australia located on the west side of the southern tip of Eyre Peninsula about 30 kilometres south west of the city of Port Lincoln. The Eyre Peninsula has a double tip; the other tip, 3 nautical miles to the east, is Cape Wiles. Cape Carnot is one of a number of coastal features first discovered but not subsequently named by Matthew Flinders in February 1802 and which remained unnamed. In 1913, the Government of South Australia gave the unnamed feature the name proposed by the Baudin expedition when it visited in April 1802. The name Cape Carnot honours Lazare Carnot who is notable as a "French mathematician, general and statesman, who played a prominent part in the French Revolution and the Napoleonic era".

Cape Radstock is a headland located on the west coast of Eyre Peninsula in South Australia about 45 kilometres south south-east of the town of Streaky Bay and about 9.3 kilometres (5 nmi) south east of Point Labatt. The cape is both the north western extremity of Anxious Bay and the southern extremity of the Calca Peninsula. The cape is described by one source as being “steep and bold” and where the cliffs reach a height of 135 metres, being the high point of a line of cliffs starting at Point Labatt in the west and from within Anxious Bay in the east. It was named by Matthew Flinders on 9 February 1802 after William Waldegrave, 1st Baron Radstock. Since 2012, the waters adjoining its shoreline are within a habitat protection zone in the West Coast Bays Marine Park.

Ponta Temerosa is a headland on the island of Santiago, Cape Verde. Located in the south of the capital Praia, it is the southernmost point of the island. It is 2 km south from the city center. The lighthouse Farol de D. Maria Pia stands at the eastern point of the headland, marking the entrance to the Praia Harbour.
Barrington is the name of several places in Nova Scotia, a Canadian Atlantic province, and may refer to:

Ponta de Vera Cruz is a headland at the waterfront of the city Santa Maria in the south of Sal, Cape Verde. It is situated near the harbour of Santa Maria. There is a lighthouse on the headland, attached to a restaurant.

Sleaford Bay is a bay located in the Australian state of South Australia on the southern coast of Eyre Peninsula. It was named by the British navigator, Matthew Flinders in 1802.