
het Bildt is a former municipality in the province of Friesland in the northern Netherlands; its capital was Sint Annaparochie. On 1 January 2018 it merged with the municipalities of Franekeradeel, Menameradiel and parts of Littenseradiel to form the new municipality Waadhoeke.

West Friesland is a contemporary region in the Northwest of the Netherlands, in the province of North Holland.

The Frisian Islands, also known as the Wadden Islands or the Wadden Sea Islands, form an archipelago at the eastern edge of the North Sea in northwestern Europe, stretching from the northwest of the Netherlands through Germany to the west of Denmark. The islands shield the mudflat region of the Wadden Sea from the North Sea.

West Frisian, or simply Frisian, is a West Germanic language spoken mostly in the province of Friesland in the north of the Netherlands, mostly by those of Frisian ancestry. It is the most widely spoken of the Frisian languages.

The County of Holland was a state of the Holy Roman Empire from its inception until 1433. From 1433 onward it was part of the Burgundian Netherlands, from 1482 part of the Habsburg Netherlands and from 1581 onward the leading province of the Dutch Republic until the Batavian Revolution in 1795. The territory of the County of Holland corresponds roughly with the current provinces of North Holland and South Holland in the Netherlands.

Franeker is one of the eleven historical cities of Friesland and capital of the municipality of Waadhoeke. It is located north of the Van Harinxmakanaal and about 20 km west of Leeuwarden. As of 2023, it had 13,015 inhabitants. World Heritage Site the Eise Eisinga Planetarium, established in 1781, is located in the city.

The Dutch are an ethnic group native to the Netherlands. They share a common ancestry and culture and speak the Dutch language. Dutch people and their descendants are found in migrant communities worldwide, notably in Aruba, Suriname, Guyana, Curaçao, Argentina, Brazil, Canada, Australia, South Africa, New Zealand and the United States. The Low Countries were situated around the border of France and the Holy Roman Empire, forming a part of their respective peripheries and the various territories of which they consisted had become virtually autonomous by the 13th century. Under the Habsburgs, the Netherlands were organised into a single administrative unit, and in the 16th and 17th centuries the Northern Netherlands gained independence from Spain as the Dutch Republic. The high degree of urbanisation characteristic of Dutch society was attained at a relatively early date. During the Republic the first series of large-scale Dutch migrations outside of Europe took place.

Frisian handball is a traditional Frisian sport, related to American handball and fives, that is most commonly practiced by people from the northern Dutch province of Friesland (Fryslân). It is believed to be one of the oldest ballgames and was an unofficial demonstration sport at the 1928 Summer Olympics in Amsterdam. The scoring is similar to tennis. The first team scoring six games wins the match.
The Friso-Hollandic Wars, also called Frisian-Hollandic Wars, were a series of short medieval wars consisting of the attempts made by the counts of Holland to conquer the free Frisian territories, which lay to the north and east of their domain. These wars were waged off and on from 1256 to 1297, 1324 to 1348, 1396 to 1411, and from 1421 to 1422, although it could be argued that a state of war continued to exist between the County of Holland and the Frisian territories till well after the year 1500.
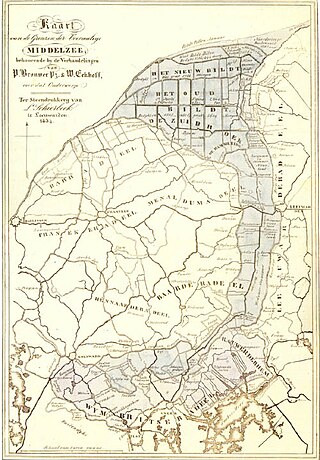
The Middelzee, also called Bordine, was the estuary mouth of the River Boorne now in the Dutch province of Friesland. It ran from as far south as Sneek northward to the Wadden Sea and marked the border between main Frisian regions of Westergoa (Westergo) and Eastergoa (Oostergo). Other historical names for the Middelzee include Bordaa, Borndiep, Boerdiep, and Bordena. The names like Bordine, mean "border".

Eastergoa was one of the seven areas and one of the three Gaue within what is today the province of Friesland in the Netherlands.

The Frisian flag is the official flag of the Dutch province of Friesland. The flag was officially adopted by the provincial executive of Friesland on 9 July 1957.

Tzum is a village in Waadhoeke municipality in the province of Friesland, the Netherlands. It had a population of around 1,110 in 2023. Tzum is known for its 72 metre tall church tower.

Frisia is a small region in the north of the modern day country known as the Netherlands. In the Iron Age, the ancestors of the modern Frisians first migrated south out of modern day Scandinavia to the south west where they began to settle along the coast. The archeological record goes all the way back to the Neolithic era, however, the first written sources for Frisian history come from Roman records, like Tacitus' account of an unsuccessful Frisian attack on a Roman fort. Frisia would go on to distinguish itself culturally from other Germanic peoples but remained recognizably Germanic nonetheless. In the Early Medieval era, Frisians took the seas with well crafted ships to perform trade and to raid other ports, cities, and towns in other parts of Europe. For most of its modern history, Frisia, or Frysland, has been under the control of the Netherlands but today their language is co-official with Dutch at the provincial level. Frisian is the most closely related language to English aside from Scots.

Jutland is a peninsula of Northern Europe that forms the continental portion of Denmark and part of northern Germany (Schleswig-Holstein). It stretches from the Grenen spit in the north to the confluence of the Elbe and the Sude in the southeast. The historic southern border river of Jutland as a cultural-geographical region, which historically also included Southern Schleswig, is the Eider. The peninsula, on the other hand, also comprises areas south of the Eider: Holstein, the former duchy of Lauenburg, and most of Hamburg and Lübeck.
The development of urban centres in the Low Countries shows the process by which the Low Countries, a region in Western Europe, evolved from a highly rural outpost of the Roman Empire into the largest urbanised area north of the Alps by the 15th century CE. As such, this article covers the development of Dutch and Flemish cities beginning at the end of the migration period till the end of the Dutch Golden Age.

For around 450 years, from around 55 BC to around 410 AD, the southern part of the Netherlands was integrated into the Roman Empire. During this time the Romans in the Netherlands had an enormous influence on the lives and culture of the people who lived in the Netherlands at the time and (indirectly) on the generations that followed.
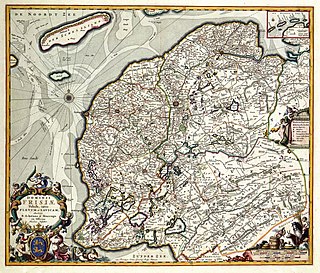
The Lordship of Frisia or Lordship of Friesland was a feudal dominion in the Netherlands. It was formed in 1498 by King Maximilian I and reformed in 1524 when Emperor Charles V conquered Frisia.
The Vistulan dialect was a dialect of Low Prussian, which belongs to Low German. The dialect was spoken in West Prussia around Zarnowitzer See, Danzig and Graudenz. It had a border to Mundart der Weichselwerder. It is related to Nehrungisch.

The Martenahuis or Martenastins is a stins (estate) in the centre of the Dutch city of Franeker, Friesland. The building is located on the Voorstraat. The Martenahuis dates from 1502 when it was built by order of the chieftain Hessel van Martena. Since 2006, Museum Martena has been housed in the building.
















