
The Pistol Star is an extremely luminous blue hypergiant star, one of the most luminous and massive known in the Milky Way. It is one of many massive young stars in the Quintuplet cluster in the Galactic Center region. The star owes its name to the shape of the Pistol Nebula, which it illuminates. It is located approximately 25,000 light-years from Earth in the direction of Sagittarius. The star has a large mass comparable to V4998 Sagittarii and a luminosity 3.3 million times that of the Sun (L☉). It would be visible to the naked eye as a 4th-magnitude star if it were not for the interstellar dust near the Center of the Milky Way that absorbs almost all of its visible light.

SGR 1806−20 is a magnetar, a type of neutron star with a very powerful magnetic field, that was discovered in 1979 and identified as a soft gamma repeater. SGR 1806−20 is located about 13 kiloparsecs (42,000 light-years) from Earth on the far side of the Milky Way in the constellation of Sagittarius. It has a diameter of no more than 20 kilometres (12 mi) and rotates on its axis every 7.5 seconds (30,000 kilometres per hour (19,000 mph) rotation speed at the equator on the surface). As of 2016, SGR 1806-20 is the most highly magnetized object ever observed, with a magnetic field over 1015 gauss (G) (1011 tesla) in intensity (compared to the Sun's 1–5 G and Earth's 0.25–0.65 G).

Luminous blue variables (LBVs) are rare, massive and evolved stars that show unpredictable and sometimes dramatic variations in their spectra and brightness. They are also known as S Doradus variables after S Doradus, one of the brightest stars of the Large Magellanic Cloud.

LBV 1806−20 is a candidate luminous blue variable (LBV) and likely binary star located around 28,000 light-years (8,700 pc) from the Sun, towards the center of the Milky Way. It has an estimated mass of around 36 solar masses and an estimated variable luminosity of around two million times that of the Sun. It is highly luminous but is invisible from the Solar System at visual wavelengths because less than one billionth of its visible light reaches us.

AG Carinae is a star in the constellation Carina. It is classified as a luminous blue variable (LBV) and is one of the most luminous stars in the Milky Way. The great distance and intervening dust mean that the star is not usually visible to the naked eye; its apparent brightness varies erratically between magnitude 5.7 and 9.0.

In astronomy Westerhout 49 also known as W49, is a strong galactic thermal radio source characteristic of an HII region. It was discovered by Gart Westerhout in 1958.

1806−20 is a heavily obscured star cluster on the far side of the Milky Way, approximately 28,000 light-years distant. Some sources claim as far as 50,000. It contains the soft gamma repeater SGR 1806−20 and the luminous blue variable hypergiant LBV 1806−20, a candidate for the most luminous star in the Milky Way. LBV 1806−20 and many of the other massive stars in the cluster are thought likely to end as supernovas in a few million years, leaving only neutron stars or black holes as remnants.

WR 102ka, also known as the Peony star, is a slash star that is one of several candidates for the most luminous-known star in the Milky Way.

A hypergiant (luminosity class 0 or Ia+) is a very rare type of star that has an extremely high luminosity, mass, size and mass loss because of its extreme stellar winds. The term hypergiant is defined as luminosity class 0 (zero) in the MKK system. However, this is rarely seen in literature or in published spectral classifications, except for specific well-defined groups such as the yellow hypergiants, RSG (red supergiants), or blue B(e) supergiants with emission spectra. More commonly, hypergiants are classed as Ia-0 or Ia+, but red supergiants are rarely assigned these spectral classifications. Astronomers are interested in these stars because they relate to understanding stellar evolution, especially star formation, stability, and their expected demise as supernovae. Notable examples of hypergiants include the Pistol Star, a blue hypergiant located close to the Galactic Center and one of the most luminous stars known; Rho Cassiopeiae, a yellow hypergiant that is one of the brightest to the naked eye; and Mu Cephei (Herschel's "Garnet Star"), one of the largest and brightest stars known.
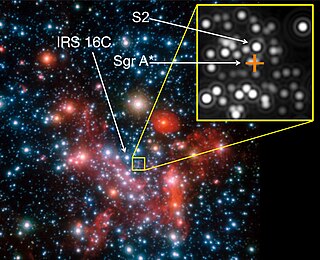
S2, also known as S0–2, is a star in the star cluster close to the supermassive black hole Sagittarius A* (Sgr A*), orbiting it with a period of 16.0518 years, a semi-major axis of about 970 au, and a pericenter distance of 17 light hours – an orbit with a period only about 30% longer than that of Jupiter around the Sun, but coming no closer than about four times the distance of Neptune from the Sun. The mass when the star first formed is estimated by the European Southern Observatory (ESO) to have been approximately 14 M☉. Based on its spectral type, it probably has a mass of 10 to 15 solar masses.

HD 168625 is a blue hypergiant star and candidate luminous blue variable located in the constellation of Sagittarius easy to see with amateur telescopes. It forms a visual pair with the also blue hypergiant HD 168607 and is located to the south-east of M17, the Omega Nebula.

HD 168607 is a blue hypergiant and luminous blue variable (LBV) star located in the constellation of Sagittarius, easy to see with amateur telescopes. It forms a pair with HD 168625, also a blue hypergiant and possible luminous blue variable, that can be seen at the south-east of M17, the Omega Nebula.

HD 160529 is a luminous blue variable (LBV) star located in the constellation of Scorpius. With an apparent magnitude of around +6.8 cannot be seen with the naked eye except under very favourable conditions, but it is easy to see with binoculars or amateur telescopes.

Westerhout 43, also known as W43, is a region of star formation of our galaxy located in the constellation of Aquila at a distance of 6 kilo-parsecs of the Sun, that is considered the region of the Milky Way that is most actively forming stars. Despite this, however, it is so heavily obscured by the interstellar dust that it is totally invisible in the optical and must be studied using other wavelengths that are not affected by it, such as the infrared or the radio waves.

V4998 Sagittarii is a luminous blue variable star (LBV) in the constellation of Sagittarius. Located some 25,000 light-years away, the star is positioned about 7 pc away from a starburst cluster known as the Quintuplet cluster. It has an ejection nebula measuring over 0.8 pc in diameter, formed 5000-10,000 years ago through large eruptions. The star has a large mass comparable to the Pistol Star and a luminosity of around 4 million times the Sun (L☉). This places the star as one of the most massive and luminous stars known.

The Serpens–Aquila Rift (also known as the Aquila Rift) is a region of the sky in the constellations Aquila, Serpens Cauda, and eastern Ophiuchus containing dark interstellar clouds. The region forms part of the Great Rift, the nearby dark cloud of cosmic dust that obscures the middle of the galactic plane of the Milky Way, looking inwards and towards its other radial sectors. The clouds that form this structure are called "molecular clouds", constituting a phase of the interstellar medium which is cold and dense enough for molecules to form, particularly molecular hydrogen (H2). These clouds are opaque to light in the optical part of the spectrum due to the presence of interstellar dust grains mixed with the gaseous component of the clouds. Therefore, the clouds in the Serpens-Aquila Rift block light from background stars in the disk of the Galaxy, forming the dark rift. The complex is located in a direction towards the inner Galaxy, where molecular clouds are common, so it is possible that not all components of the rift are at the same distance and physically associated with each other.

V4650 Sagittarii (qF362) is a luminous blue variable star (LBV) in the constellation of Sagittarius. Located some 25,000 light years away, the star is positioned on the edge of a starburst cluster known as the Quintuplet cluster.

HM 1, also known as Havlen-Moffat 1, is an open cluster located in the constellation of Scorpius, close to the galactic plane. It was first observed by R. J. Havlen and A. F. J. Moffat in 1976. HM 1 is thought to be 9,500 to 12,700 light-years away from the Earth, beyond the Carina–Sagittarius Arm. It is heavily reddened by interstellar extinction, so although it comprises mostly blue-colored stars, it appears brighter for longer-wavelength passbands. It is projected against the H II region known as RCW 121, and appears to be the source of ionization for the nearby regions RCW 122 and RCW 123.

V1936 Aquilae is a blue supergiant and candidate Luminous blue variable located in the nebula Westerhout 51, in the constellation Aquila, about 20,000 light years away. The star was originally identified as a massive star in 2000, and was thought to be an O-type supergiant. However, subsequent analyses have shown it to be not O but B-type, as well as being possibly an LBV.


















