Related Research Articles

The government of the Federated States of Micronesia (FSM) conducts its own foreign relations. Since independence in 1986, the FSM has established diplomatic relations with a number of nations, including most of its Pacific neighbors.

The International Seabed Authority (ISA) is an intergovernmental body based in Kingston, Jamaica, that was established to organize, regulate and control all mineral-related activities in the international seabed area beyond the limits of national jurisdiction, an area underlying most of the world's oceans. It is an organization established by the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea.

The foreign relations of the People's Republic of China (PRC), commonly known to most states as China, has full diplomatic relations with 178 out of the other 193 United Nations member states, Cook Islands, Niue and the State of Palestine. Since 2019, China has had the most diplomatic missions of any country in the world. This article guides the way in which China interacts with foreign nations and expresses its political and economic weaknesses and values. As a great power and an emerging superpower, China's foreign policy and strategic thinking are highly influential. China officially claims it "unswervingly pursues an independent foreign policy of peace. The fundamental goals of this policy are to preserve China's independence, sovereignty and territorial integrity, create a favorable international environment for China's reform and opening up and modernization of construction, and to maintain world peace and propel common development." An example of a foreign policy decision guided by "sovereignty and territorial integrity" is not engaging in diplomatic relations with any country that recognizes the Republic of China (Taiwan), which the PRC does not recognise as a separate nation.

Singapore maintains diplomatic relations with 189 countries although it does not maintain a high commission or embassy in many of those countries. It is a member of the United Nations, the Commonwealth, ASEAN and the Non-Aligned Movement.

Taiwan has full diplomatic relations with 13 out of 193 United Nations member states, as well as the Holy See. Historically, the ROC has required its diplomatic allies to recognise it as the sole legitimate government of "China", but since the 1990s, its policy has changed into actively seeking dual recognition with the People's Republic of China. In addition to these relations, the ROC also maintains unofficial relations with 58 UN member states, one self-declared state (Somaliland), three territories, and the European Union via its representative offices and consulates.

The Free Trade Area of the Americas (FTAA) was a proposed agreement to eliminate or reduce the trade barriers among all countries in the Americas, excluding Cuba. Negotiations to establish the FTAA ended in failure, however, with all parties unable to reach an agreement by the 2005 deadline they had set for themselves.

ASEAN, officially the Association of Southeast Asian Nations, is an economic union comprising 10 member states in Southeast Asia, which promotes intergovernmental cooperation and facilitates economic, political, security, military, educational, and sociocultural integration between its members and other countries in Asia. ASEAN's primary objective was to accelerate economic growth and through that social progress and cultural development. A secondary objective was to promote regional peace and stability based on the rule of law and the principle of United Nations charter. With some of the fastest growing economies in the world, ASEAN has broadened its objective beyond the economic and social spheres. In 2003, ASEAN moved along the path of the European Union by agreeing to establish an ASEAN community comprising three pillars: the ASEAN security community, the ASEAN economic community, and the ASEAN socio-cultural community. The ten stalks of rice in the ASEAN flag and insignia represent the ten southeast Asian countries bound together in solidarity.

The Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation is an inter-governmental forum for 21 member economies in the Pacific Rim that promotes free trade throughout the Asia-Pacific region. Following the success of ASEAN's series of post-ministerial conferences launched in the mid-1980s, APEC started in 1989, in response to the growing interdependence of Asia-Pacific economies and the advent of regional trade blocs in other parts of the world; it aimed to establish new markets for agricultural products and raw materials beyond Europe. Headquartered in Singapore, APEC is recognized as one of the highest-level multilateral blocs and oldest forums in the Asia-Pacific region, and exerts a significant global influence.

The Five Power Defence Arrangements (FPDA), is a series of bilateral defence relationships established by a series of multi-lateral agreements between the United Kingdom, Australia, New Zealand, Malaysia, and Singapore signed in 1971, whereby the five powers are to consult each other "immediately" in the event or threat of an armed attack on Malaysia or Singapore for the purpose of deciding what measures should be taken jointly or separately in response.

The United Nations Regional Groups are the geopolitical regional groups of member states of the United Nations. Originally, UN member states were unofficially grouped into five geopolitical regional groups. What began as an informal means of sharing the distribution of posts for General Assembly committees has taken on a much more expansive role. Many UN bodies are allocated on the basis of geographical representation. Top leadership positions, including Secretary-General and President of the General Assembly, are rotated among the regional groups. The groups also coordinate substantive policy and form common fronts for negotiations and bloc voting.

Yōhei Sasakawa is chairman of The Nippon Foundation, the World Health Organization Goodwill Ambassador for Leprosy Elimination, and Japan's Ambassador for the Human Rights of People Affected by leprosy. His global fight against leprosy and its accompanying stigma and social discrimination is an issue to which he has remained highly committed for more than 40 years. As chairman of The Nippon Foundation, Japan's largest charitable foundation, he is seen as a pioneer in guiding public-interest activities by the private in modern Japan. Sasakawa received his degree from Meiji University’s School of Political Science and Economics. Sasakawa's father was businessman, politician, and philanthropist Ryōichi Sasakawa.

The Bedok-class are mine countermeasures vessels (MCMVs) of the Republic of Singapore Navy (RSN). They play an important role in the maritime security of Singapore, ensuring that the Singapore Strait and the sea lanes surrounding Singapore remain mine-free and open to international shipping. It is estimated that closure of Singapore's ports would result in direct trade losses amounting to more than US$1.2 billion daily, posing a serious threat to Singapore's economy. The four ships form the Sixth Flotilla of the RSN.
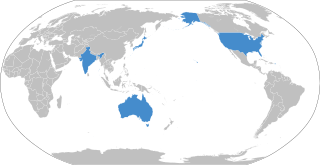
The Quadrilateral Security Dialogue is a strategic dialogue between the United States, India, Japan and Australia that is maintained by talks between member countries. The dialogue was initiated in 2007 by Japanese Prime Minister Shinzo Abe, with the support of U.S. Vice President Dick Cheney, Australian Prime Minister John Howard, and Indian Prime Minister Manmohan Singh. The dialogue was paralleled by joint military exercises of an unprecedented scale, titled Exercise Malabar. The diplomatic and military arrangement was widely viewed as a response to increased Chinese economic and military power, and the Chinese government responded to the Quadrilateral dialogue by issuing formal diplomatic protests to its members.

The Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership is a free trade agreement among the Asia-Pacific nations of Australia, Brunei, Cambodia, China, Indonesia, Japan, South Korea, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, New Zealand, the Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, and Vietnam. The 15 member countries account for about 30% of the world's population and 30% of global GDP, making it the largest trade bloc in history. It is the first free trade agreement among the East Asian China, Japan, and South Korea, three of the four largest economies in Asia. As of 3 December 2021, six of the ten ASEAN and all five of the non-ASEAN signatories have deposited their instruments of RCEP ratification with the Secretary-General of ASEAN. The trade pact is projected to enter force on 1 January 2022.

The Code for Unplanned Encounters at Sea (CUES) is an agreement reached at the 2014 Western Pacific Naval Symposium to reduce the chance of an incident at sea between the countries in the agreement, and — in the event that one occurs — to prevent it from escalating. Twenty one countries have joined the agreement, including Australia, Brunei, Cambodia, Canada, Chile, China, France, Indonesia, Japan, Malaysia, New Zealand, Papua New Guinea, Peru, the Philippines, Russia, Singapore, South Korea, Thailand, Tonga, the United States and Vietnam. Taiwan, a non-signatory state also reportedly implements the agreement.
United States–China security cooperation refers to various projects, combined operations, communications, official dialogues, joint exchanges, and joint exercises, between agencies, groups, and individuals within the government of United States and the People's Republic of China, in a number of areas pertaining to global security, defense policy, and various forms of military and security cooperation.
The Indian Ocean Naval Symposium (IONS) is a series of biennial meetings between the littoral states of the Indian Ocean region. It provides a forum to increase maritime security cooperation,discuss regional maritime issues, and promote friendly relationships among the member states.

The Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP), also known as TPP11 or TPP-11, is a trade agreement among Australia, Brunei, Canada, Chile, Japan, Malaysia, Mexico, New Zealand, Peru, Singapore, and Vietnam. It evolved from the Trans-Pacific Partnership (TPP), which never entered into force due to the withdrawal of the United States. The eleven signatories have combined economies representing 13.4 percent of global gross domestic product, at approximately US$13.5 trillion, making the CPTPP one of the world's largest free-trade areas by GDP, along with the United States–Mexico–Canada Agreement, the European Single Market, and the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership.

KDB Darulehsan (07) is the second ship of the Darussalam-class offshore patrol vessels. The vessel is in active service in the Royal Brunei Navy (RBN).
References
- ↑ WPNS WORKSHOP 2013
- ↑ "Fact Sheet: Background of the Western Pacific Naval Symposium, MCMEX, DIVEX and NMS". www.mindef.gov.sg. Ministry of Defence (Singapore). 25 March 2011. Retrieved 17 May 2015.
- ↑ "File Not Found".