Related Research Articles

Edna Ferber was an American novelist, short story writer and playwright. Her novels include the Pulitzer Prize-winning So Big (1924), Show Boat, Cimarron, Giant and Ice Palace (1958), which also received a film adaptation in 1960. She helped adapt her short story "Old Man Minick", published in 1922, into a play (Minick) and it was thrice adapted to film, in 1925 as the silent film Welcome Home, in 1932 as The Expert, and in 1939 as No Place to Go.

The Wonderful Wizard of Oz is a 1900 children's novel written by author L. Frank Baum and illustrated by W. W. Denslow. It is the first novel in the Oz series of books. A Kansas farm girl named Dorothy ends up in the magical Land of Oz after she and her pet dog Toto are swept away from their home by a cyclone. Upon her arrival in the magical world of Oz, she learns she cannot return home until she has destroyed the Wicked Witch of the West.

"Alexander's Ragtime Band" is a Tin Pan Alley song by American composer Irving Berlin released in 1911; it is often inaccurately cited as his first global hit. Despite its title, the song is a march as opposed to a rag and contains little syncopation. The song is a narrative sequel to Berlin's earlier 1910 composition "Alexander and His Clarinet". This earlier composition recounts the reconciliation between an African-American musician named Alexander Adams and his flame Eliza Johnson as well as highlights Alexander's innovative musical style. Berlin's friend Jack Alexander, a cornet-playing African-American bandleader, inspired the title character.

Newton Booth Tarkington was an American novelist and dramatist best known for his novels The Magnificent Ambersons (1918) and Alice Adams (1921). He is one of only four novelists to win the Pulitzer Prize for Fiction more than once, along with William Faulkner, John Updike, and Colson Whitehead. In the 1910s and 1920s he was considered the United States' greatest living author. Several of his stories were adapted to film.

Stephen Vincent Benét was an American poet, short story writer, and novelist. He wrote a book-length narrative poem of the American Civil War, John Brown's Body, published in 1928, for which he received the Pulitzer Prize for Poetry, and for the short stories "The Devil and Daniel Webster", published in 1936, and "By the Waters of Babylon", published in 1937.
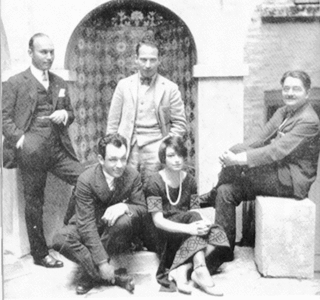
The Algonquin Round Table was a group of New York City writers, critics, actors, and wits. Gathering initially as part of a practical joke, members of "The Vicious Circle", as they dubbed themselves, met for lunch each day at the Algonquin Hotel from 1919 until roughly 1929. At these luncheons they engaged in wisecracks, wordplay, and witticisms that, through the newspaper columns of Round Table members, were disseminated across the country.

Alexander Humphreys Woollcott was an American drama critic and commentator for The New Yorker magazine, a member of the Algonquin Round Table, an occasional actor and playwright, and a prominent radio personality.

Harold Wallace Ross was an American journalist who co-founded The New Yorker magazine in 1925 with his wife Jane Grant, and was its editor-in-chief until his death.

The Baker Street Irregulars is an organization of Sherlock Holmes enthusiasts founded in 1934 by Christopher Morley. As of 2015, the nonprofit organization had about 300 members worldwide.

Neysa Moran McMein was an American illustrator and portrait painter who studied at The School of The Art Institute of Chicago and Art Students League of New York. She began her career as an illustrator and during World War I, she traveled across France entertaining military troops with Anita P. Wilcox and Jane Bulley and made posters to support the war effort. She was made an honorary non-commissioned officer in the United States Marine Corps for her contributions to the war effort.

Charles Robert Starrett was an American actor, best known for his starring role in the Durango Kid westerns. Starrett still holds the record for starring in the longest series of theatrical features: 131 westerns, all produced by Columbia Pictures.
Christopher Lehmann-Haupt was an American journalist, editor of the New York Times Book Review, critic, and novelist, based in New York City. He served as senior Daily Book Reviewer from 1969 to 1995.

The Man Who Came to Dinner is a comedy play by George S. Kaufman and Moss Hart. It debuted on October 16, 1939, at the Music Box Theatre in New York City, where it ran until 1941, closing after 739 performances. It then enjoyed a number of New York and London revivals. The first London production was staged at The Savoy Theatre starring Robert Morley and Coral Browne. In 1990, Browne stated in a televised biographical interview, broadcast on UK Channel 4, that she bought the rights to the play, borrowing money from her dentist to do so. When she died, her will revealed that she had received royalties for all later productions and adaptations of the play.
Charles Vincent Emerson Starrett, known as Vincent Starrett, was a Canadian-born American writer, newspaperman, and bibliophile.

Frederic Dorr Steele was an American illustrator best known for his work on Arthur Conan Doyle's Sherlock Holmes stories.

Charles Gibbs was the pseudonym of an American pirate, born James D. Jeffers. Jeffers was one of the last active pirates in the Caribbean during the early 19th century, and was among the last persons to be executed for piracy by the United States.

Central Theatre was a Broadway theatre in New York City built in 1918. It was located at 1567 Broadway, at the southwest corner with 47th Street, and seated approximately 1,100 patrons. The architect was Herbert J. Krapp. The theatre was built by the Shubert family on a site previously occupied by the Mathushek & Son piano factory.
I say it's spinach is a twentieth-century American idiom with the approximate meaning of "nonsense" or "rubbish". It is usually spoken or written as an anapodoton, thus only the first part of the complete phrase is given to imply the second part, which is what is actually meant: "I say the hell with it."
The Private Life of Sherlock Holmes is a book by Vincent Starrett originally published in 1933. It is considered the first book on Sherlock Holmes scholarship, as well as a cornerstone of the study of Sherlockiana. It has been credited with jumpstarting the creation of Sherlockian Societies. It has been used as an inspiration and a reference for "biographies" of Sherlock Holmes such as Nick Rennison's 2005 Sherlock Holmes: The Unauthorized Biography.

The Vanishing Hotel Room is an urban legend which alleges that during an international exposition in Paris, a daughter who returned after leaving her mother in a hotel room found the woman gone, and the hotel staff professed to have no knowledge of the missing woman.
References
- ↑ "WHILE ROME BURNS by Alexander Woollcott" – via www.kirkusreviews.com.
- 1 2 Wallace, David. "The Round Table". Capital of the World: A Portrait of New York City in the Roaring Twenties. Guilford, CT: Lyons Press. p. 168. ISBN 978-0-7627-7010-6.
- ↑ Poore, C. g (4 March 1934). "Mr. Woollcott Runs On and On;" – via NYTimes.com.
- ↑ "Asia and the Americas". 24 December 2018 – via Google Books.
- ↑ "Vincent Starrett and the 1934 Baker Street Irregulars Dinner". Studies in Starrett.