Related Research Articles

Basel Convention, is an international treaty that was designed to reduce the movements of hazardous waste between nations, and specifically to prevent transfer of hazardous waste from developed to less developed countries (LDCs). It does not, however, address the movement of radioactive waste. The convention is also intended to minimize the rate and toxicity of wastes generated, to ensure their environmentally sound management as closely as possible to the source of generation, and to assist LDCs in environmentally sound management of the hazardous and other wastes they generate.

The International Labour Organization (ILO) is a United Nations agency whose mandate is to advance social and economic justice through setting international labour standards. Founded in October 1919 under the League of Nations, it is the first and oldest specialised agency of the UN. The ILO has 187 member states: 186 out of 193 UN member states plus the Cook Islands. It is headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland, with around 40 field offices around the world, and employs some 3,381 staff across 107 nations, of whom 1,698 work in technical cooperation programmes and projects.
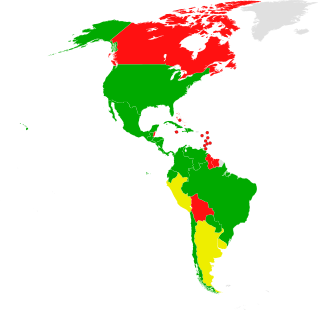
The Montevideo Convention on the Rights and Duties of States is a treaty signed at Montevideo, Uruguay, on December 26, 1933, during the Seventh International Conference of American States. The Convention codifies the declarative theory of statehood as accepted as part of customary international law. At the conference, United States President Franklin D. Roosevelt and Secretary of State Cordell Hull declared the Good Neighbor Policy, which opposed U.S. armed intervention in inter-American affairs. The convention was signed by 19 states. The acceptance of three of the signatories was subject to minor reservations. Those states were Brazil, Peru and the United States.

The Nineteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution prohibits the United States and its states from denying the right to vote to citizens of the United States on the basis of sex, in effect recognising the right of women to a vote. The amendment was the culmination of a decades-long movement for women's suffrage in the United States, at both the state and national levels, and was part of the worldwide movement towards women's suffrage and part of the wider women's rights movement. The first women's suffrage amendment was introduced in Congress in 1878. However, a suffrage amendment did not pass the House of Representatives until May 21, 1919, which was quickly followed by the Senate, on June 4, 1919. It was then submitted to the states for ratification, achieving the requisite 36 ratifications to secure adoption, and thereby go into effect, on August 18, 1920. The Nineteenth Amendment's adoption was certified on August 26, 1920.

The Vienna Convention on Diplomatic Relations of 1961 is an international treaty that defines a framework for diplomatic relations between independent countries. It specifies the privileges of a diplomatic mission that enable diplomats to perform their function without fear of coercion or harassment by the host country. This forms the legal basis for diplomatic immunity. Its articles are considered a cornerstone of modern international relations. As of June 2020, it has been ratified by 193 states.

The United Nations Convention on the Rights of the Child is an international human rights treaty which sets out the civil, political, economic, social, health and cultural rights of children. The Convention defines a child as any human being under the age of eighteen, unless the age of majority is attained earlier under national legislation.

The Convention for the Suppression of the Traffic in Persons and of the Exploitation of the Prostitution of Others was approved by the United Nations General Assembly on 2 December 1949 and entered into force on 25 July 1951. The preamble states:
"Whereas prostitution and the accompanying evil of the traffic in persons for the purpose of prostitution are incompatible with the dignity and worth of the human person and endanger the welfare of the individual, the family and the community"

The Vienna Convention on the Law of Treaties (VCLT) is an international agreement regulating treaties between states. Known as the "treaty on treaties", it establishes comprehensive rules, procedures, and guidelines for how treaties are defined, drafted, amended, interpreted, and generally operated. An international treaty is a written agreement between international law subjects reflecting their consent to the creation, alteration, or termination of their rights and obligations. The VCLT is considered a codification of customary international law and state practice concerning treaties.

The United Nations Commission on International Trade Law (UNCITRAL) is a subsidiary body of the U.N. General Assembly (UNGA) responsible for helping to facilitate international trade and investment.
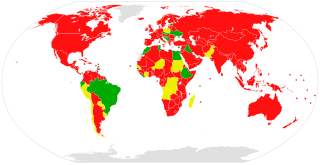
The Vienna Convention on Succession of States in Respect of Treaties is an international treaty opened for signature in 1978 to set rules on succession of states. It was adopted partly in response to the "profound transformation of the international community brought about by the decolonization process". It entered into force on 6 November 1996, which was triggered by the succession of the Republic of Macedonia to the treaty giving it the requisite 15 parties.
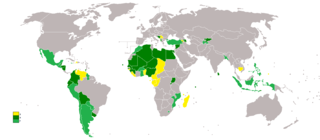
The International Convention on the Protection of the Rights of All Migrant Workers and Members of Their Families is a United Nations multilateral treaty governing the protection of migrant workers and families. Signed on 18 December 1990, it entered into force on 1 July 2003 after the threshold of 20 ratifying States was reached in March 2003. The Committee on Migrant Workers (CMW) monitors implementation of the convention, and is one of the seven UN-linked human rights treaty bodies. The convention applies as of August 2021 in 56 countries.
Vocational Rehabilitation and Employment Convention, 1983 is an International Labour Organization Convention.

The Convention on Road Signs and Signals, commonly known as the Vienna Convention on Road Signs and Signals, is a multilateral treaty designed to increase road safety and aid international road traffic by standardising the signing system for road traffic in use internationally.
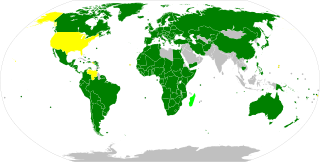
The Protocol Relating to the Status of Refugees is a key treaty in international refugee law. It entered into force on 4 October 1967, and 146 countries are parties.
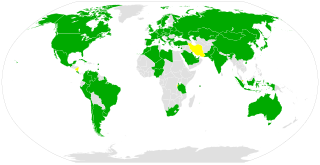
The Convention on Registration of Objects Launched into Outer Space was adopted by the United Nations General Assembly in 1974 and went into force in 1976. As of July 2021, it has been ratified by 71 states.

The Hague Convention on the International Recovery of Child Support and Other Forms of Family Maintenance, also referred to as the Hague Maintenance Convention or the Hague Child Support Convention is a multilateral treaty governing the enforcement of judicial decisions regarding child support extraterritorially. It is one of a number of conventions in the area of private international law of the Hague Conference on Private International Law in 2007. The convention is open to all states as well as to Regional Economic Integration Organizations as long as they are composed of sovereign states only and have sovereignty in the content of the convention. The convention entered into force on 1 January 2013 between Norway and Albania, with Bosnia-Herzegovina (2013), Ukraine (2013), the European Union, Montenegro (2017), United States (2017), Turkey (2017), Kazakhstan (2017), Brazil (2017), Honduras (2017), Belarus (2018), Guyana (2020), Nicaragua (2020), United Kingdom (2021), Serbia (2021) and New Zealand (2021) following suit. Because the EU acceptance of the convention applies in 27 EU countries, the convention applies in 42 countries worldwide.
The International Convention for the Suppression of the Traffic in Women and Children is a 1921 multilateral treaty of the League of Nations that addressed the problem of international trafficking of women and children.

The Convention Relating to the Distribution of Programme-Carrying Signals Transmitted by Satellite was opened for signature on 21 May 1974 in Brussels and entered into force on 25 August 1979. It is overseen by the United Nations Committee on the Peaceful Uses of Outer Space.
References
- ↑ Referred to by the United Nations as "The Former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia" due to the Macedonia naming dispute.