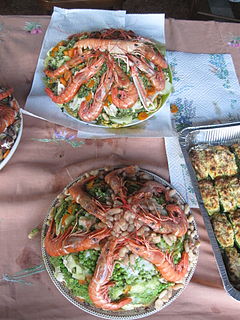Chicken soup is a soup made from chicken, simmered in water, usually with various other ingredients. The classic chicken soup consists of a clear chicken broth, often with pieces of chicken or vegetables; common additions are pasta, noodles, dumplings, or grains such as rice and barley. Chicken soup has acquired the reputation of a folk remedy for colds and influenza, and in many countries is considered a comfort food.

Rutabaga or swede is a root vegetable, a form of Brassica napus. Other names include Swedish turnip, neep (Scottish), snagger and turnip – however, elsewhere the name "turnip" usually refers to the related white turnip. The species Brassica napus originated as a hybrid between the cabbage and the turnip. Rutabaga roots are eaten as human food in a variety of ways, and the leaves can be eaten as a leaf vegetable. The roots and tops are also used for livestock, either fed directly in the winter or foraged in the field during the other seasons. Scotland, Northern England, West England and Ireland had a tradition of carving the roots into lanterns at Halloween.

Daikon, Raphanus sativus var. longipinnatus, also known by many other names depending on context, is a mild-flavored winter radish usually characterized by fast-growing leaves and a long, white, napiform root. Originally native to continental East Asia, daikon is harvested and consumed throughout the region, as well as in South Asia, and is now available internationally. In some locations, daikon may be planted but not harvested, for its ability to break up compacted soils and recover nutrients.

A mirepoix is a flavor base made from cooked, diced vegetables, usually with butter, oil, or other fat, for a long time on a low heat without coloring or browning, as further cooking, often with the addition of tomato purée, creates a darkened brown mixture called pincage. It is not sautéed or otherwise hard cooked, because the intention is to sweeten the ingredients rather than caramelize them. It is a long-standing cooking technique in French cuisine.

Daucus carota, whose common names include wild carrot, bird's nest, bishop's lace, and Queen Anne's lace, is a white, flowering plant in the family Apiaceae, native to temperate regions of Europe and southwest Asia, and naturalized to North America and Australia.

The parsnip, Pastinaca sativa, is a root vegetable closely related to carrot and parsley; all belong to the family Apiaceae. It is a biennial plant usually grown as an annual. Its long, tuberous root has cream-colored skin and flesh, and, left in the ground to mature, it becomes sweeter in flavor after winter frosts. In its first growing season, the plant has a rosette of pinnate, mid-green leaves. If unharvested, in its second growing season it produces a flowering stem topped by an umbel of small yellow flowers, later producing pale brown, flat, winged seeds. By this time, the stem has become woody and the tuberous root inedible.

Arracacha is a root vegetable originally from the Andes, somewhat intermediate between the carrot and celery root. Its starchy taproot is a popular food item in South America where it is a major commercial crop.

Pickling is the process of preserving or extending the shelf life of food by either anaerobic fermentation in brine or immersion in vinegar. The pickling procedure typically affects the food's texture, taste and flavor. The resulting food is called a pickle, or, to prevent ambiguity, prefaced with pickled. Foods that are pickled include vegetables, fruits, meats, fish, dairy and eggs.

Sopa de mondongo is a soup made from diced tripe slow-cooked with vegetables such as bell peppers, onions, carrots, cabbage, celery, tomatoes, cilantro (coriander), garlic or root vegetables. The dish is generally prepared in former Spanish colonies in Latin America, Caribbean, and in the Philippines.

Hutspot (Dutch), hochepot (French), or hotchpotch (English), is a dish of boiled and mashed potatoes, carrots, and onions with a long history in traditional Dutch cuisine. Hutspot also found in Indonesian cuisine due to their historical ties.

A root cellar is a structure, usually underground or partially underground, used for storage of vegetables, fruits, nuts, or other foods. Its name reflects the traditional focus on root crops stored in an underground cellar, which is still often true. A wide variety of foods can be stored for weeks to months, depending on the crop and conditions. The structure may not always be underground.

The carrot is a root vegetable, usually orange in color, though purple, black, red, white, and yellow cultivars exist. They are a domesticated form of the wild carrot, Daucus carota, native to Europe and Southwestern Asia. The plant probably originated in Persia and was originally cultivated for its leaves and seeds. The most commonly eaten part of the plant is the taproot, although the stems and leaves are also eaten. The domestic carrot has been selectively bred for its greatly enlarged, more palatable, less woody-textured taproot.
Molagoottal is a South Indian stew with coconut and lentils as a base. It is a dish unique to the Nairs and Iyers of Kerala.
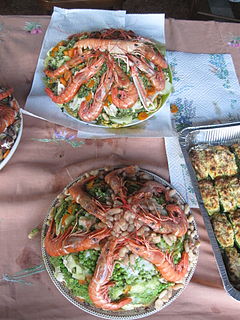
Cappon magro[kapˌpom ˈmaːɡro], is an elaborate Genoese salad of seafood and vegetables over hardtack arranged into a decorative pyramid and dressed with a rich sauce.

Olivier salad is a traditional salad dish in Russian cuisine, which is also popular in other post-Soviet countries, many European countries, Iran, Israel, Mongolia and also throughout Latin America. In different modern recipes, it is usually made with diced boiled potatoes, carrots, brined dill pickles, green peas, eggs, celeriac, onions, diced boiled chicken or bologna sausage, and tart apples, with salt, pepper, and mustard added to enhance flavor, dressed with mayonnaise. In many countries, the dish is commonly referred to as Russian salad. A variation called Stolichny salad exists, and is also popular in the Russian cuisine.

Chikuzenni is a dish that originated from northern Kyushu, Japan, made of braised chicken and vegetables. It is often eaten when bringing in the new year in Japan.

Vegetable chips are chips or crisps that are prepared using vegetables. Vegetable chips may be fried, deep-fried, dehydrated, dried or baked. Many different root vegetables or leaf vegetables may be used. Vegetable chips may be eaten as a snack food, and may accompany other foods such as dips, or be used as a topping on dishes. In the United States, vegetable chips are often mass-produced, with many brands marketed to consumers.

Carrot soup is a soup prepared with carrot as a primary ingredient. It can be prepared as a cream- or broth-style soup. Additional vegetables, root vegetables and various other ingredients can be used in its preparation. It may be served hot or cold, and several recipes exist.