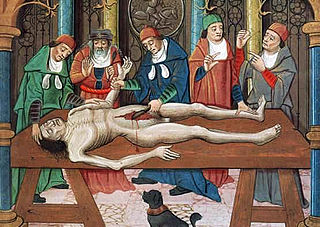
The history of anatomy extends from the earliest examinations of sacrificial victims to the sophisticated analyses of the body performed by modern scientists. The study of human anatomy can be traced back thousands of years, at least to the Egyptians, but the science of anatomy, as we know it today, did not develop until far later. The development of the study of anatomy gradually built upon concepts that were understood during the time of Galen and slowly became a part of the traditional medical curriculum. It has been characterized, over time, by a continually developing understanding of the functions of organs and structures in the body.
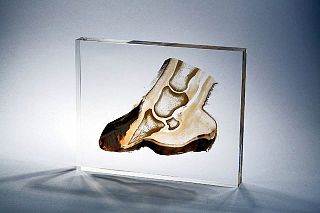
Plastination is a technique or process used in anatomy to preserve bodies or body parts, first developed by Gunther von Hagens in 1977. The water and fat are replaced by certain plastics, yielding specimens that can be touched, do not smell or decay, and even retain most properties of the original sample.
Neurophysiology is a branch of physiology and neuroscience that is concerned with the study of the functioning of the nervous system. The primary tools of basic neurophysiological research include electrophysiological recordings, such as patch clamp, voltage clamp, extracellular single-unit recording and recording of local field potentials, as well as some of the methods of calcium imaging, optogenetics, and molecular biology.

Dissection is the dismembering of the body of a deceased animal or plant to study its anatomical structure. Autopsy is used in pathology and forensic medicine to determine the cause of death in humans. Less extensive dissection of plants and smaller animals preserved in a formaldehyde solution is typically carried out or demonstrated in biology and natural science classes in middle school and high school, while extensive dissections of cadavers of adults and children, both fresh and preserved are carried out by medical students in medical schools as a part of the teaching in subjects such as anatomy, pathology and forensic medicine. Consequently, dissection is typically conducted in a morgue or in an anatomy lab.

The longitudinal fissure is the deep groove that separates the two cerebral hemispheres of the vertebrate brain. Lying within it is a continuation of the dura mater called the falx cerebri. The inner surfaces of the two hemispheres are convoluted by gyri and sulci just as is the outer surface of the brain.

In neuroanatomy, the corona radiata is a white matter sheet that continues ventrally as the internal capsule and dorsally as the centrum semiovale. This sheet of both ascending and descending axons carries most of the neural traffic from and to the cerebral cortex. The corona radiata is associated with the corticopontine tract, the corticobulbar tract, and the corticospinal tract.
Gross anatomy is the study of anatomy at the visible or macroscopic level. The counterpart to gross anatomy is the field of histology, which studies microscopic anatomy. Gross anatomy of the human body or other animals seeks to understand the relationship between components of an organism in order to gain a greater appreciation of the roles of those components and their relationships in maintaining the functions of life. The study of gross anatomy can be performed on deceased organisms using dissection or on living organisms using medical imaging. Education in the gross anatomy of humans is included training of most health professionals.
Brain mapping is a set of neuroscience techniques predicated on the mapping of (biological) quantities or properties onto spatial representations of the brain resulting in maps.
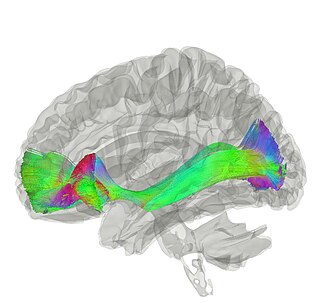
The occipitofrontal fasciculus passes backward from the frontal lobe, along the lateral border of the caudate nucleus, and on the medial aspect of the corona radiata; its fibers radiate in a fan-like manner and pass into the occipital and temporal lobes lateral to the posterior and inferior cornua.

The uncinate fasciculus is a white matter association tract in the human brain that connects parts of the limbic system such as the parahippocampus and amygdala in the temporal lobe with portions of the frontal lobe such as the orbitofrontal cortex. Its function is unknown though it is affected in several psychiatric conditions. It is one of the last white matter tract to mature in the human brain.

Voxel-based morphometry is a computational approach to neuroanatomy that measures differences in local concentrations of brain tissue, through a voxel-wise comparison of multiple brain images.

The inferior longitudinal fasciculus is traditionally considered one of the major occipitotemporal association tracts. It connects the anterior temporal lobe and the extrastriate cortex of the occipital lobe, running along the lateral and inferior wall of the lateral ventricle.

Luigi Rolando was an Italian anatomist known for his pioneering research in brain localization of function.
A cadaver is a dead human body that is used by medical students, physicians and other scientists to study anatomy, identify disease sites, determine causes of death, and provide tissue to repair a defect in a living human being. Students in medical school study and dissect cadavers as a part of their education. Others who study cadavers include archaeologists and artists.

The Medical Renaissance, from 1400 to 1700 CE, is the period of progress in European medical knowledge, and a renewed interest in the ideas of the ancient Greek and Roman civilizations, along with Arabic-Persian medicine, after the Latin translation movement. Such medical discoveries during the Medical Renaissance are credited with paving the way for modern medicine.
A prosection is the dissection of a cadaver or part of a cadaver by an experienced anatomist in order to demonstrate for students anatomic structure. In a dissection, students learn by doing; in a prosection, students learn by either observing a dissection being performed by an experienced anatomist or examining a specimen that has already been dissected by an experienced anatomist
Brain morphometry is a subfield of both morphometry and the brain sciences, concerned with the measurement of brain structures and changes thereof during development, aging, learning, disease and evolution. Since autopsy-like dissection is generally impossible on living brains, brain morphometry starts with noninvasive neuroimaging data, typically obtained from magnetic resonance imaging. These data are born digital, which allows researchers to analyze the brain images further by using advanced mathematical and statistical methods such as shape quantification or multivariate analysis. This allows researchers to quantify anatomical features of the brain in terms of shape, mass, volume, and to derive more specific information, such as the encephalization quotient, grey matter density and white matter connectivity, gyrification, cortical thickness, or the amount of cerebrospinal fluid. These variables can then be mapped within the brain volume or on the brain surface, providing a convenient way to assess their pattern and extent over time, across individuals or even between different biological species. The field is rapidly evolving along with neuroimaging techniques—which deliver the underlying data—but also develops in part independently from them, as part of the emerging field of neuroinformatics, which is concerned with developing and adapting algorithms to analyze those data.
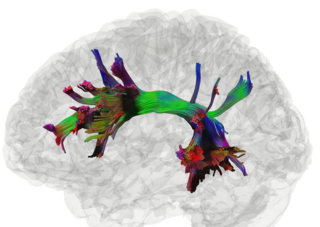
High definition fiber tracking (HDFT) is a tractography technique where data from MRI scanners is processed through computer algorithms to reveal the detailed wiring of the brain and to pinpoint fiber tracts. Each tract contains millions of neuronal connections. HDFT is based on data acquired from diffusion spectrum imaging and processed by generalized q-sampling imaging. The technique makes it possible to virtually dissect 40 major fiber tracts in the brain. The HDFT scan is consistent with brain anatomy unlike diffusion tensor imaging (DTI). Thus, the use of HDFT is essential in pinpointing damaged neural connections.
Saleem Abdulrauf is an American neurosurgeon. He is a physician specializing in neurosurgery in St. Louis, Missouri, who has helped develop high-flow brain bypass surgery, a procedure for treating intracranial aneurysm, a less-invasive procedure than traditional methods.
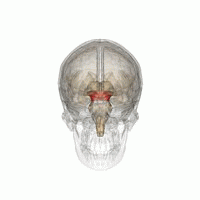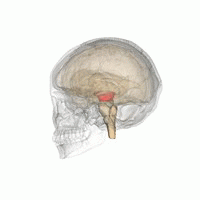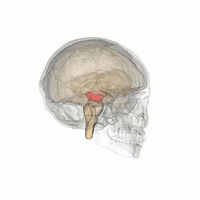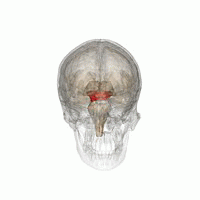
The mesencephalic locomotor region (MLR) is a functionally defined area of the midbrain that is associated with the initiation and control of locomotor movements in vertebrate species.












