Related Research Articles
The economy of Gibraltar consists largely of the services sector. While part of the European Union until Brexit, the British overseas territory of Gibraltar has a separate legal jurisdiction from the United Kingdom and a different tax system. The role of the UK Ministry of Defence, which at one time was Gibraltar's main source of income, has declined, with today's economy mainly based on shipping, tourism, financial services, and the Internet.

A bookmaker, bookie, or turf accountant is an organization or a person that accepts and pays out bets on sporting and other events at agreed-upon odds.

The Crown Dependencies are three island territories in the British Islands that are self-governing possessions of the British Crown: the Bailiwick of Guernsey and the Bailiwick of Jersey, both located in the English Channel and together known as the Channel Islands, and the Isle of Man in the Irish Sea between Great Britain and Ireland. They are not part of the United Kingdom (UK) nor are they British Overseas Territories. They have the status of "territories for which the United Kingdom is responsible", rather than sovereign states. As a result, they are not member states of the Commonwealth of Nations. However, they do have relationships with the Commonwealth and other international organizations, and are members of the British–Irish Council. They have their own teams in the Commonwealth Games.

The European Health Insurance Card (EHIC) is issued free of charge and allows anyone who is insured by or covered by a statutory social security scheme of the EEA countries, Switzerland, and the United Kingdom to receive medical treatment in another member state in the same way as residents of that state—i.e., free or at a reduced cost—if treatment becomes necessary during their visit, or if they have a chronic pre-existing condition which requires care such as kidney dialysis. The term of validity of the card varies according to the issuing country. Continued reciprocal healthcare access between the EU and the UK was agreed, and the UK issues a UK Global Health Insurance Card (GHIC) valid in the EU, but not other EEA countries.
Online gambling is any kind of gambling conducted on the internet. This includes virtual poker, casinos, and sports betting. The first online gambling venue opened to the general public was ticketing for the Liechtenstein International Lottery in October 1994. Today, the market is worth around $40 billion globally each year, according to various estimates.

A British Overseas Territories citizen (BOTC), formerly called British Dependent Territories citizen (BDTC), is a member of a class of British nationality granted to people connected with one or more of the British Overseas Territories.
Gambling in the United Kingdom is regulated by the Gambling Commission on behalf of the government's Department for Digital, Culture, Media and Sport (DCMS) under the Gambling Act 2005. This Act of Parliament significantly updated the UK's gambling laws, including the introduction of a new structure of protections for children and vulnerable adults, as well as bringing the burgeoning Internet gaming sector within British regulation for the first time.
A gaming control board (GCB), also called by various names including gambling control board, casino control board, gambling board, and gaming commission, is a government agency charged with regulating casino and other types of gaming in a defined geographical area, usually a state, and of enforcing gaming law in general.
The Isle of Man is not part of the United Kingdom, but to a large extent its relations with other countries are handled by the United Kingdom.

The Gambling Commission is an executive, non-departmental public body of the Government of the United Kingdom responsible for regulating gambling and supervising gaming law in Great Britain. Its remit covers arcades, betting, bingo, casinos, slot machines and lotteries, as well as remote gambling, but not spread betting. Free prize competitions and draws are free of the Commission’s control under the "Gambling Act 2005"

The Schengen Area is an area comprising 27 European countries that have officially abolished many passport and many other types of border control at their mutual borders. Being an element within the wider area of freedom, security and justice policy of the European Union (EU), it mostly functions as a single jurisdiction under a common visa policy for international travel purposes. The area is named after the 1985 Schengen Agreement and the 1990 Schengen Convention, both signed in Schengen, Luxembourg.

The Gibraltar variant British passport is a British passport issued to British Citizens and British Overseas Territory Citizens who work or live in Gibraltar. Having Gibraltarian status alone, and not being resident in Gibraltar, is insufficient criteria to obtain a Gibraltar Passport. Gibraltar passports are issued by the Passport Office of the Gibraltar Civil Status and Registration Office. Since 2005, passports issued in Gibraltar have been biometric.
A qualifying recognised overseas pension scheme, or QROPS is an overseas pension scheme that meets certain requirements set by HM Revenue and Customs (HMRC). A QROPS can receive transfers of British pension benefits. The QROPS programme was part of British legislation launched on 6 April 2006 as a direct result of EU human rights requirements of the freedom of capital movement.

The Isle of Man Gambling Supervision Commission is the Gaming Control Board of the Isle of Man. It regulates most forms of gambling in its territory including land based and online gambling services.
The Interactive Gambling Act (IGA) was passed in June 2001 by the Australian Government with the purpose of protecting the Australian public from the detrimental effects of online gambling.
Blasphemy is not a criminal offence under Australian federal law, but the de jure situation varies at state and territory level; it is currently not enforced in any Australian jurisdiction. The offences of blasphemy and blasphemous libel in English common law were carried over to the Australian colonies and "received" into state law following Federation in 1901. The common-law offences have been abolished totally in Queensland and Western Australia, when those jurisdictions adopted criminal codes that superseded the common law. In South Australia, Victoria, and the Northern Territory the situation is ambiguous, as the local criminal codes do not mention blasphemy but also did not specifically abolish the common-law offences. In New South Wales and Tasmania, the criminal codes do include an offence of blasphemy or blasphemous libel, but the relevant sections are not enforced and generally regarded as obsolete.

The visa policy of the United Kingdom is the policy by which His Majesty's Government determines visa requirements for visitors to the United Kingdom, and the Crown dependencies of Guernsey, Jersey, and the Isle of Man and those seeking to work, study or reside there. All intended entrants must obtain a visa unless they are exempt.
Financial services in Gibraltar refers to the services provided in the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar by the finance industry: banks, investment banks, insurance companies, credit card companies, consumer finance companies, government-sponsored enterprises, and stock brokerages.
Gibraltar Betting and Gaming Association is a trade association representing online gambling businesses with remote gambling licences issued in Gibraltar.
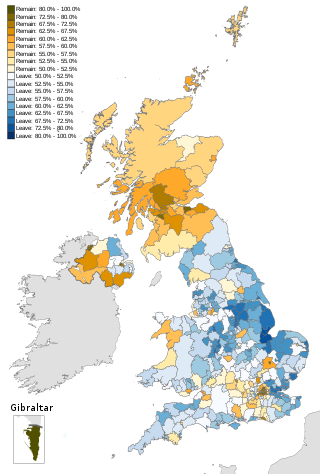
The 2016 United Kingdom European Union membership referendum took place in the United Kingdom and Gibraltar on 23 June 2016. Membership of the European Union had been a topic of political debate in the United Kingdom since the country joined the European Communities in 1973. This referendum was conducted very differently from the European Communities membership referendum in 1975; a more localised and regionalised counting procedure was used, and the ballot was overseen by the Electoral Commission, a public body which did not exist at the time of the first vote. This article lists, by voting area for Great Britain and Gibraltar and by parliamentary constituency for Northern Ireland, all the results of the referendum, each ordered into national and regional sections.
References
- 1 2 Whitelisting criteria
- ↑ Gambling: Ad Ban
- ↑ Written Ministerial Statements, 16 July 2007 : Column 3WS
- ↑ Gambling Commission: Do I need a license – remote?
- 1 2 3 Gambling Consultant: Offshore regulation consultation
- ↑ UK admits Tasmania to the whitelist
- ↑ Ban on Gambling Advertising
- ↑ Royal College of Psychiatrists: Submission to the Secretary of State for Culture, Media and Sport
- ↑ Session of the Select Committee: Transcript of Oral Evidence