Related Research Articles

The ANF Les Mureaux 110 and its derivatives were a family of French reconnaissance aircraft developed in the 1930s. They were all-metal, parasol-wing monoplanes that seated the pilot and observer in tandem open cockpits. The aircraft were widely used in the Battle of France, but were all scrapped soon thereafter.

The Dewoitine D.27 was a parasol monoplane fighter aircraft designed by Émile Dewoitine in 1928.

The Morane-Saulnier M.S.225 was a French fighter aircraft of the 1930s. It was produced in limited quantities to be used as a transitional aircraft between the last of the biplanes and the first monoplane fighters.

The Bloch MB.120 was a French three-engine colonial transport aircraft built by Société des Avions Marcel Bloch during the 1930s.

The Blériot 165 was a French airliner of the 1920s. It was a four-engined biplane, a final development in the family of designs that began with the Blériot 115. Two were built for Air Union to replace the Farman Goliath on their Paris–London route and were christened Leonardo da Vinci and Octave Chanute. The airline found that it preferred the Lioré et Olivier LeO 21s that it had ordered alongside this aircraft, meaning that no further examples were produced.
The Potez XV was a French single-engine, two-seat observation biplane designed as a private venture by Louis Coroller and built by Potez and under licence in Poland.

The Potez 540 was a French multi-role aircraft of the 1930s. Designed and built by Potez, it served with the French Air Force as a reconnaissance bomber, also serving with the Spanish Republican Air Force during the Spanish Civil War. Although obsolete as a bomber, it remained in service in support roles and in France's overseas colonies at the start of World War II.

The DINFIA IA 35 Huanquero was a 1950s Argentine twin-engined general-purpose monoplane aircraft built by the DINFIA.

The Dewoitine D.21 was 1920s French open-cockpit, fixed-undercarriage monoplane fighter aircraft.
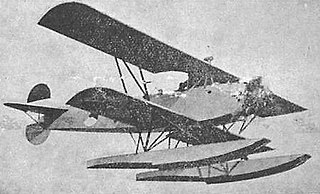
The Fokker C.VII-W was a reconnaissance seaplane built in the Netherlands in the late 1920s. Sharing elements of the highly successful C.V design, the C.VII-W was a conventional, single-bay biplane with wings of unequal span braced with N-struts. The undercarriage consisted of a standard twin-pontoon arrangement, and the fin and rudder continued through to the ventral side of the fuselage, creating a cruciform tail. The pilot and observer sat in tandem, open cockpits. The wing structure was wooden with fabric and plywood covering, and the fuselage was of steel tube construction with fabric covering.

The Dornier Do Y was a German bomber of the 1930s, the second bomber design by Dornier Flugzeugwerke.

The Wibault 7 was a 1920s French monoplane fighter designed and built by Société des Avions Michel Wibault. Variants were operated by the French and Polish military and built under licence for Chile as the Vickers Wibault.

The Bréguet 410 was a French bomber of the early 1930s. Not many of these twin-engined sesquiwing biplanes were built. At least one Breguet 413, one of its variants, was sold to the Spanish Republican Air Force during the Spanish Civil War.

The Wibault Wib 210 C.1 was a single engine, single seat low wing monoplane fighter aircraft, designed and built in France in the late 1920s. Flight tests revealed vibration problems and development was quickly abandoned.
The Wibault 313, Wibault Wib 313 or Penhoët Wibault Wib 313 was a single engine, single seat low wing monoplane fighter aircraft, designed and built in France in the early 1930s. It was entered into a government competitive tender programme but was not ordered.

The Wibault 10/II Tramontane was a two-seat reconnaissance aircraft designed and built by Société des Avions Michel Wibault in France for the French military 1923 A.2 competition for a 2-seater reconnaissance aircraft.

The Bréguet 670, Bréguet 670T or Bréguet-Wibault 670 was a French twin engine, all metal eighteen seat airliner with a retractable undercarriage flown in 1935. Only one was built.
The Caudron C.860 was a single engine, single seat monoplane ordered by the French government as a long distance communications aircraft. First flown in 1938, it was also expected to set speed and altitude records but the outbreak of World War II ended developments.

The Wibault 260 R.2 was a contender for a French government contract for a long range, two seat reconnaissance aircraft, issued in 1928. There were eight prototypes in the 1931-2 contest and the Wibault was not selected for production.

The Wibault 220 or Wibault R.N.3 220 was a twin-engined French night reconnaissance aircraft. Two were built in 1930 to a government contract.
References
- ↑ Cortet, p. 30