Related Research Articles

In the United States, a conservation easement is a power invested in a qualified private land conservation organization or government to constrain, as to a specified land area, the exercise of rights otherwise held by a landowner so as to achieve certain conservation purposes. It is an interest in real property established by agreement between a landowner and land trust or unit of government. The conservation easement "runs with the land", meaning it is applicable to both present and future owners of the land. The grant of conservation easement, as with any real property interest, is part of the chain of title for the property and is normally recorded in local land records.

An agricultural subsidy is a government incentive paid to agribusinesses, agricultural organizations and farms to supplement their income, manage the supply of agricultural commodities, and influence the cost and supply of such commodities. Examples of such commodities include: wheat, feed grains, cotton, milk, rice, peanuts, sugar, tobacco, oilseeds such as soybeans and meat products such as beef, pork, and lamb and mutton.

Conservation agriculture (CA) can be defined by a statement given by the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations as "A farming system that promotes minimum soil disturbance, maintenance of a permanent soil cover, and diversification of plant species. It enhances biodiversity and natural biological processes above and below the ground surface, which contribute to increased water and nutrient use efficiency and to improved and sustained crop production."

The nutria, also known as the coypu, is a large, herbivorous, semiaquatic rodent. Classified for a long time as the only member of the family Myocastoridae, Myocastor is now included within Echimyidae, the family of the spiny rats. The nutria lives in burrows alongside stretches of water, and feeds on river plant stems. Originally native to subtropical and temperate South America, it has since been introduced to North America, Europe, Asia, and Africa, primarily by fur farmers. Although it is still hunted and trapped for its fur in some regions, its destructive burrowing and feeding habits often bring it into conflict with humans, and it is considered an invasive species. Nutria also transmit various diseases to humans and animals mainly through water contamination.
Natural Resources Conservation Service (NRCS), formerly known as the Soil Conservation Service (SCS), is an agency of the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) that provides technical assistance to farmers and other private landowners and managers.
England Rural Development Programme is the instrument by which the UK Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs (Defra) fulfills its rural development obligations in England, as set out by the European Union. It is derived primarily from Council Regulation European Union Regulation No. 1257/1999 and the related successive implementing Commission Regulations.
The Commodity Credit Corporation (CCC) is a wholly owned United States government corporation that was created in 1933 to "stabilize, support, and protect farm income and prices". The CCC is authorized to buy, sell, lend, make payments, and engage in other activities for the purpose of increasing production, stabilizing prices, assuring adequate supplies, and facilitating the efficient marketing of agricultural commodities.

The Conservation Reserve Program (CRP) is a cost-share and rental payment program of the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA). Under the program, the government pays farmers to take certain agriculturally used croplands out of production and convert them to vegetative cover, such as cultivated or native bunchgrasses and grasslands, wildlife and pollinators food and shelter plantings, windbreak and shade trees, filter and buffer strips, grassed waterways, and riparian buffers. The purpose of the program is to reduce land erosion, improve water quality and effect wildlife benefits.

The Food, Conservation, and Energy Act of 2008 was a $288 billion, five-year agricultural policy bill that was passed into law by the United States Congress on June 18, 2008. The bill was a continuation of the 2002 Farm Bill. It continues the United States' long history of agricultural subsidies as well as pursuing areas such as energy, conservation, nutrition, and rural development. Some specific initiatives in the bill include increases in Food Stamp benefits, increased support for the production of cellulosic ethanol, and money for the research of pests, diseases and other agricultural problems.
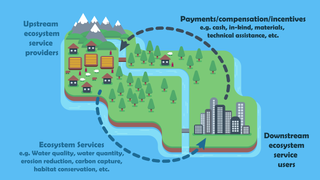
Payments for ecosystem services (PES), also known as payments for environmental services, are incentives offered to farmers or landowners in exchange for managing their land to provide some sort of ecological service. They have been defined as "a transparent system for the additional provision of environmental services through conditional payments to voluntary providers". These programmes promote the conservation of natural resources in the marketplace.

A riparian buffer or stream buffer is a vegetated area near a stream, usually forested, which helps shade and partially protect the stream from the impact of adjacent land uses. It plays a key role in increasing water quality in associated streams, rivers, and lakes, thus providing environmental benefits. With the decline of many aquatic ecosystems due to agriculture, riparian buffers have become a very common conservation practice aimed at increasing water quality and reducing pollution.
The Conservation Security Program (CSP) was a voluntary conservation program in the United States that supported stewardship of private agricultural lands by providing payments and technical assistance for maintaining and enhancing natural resources. The program promoted the conservation and improvement of soil, water, air, energy, plant and animal life, and other conservation purposes. Congress established the CSP under the Farm Security and Rural Investment Act of 2002 (FSRIA), which amended the Food Security Act of 1985. The program was administered by the Natural Resources Conservation Service (NRCS), an agency of the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA).

Hill farming is extensive farming in upland areas, primarily rearing sheep, although historically cattle were often reared extensively in upland areas. Fell farming is the farming of fells, a fell being an area of uncultivated high ground used as common grazing. It is a term commonly used in Northern England, especially in the Lake District and the Pennine Dales. Elsewhere, the terms hill farming or pastoral farming are more commonly used.
Private landowner assistance program (PLAP) is a class of government assistance program available throughout the U.S. for landowners interested in maintaining, developing, improving and protecting wildlife on their property. Each state provides various programs that assist landowners in agriculture, forestry and conserving wildlife habitat. This helps landowners in the practice of good land stewardship and provides multiple benefits to the environment. Some states offer technical assistance which includes:
The agricultural policy of the United States is composed primarily of the periodically renewed federal U.S. farm bills. The Farm Bills have a rich history which initially sought to provide income and price support to US farmers and prevent them from adverse global as well as local supply and demand shocks. This implied an elaborate subsidy program which supports domestic production by either direct payments or through price support measures. The former incentivizes farmers to grow certain crops which are eligible for such payments through environmentally conscientious practices of farming. The latter protects farmers from vagaries of price fluctuations by ensuring a minimum price and fulfilling their shortfalls in revenue upon a fall in price. Lately, there are other measures through which the government encourages crop insurance and pays part of the premium for such insurance against various unanticipated outcomes in agriculture.

The Environmental Quality Incentives Program (EQIP) is a United States government program designed to assist farmers in improving environmental quality, particularly water quality and soil conservation. Congress established the program in the 1996 farm bill to provide primarily cost-sharing assistance, but also technical and educational assistance, aimed at promoting production and environmental quality, and optimizing environmental benefits.
The Environmental Conservation Acreage Reserve Program (ECARP) was a United States umbrella program authorized by the Food, Agriculture, Conservation, and Trade Act of 1990 that includes the Conservation Reserve Program, and the Wetland Reserve Program. The Federal Agriculture Improvement and Reform Act of 1996 continued the CRP and WRP and created the Environmental Quality Incentives Program.

The Food Security Act of 1985, a 5-year omnibus farm bill, allowed lower commodity price and income supports and established a dairy herd buyout program. This 1985 farm bill made changes in a variety of other USDA programs. Several enduring conservation programs were created, including sodbuster, swampbuster, and the Conservation Reserve Program.

A Limited Resource Farmer or Rancher is one of a larger group of “targeted farmers" that also includes beginning farmers and ranchers and socially disadvantaged farmers and ranchers. Limited Resource Farmers are characterized by having limited farm sales and income. The USDA created the Limited Resource Farmer and Rancher program to ensure that these farmers and ranchers can develop economically viable farms, have access to USDA support, and ensure that programs are in alignment with farmer and rancher needs and concerns.
The Grasslands Reserve Program (GRP) was a United States government program, administered by the Natural Resources Conservation Service, that provided financial assistance to farmers and landowners to restore grasslands. The 2002 farm bill authorized enrollment of 2 million acres (8,100 km2) of restored or improved grassland, range land and pastureland under temporary and permanent easements, or contracts of at least 10 years. Under the GRP enrolled land must be in parcels that exceed 40 acres (160,000 m2). Technical assistance was provided to restore grasslands. A total of $254 million in mandatory funding from the Commodity Credit Corporation (CCC) was provided between Fiscal Years 2003 and 2007. It also provided cost sharing payments at 75% to restore disturbed grasslands and 90% to protect virgin grasslands.
References
 This article incorporates public domain material from the Congressional Research Service document: Jasper Womach. "Report for Congress: Agriculture: A Glossary of Terms, Programs, and Laws, 2005 Edition" (PDF).
This article incorporates public domain material from the Congressional Research Service document: Jasper Womach. "Report for Congress: Agriculture: A Glossary of Terms, Programs, and Laws, 2005 Edition" (PDF).