
Arthur St. Clair was a Scottish-American soldier and politician. Born in Thurso, Scotland, he served in the British Army during the French and Indian War before settling in Pennsylvania, where he held local office. During the American Revolutionary War, he rose to the rank of major general in the Continental Army, but lost his command after a controversial retreat from Fort Ticonderoga.

Thomas Bruce, 7th Earl of Elgin and 11th Earl of Kincardine, often known as Lord Elgin, was a British nobleman, soldier, politician and diplomat, known primarily for the controversial procurement of marble sculptures from the Parthenon and other structures on the Acropolis of Athens.

The 1777 Siege of Fort Ticonderoga occurred between the 2nd and 6 July 1777 at Fort Ticonderoga, near the southern end of Lake Champlain in the state of New York. Lieutenant General John Burgoyne's 8,000-man army occupied high ground above the fort, and nearly surrounded the defenses. These movements precipitated the occupying Continental Army, an under-strength force of 3,000 under the command of General Arthur St. Clair, to withdraw from Ticonderoga and the surrounding defenses. Some gunfire was exchanged, and there were some casualties, but there was no formal siege and no pitched battle. Burgoyne's army occupied Fort Ticonderoga and Mount Independence, the extensive fortifications on the Vermont side of the lake, without opposition on 6 July. Advance units pursued the retreating Americans.

The Northwest Indian War (1785–1795), also known by other names, was an armed conflict for control of the Northwest Territory fought between the United States and a united group of Native American nations known today as the Northwestern Confederacy. The United States Army considers it the first of the American Indian Wars.
Arthur Walderne St. Clair Tisdall VC was a British recipient of the Victoria Cross, the highest and most prestigious award for gallantry in the face of the enemy that can be awarded to British and Commonwealth forces.
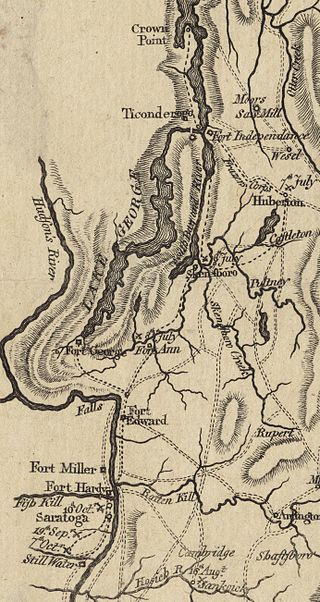
The Battle of Hubbardton was an engagement in the Saratoga campaign of the American Revolutionary War fought in the village of Hubbardton, Vermont. Vermont was then a disputed territory sometimes called the New Hampshire Grants, claimed by New York, New Hampshire, and the newly organized, not yet recognized, but de facto independent government of Vermont. On the morning of July 7, 1777, British forces, under General Simon Fraser, caught up with the American rear guard of the forces retreating after the withdrawal from Fort Ticonderoga. It was the only battle in Vermont during the revolution.

Dean Close School is a public school in Cheltenham, Gloucestershire, England. The school is divided into pre-prep, preparatory and senior schools located on separate but adjacent sites outside Cheltenham town centre, occupying the largest private land area in the town at 50 acres. The school is now co-educational, with both day and boarding pupils, who may be enrolled as young as 3 in the pre-preparatory school, and continue through to 18 at the senior school. Dean Close is a member of the Headmasters' and Headmistresses' Conference.

The Origins of The Koran: Classic Essays on Islam’s Holy Book is a 1998 book edited by Ibn Warraq. It contains a collection of 13 critical studies of the Qur'an written over the past two centuries by historians and scholars of the Middle East: Ibn Warraq, Theodor Nöldeke, Leone Caetani, Alphonse Mingana, Arthur Jeffery, David Samuel Margoliouth, Abraham Geiger, William St. Clair Tisdall, Charles Cutler Torrey and Andrew Rippin. Most of these authors wrote their essays on the Qur'an before World War II (1939–1945).
William St. Clair Tisdall (1859–1928) was a British Anglican priest, linguist, historian and philologist who served as the Secretary of the Church of England's Missionary Society in Isfahan, Persia.
Major Charles Murray Kennedy St Clair, 17th Lord Sinclair, CVO, DL was a Scottish peer who spent his entire life in the service of the Crown; as a soldier, an officer of arms, an equerry in the Queen Mother's Household, a representative peer and as a Lord Lieutenant.

The Demi-Paradise is a 1943 British comedy film made by Two Cities Films. It stars Laurence Olivier as a Soviet Russian inventor who travels to England to have his revolutionary propeller manufactured, and Penelope Dudley-Ward as the woman who falls in love with him. It was directed by Anthony Asquith and produced by Anatole de Grunwald and Filippo Del Giudice from a screenplay by de Grunwald. The music score was by Nicholas Brodszky and the cinematography by Bernard Knowles. The film was shot at Denham Studios with sets designed by the art director Carmen Dillon.
Malcolm Archibald James St Clair was a British Conservative Party politician and Army officer.
The Shia view of the Qur'an differs from the Sunni view, but the majority of both groups believe that the text is identical. While some Shia disputed the canonical validity of the Uthmanic codex, the Shia Imams always rejected the idea of alteration of Qur'an's text. Only seven Shia scholars have believed in omissions in the Uthmanic codex.

The Harmar campaign was an attempt by the United States Army to subdue confederated Native Americans nations in the Northwest Territory that were seen as hostile in Autumn 1790. The campaign was led by General Josiah Harmar and is considered a significant campaign of the Northwest Indian War. The campaign ended with a series of battles on 19–22 October 1790 near the Fort Miami and Miami village of Kekionga. These were all overwhelming victories for the Native Americans and are sometimes collectively referred to as Harmar's Defeat.
William Tisdall may refer to:
Tisdall is a surname. Notable people with the surname include:

St. Clair's defeat, also known as the Battle of the Wabash, the Battle of Wabash River or the Battle of a Thousand Slain, was a battle fought on 4 November 1791 in the Northwest Territory of the United States. The U.S. Army faced the Western Confederacy of Native Americans, as part of the Northwest Indian War. It was "the most decisive defeat in the history of the American military" and its largest defeat ever by Native Americans.

Major General Thomas Staunton St Clair (1785–1847) was a Scottish officer in the British Army known for his water-colour paintings which recorded British colonies in Gibraltar.

Mabel Annie St Clair Stobart was a British suffragist and aid-worker. She created and commanded all-women medical units to serve in the Balkan Wars and the First World War. She became the first woman to achieve the rank of Major in any national army. She was also the author of several books and articles.
William Saint Clair may refer to:










