Related Research Articles

The Jamestown settlement in the Colony of Virginia was the first permanent English settlement in the Americas. It was located on the northeast bank of the James River, about 2.5 mi (4 km) southwest of present-day Williamsburg. It was established by the London Company as "James Fort" on May 4, 1607 O.S., and considered permanent, after brief abandonment in 1610. It followed failed attempts, including the Roanoke Colony, established in 1585. Despite the dispatch of more supplies, only 60 of the original 214 settlers survived the 1609–1610 Starving Time. In mid-1610, the survivors abandoned Jamestown, though they returned after meeting a resupply convoy in the James River.

Jamestown Settlement is a living history museum operated by the Commonwealth of Virginia, created in 1957 as Jamestown Festival Park for the 350th anniversary celebration. Today it includes a recreation of the original James Fort, a Powhatan Native American town, indoor and outdoor displays, and replicas of the original settlers' ships: the Susan Constant, Godspeed, and Discovery.

The Colony of Virginia was a British colonial settlement in North America between 1606 and 1776.

Colonial Williamsburg is a living-history museum and private foundation presenting a part of the historic district in the city of Williamsburg, Virginia. Its 301-acre (122 ha) historic area includes several hundred restored or recreated buildings from the 18th century, when the city was the capital of the Colony of Virginia; 17th-century, 19th-century, and Colonial Revival structures; and more recent reconstructions. The historic area includes three main thoroughfares and their connecting side streets that attempt to suggest the atmosphere and the circumstances of 18th-century Americans. Costumed employees work and dress as people did in the era, sometimes using colonial grammar and diction.

Poplar Forest is a plantation and retreat home in Forest, Virginia, United States, that belonged to Thomas Jefferson, Founding Father and third U.S. president. Jefferson inherited the property in 1773 and began designing and working on his retreat home in 1806. While Jefferson is the most famous individual associated with the property, it had several owners before being purchased for restoration, preservation, and exhibition in 1984.

Sir George Yeardley was a planter and colonial governor of the colony of Virginia. He was also among the first slaveowners in Colonial America. A survivor of the Virginia Company of London's ill-fated 1609 Third Supply Mission, whose flagship, the Sea Venture, was shipwrecked on Bermuda for ten months, he is best remembered for presiding over the initial session of the first representative legislative body in Virginia in 1619. With representatives from throughout the settled portion of the colony, the group became known as the House of Burgesses. Burgesses have met continuously since, and is known in modern times as the Virginia General Assembly.
Founded in 1889, the Association for the Preservation of Virginia Antiquities was the United States' first statewide historic preservation group. In 2003 the organization adopted the new name APVA Preservation Virginia to reflect a broader focus on statewide Preservation and in 2009 it shortened its name to Preservation Virginia. Preservation Virginia owns historic sites across Virginia including Historic Jamestowne, located at Jamestown, Virginia, site of the first permanent English settlement in North America, and the Cape Henry Light house, one of the first public works projects of the United States of America.
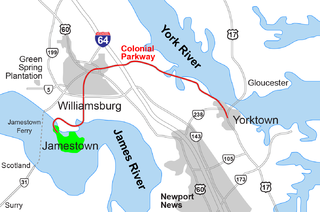
The Historic Triangle includes three historic colonial communities located on the Virginia Peninsula, bounded by the York River on the north and James River on the south. The three points that form the triangle are Jamestown, Colonial Williamsburg, and Yorktown. They feature many restored attractions and are linked by the Colonial Parkway in James City and York counties, and the City of Williamsburg.
Carmel Schrire is a professor of anthropology at Rutgers University whose research focuses on historical archaeology, particularly in South Africa and Europe.

Shadwell is a census-designated place (CDP) in Albemarle County, Virginia. It is located by the Rivanna River near Charlottesville. The site today is marked by a Virginia Historical Marker to mark the birthplace of President Thomas Jefferson. It is listed on the National Register of Historic Places along with Clifton.
Ivor Noël Hume, OBE was a British-born archaeologist who did research in the United States. A former director of Colonial Williamsburg’s archaeological research program and the author of more than 20 books, he was heralded by his peers as the "father of historical archaeology".

Historic Jamestown is the cultural heritage site that was the location of the 1607 James Fort and the later 17th-century town of Jamestown in America. It is located on Jamestown Island, on the James River at Jamestown, Virginia, and operated as a partnership between Preservation Virginia and the U.S. National Park Service as part of Colonial National Historical Park.

The Starving Time at Jamestown in the Colony of Virginia was a period of starvation during the winter of 1609–1610. There were about 500 Jamestown residents at the beginning of the winter; by spring only 61 people remained alive.

Henry Town, Henry Towne, or Henries Towne was an early English colonial settlement near Cape Henry, the southern point and gateway to the Chesapeake Bay in the Colony and Dominion of Virginia, now in modern Virginia Beach, Virginia, on the East Coast of the United States. Archaeologist Floyd Painter of the Norfolk Museum of Arts and Sciences originally excavated the site in 1955, but it was only conclusively determined to be Henry Town in 2007 by United States Army scientists reviewing the site's artifacts, and no primary source documents exist. It was located east of Norfolk, Virginia and north of Chesapeake and south of the Hampton Roads harbor at approximately 36°54′30″N76°7′20″W. The historical and archeological site is immediately north of U.S. Route 60 on what is now Lake Joyce, formerly an inlet connecting with Pleasure House Creek, a western branch of the Lynnhaven River, itself an estuary of the Chesapeake Bay and Hampton Roads.

Jamestown Rediscovery is an archaeological project of Preservation Virginia investigating the remains of the original English settlement at Jamestown established in the Virginia Colony in North America beginning on May 14, 1607.

Jamestown Church, constructed in brick from 1639 onward, in Jamestown in the Mid-Atlantic state of Virginia, is one of the oldest surviving building remnants built by Europeans in the original Thirteen Colonies and in the United States overall. It is now part of Historic Jamestown, and is owned by Preservation Virginia. There have been several sites and stages in the church's history, and its later tower is now the last surviving above-ground structure from the days when Jamestown was the capital of Virginia. The current structure, active as part of the Continuing Anglican movement, is still in use today. The ruins are currently being researched by members of the Jamestown Rediscovery project.

Jamestown, also Jamestowne, was the first settlement of the Virginia Colony, founded in 1607, and served as the capital of Virginia until 1699, when the seat of government was moved to Williamsburg. This article covers the history of the fort and town at Jamestown proper, as well as colony-wide trends resulting from and affecting the town during the time period in which it was the colonial capital of Virginia.
John Wayles was a colonial American planter, slave trader and lawyer in colonial Virginia. He is historically best known as the father-in-law of Thomas Jefferson, the third president of the United States. Wayles married three times, with these marriages producing eleven children; only five of them lived to adulthood. Through Betty Hemings, a woman he enslaved, Wayles fathered six additional children, including Sally Hemings, who was the mother of six children by Thomas Jefferson and half-sister of Martha Jefferson.
Barbara J. Heath is a professor in the Department of Anthropology at The University of Tennessee, Knoxville who specializes in historical archaeology of eastern North America and the Caribbean. Her research and teaching focus on the archaeology of the African diaspora, colonialism, historic landscapes, material culture, public archaeology and interpretation, and Thomas Jefferson.
Whitney Battle-Baptiste is an American historical archaeologist of African and Cherokee descent. She is an associate professor at the University of Massachusetts Amherst and director of the W.E.B. Du Bois Center at the University. Battle-Baptiste's research focuses on "how the intersection of race, gender, class, and sexuality look through an archaeological lens". She is also the president of American Anthropological Association.
References
- 1 2 Pierce, Thomas (13 February 2007). "Bill Kelso: Digging Up the Truth About Jamestown". NPR . Retrieved 25 May 2018.
- ↑ Wallace, John (8 June 2010). "2010 Gift to W&M honors renowned Jamestown archaeologist". College of William & Mary press release. Retrieved 28 September 2011.
- ↑ "Jamestown Rediscovery Foundation Board of Directors". Jamestown Rediscovery. Retrieved 22 September 2024.
- ↑ "Lakeside native earns one of Britain's highest honors". The Beacon. 16 July 2012. Archived from the original on 14 October 2013. Retrieved 22 September 2024.
- ↑ "Short Kelso Bio" (PDF). apva.org. Archived from the original (PDF) on 24 February 2012.
- 1 2 Cain, Áine (19 April 2016). "Digging up History". Flat Hat News. Retrieved 22 September 2024.
- ↑ "Ellen Kelso Obituary (1940-2022)". Legacy.com. 6 July 2022. Retrieved 22 September 2024.
- ↑ Grizzard, Frank E., Jr., and D. Boyd Smith. The Jamestown Colony: An Encyclopedia, ABC-CLIO, 2007.
- ↑ "William M. Kelso - American archaeologist". Encyclopedia Brittanica. Retrieved 25 May 2018.
- ↑ "Awards and Prizes". Society for Historical Archaeology. Retrieved 30 September 2016.