Related Research Articles

Jacob Armstead Lawrence was an American painter known for his portrayal of African-American historical subjects and contemporary life. Lawrence referred to his style as "dynamic cubism," an art form popularized in Europe which drew great inspiration from West African and Meso-American art. For his compositions, Lawrence found inspiration in everyday life in Harlem. He brought the African-American experience to life using blacks and browns juxtaposed with vivid colors. He also taught and spent 16 years as a professor at the University of Washington.

The Detroit Institute of Arts (DIA), located in Midtown Detroit, Michigan, has one of the largest and most significant art collections in the United States. With over 100 galleries, it covers 658,000 square feet (61,100 m2) with a major renovation and expansion project completed in 2007 that added 58,000 square feet (5,400 m2). The DIA collection is regarded as among the top six museums in the United States with an encyclopedic collection which spans the globe from ancient Egyptian and European works to contemporary art. Its art collection is valued in billions of dollars, up to $8.1 billion USD according to a 2014 appraisal. The DIA campus is located in Detroit's Cultural Center Historic District, about 2 miles (3.2 km) north of the downtown area, across from the Detroit Public Library near Wayne State University.

The Nelson-Atkins Museum of Art is an art museum in Kansas City, Missouri, known for its encyclopedic collection of art from nearly every continent and culture, and especially for its extensive collection of Asian art.

Volunteer Park is a 48.3-acre (19.5 ha) park in the Capitol Hill neighborhood of Seattle, Washington, United States.

The Seattle Art Museum is an art museum located in Seattle, Washington, United States. The museum operates three major facilities: its main museum in downtown Seattle; the Seattle Asian Art Museum in Volunteer Park, Capitol Hill; and Olympic Sculpture Park on the central Seattle waterfront, which opened in 2007.

Peter Voulkos was an American artist of Greek descent. He is known for his abstract expressionist ceramic sculptures, which crossed the traditional divide between ceramic crafts and fine art. He established the ceramics department at the Los Angeles County Art Institute and at UC Berkeley.

The Figge Art Museum is an art museum in Davenport, Iowa. The Figge, as it is commonly known, has an encyclopedic collection and serves as the major art museum for the eastern Iowa and western Illinois region. The Figge works closely with several regional universities and colleges as an art resource and collections hub for a number of higher education programs.

Elizabeth Catlett, born as Alice Elizabeth Catlett, also known as Elizabeth Catlett Mora was an African American sculptor and graphic artist best known for her depictions of the Black-American experience in the 20th century, which often focused on the female experience. She was born and raised in Washington, D.C., to parents working in education, and was the grandchild of formerly enslaved people. It was difficult for a black woman at this time to pursue a career as a working artist. Catlett devoted much of her career to teaching. However, a fellowship awarded to her in 1946 allowed her to travel to Mexico City, where she worked with the Taller de Gráfica Popular for twenty years and became head of the sculpture department for the Escuela Nacional de Artes Plásticas. In the 1950s, her main means of artistic expression shifted from print to sculpture, though she never gave up the former.

Richard Hunt is an American sculptor. In the second half of the 20th century, he became "the foremost African-American abstract sculptor and artist of public sculpture." Hunt, the descendant of enslaved people brought from West Africa through the port of Savannah, studied at the School of the Art Institute of Chicago in the 1950s. While there received multiple prizes for his work. In 1971, he was the first African American sculptor to have a retrospective at Museum of Modern Art. Hunt has created over 160 public sculpture commissions, more than any other sculptor in prominent locations in 24 states across the United States.

Robert Seldon Duncanson was a 19th-century American landscapist of European and African ancestry. Inspired by famous American landscape artists like Thomas Cole, Duncanson created renowned landscape paintings and is considered a second generation Hudson River School artist. Duncanson spent the majority of his career in Cincinnati, Ohio and helped develop the Ohio River Valley landscape tradition. As a free black man in antebellum America, Duncanson engaged the abolitionist community in America and England to support and promote his work. Duncanson is considered the first African-American artist to be internationally known. He operated in the cultural circles of Cincinnati, Detroit, Montreal, and London. The primary art historical debate centered on Duncanson concerns the role that contemporary racial issues played in his work. Some art historians, like Joseph D. Ketner, believe that Duncanson used racial metaphors in his artwork, while others, like Margaret Rose Vendryes, discourage viewers from approaching his art with a racialized perspective.

911 Media Arts Center is a non-profit media arts and access center located in Seattle, Washington. 911 Media Arts Center was incorporated on August 14, 1984, to support the expressive use of media tools through training, equipment, and access grants. The organization also provides a forum and venue for those working in the new media disciplines. The center is a member-supported non-profit organization and receives other funding from education tuition and state, city, and county grants, along with grants from private foundations and individuals.
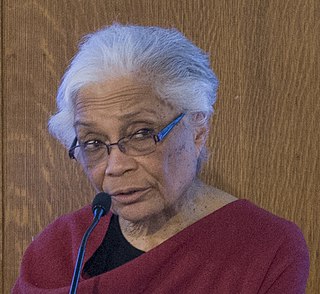
Sharon Egretta Sutton, is an American architect, educator, visual artist, and author. Her work is focused on community-based participatory research and design. She is a professor emerita at the University of Washington. In 1984, she became the first African American woman to become a full professor in an accredited architectural degree program while teaching at the University of Michigan. She has also taught at Parsons School of Design, and Columbia University.

Frans Wildenhain also known as Franz Rudolf Wildenhain was a Bauhaus-trained German potter and sculptor, who taught for many years at the School for American Craftsmen at the Rochester Institute of Technology in Rochester, New York.

Rashid Johnson is an American artist who produces conceptual post-black art. Johnson first received critical attention in 2001 at the age of 24, when his work was included in Freestyle (2001) curated by Thelma Golden at the Studio Museum in Harlem. He studied at Columbia College Chicago and the School of the Art Institute of Chicago and his work has been exhibited around the world.

Nick Cave is an American sculptor, dancer, performance artist, and professor. He is best known for his Soundsuit series: wearable assemblage fabric sculptures that are bright, whimsical, and other-worldly, often made with found objects. He also trained as a dancer with Alvin Ailey and often incorporates dance and performance into his works. His later sculptures have focused on color theory and included mixed media and large-scale installations. He lives in Chicago, Illinois, and directs the graduate fashion program at the School of the Art Institute of Chicago. He continues to work on Soundsuits as well as works completed as a sculptor, dancer, and performance artist.

The Archives of American Art is the largest collection of primary resources documenting the history of the visual arts in the United States. More than 20 million items of original material are housed in the Archives' research centers in Washington, D.C., and New York City.
Therman Statom is an American Studio Glass artist whose primary medium is sheet glass. He cuts, paints, and assembles the glass - adding found glass objects along the way – to create three-dimensional sculptures. Many of these works are large in scale. Statom is known for his site-specific installations in which his glass structures dwarf the visitor. Sound and projected digital imagery are also features of the environmental works.

Heather T. Hart is an American visual artist who works in a variety of media including interactive and participatory Installation art, drawing, collage, and painting. She is a co-founder of the Black Lunch Table Project, which includes a Wikipedia initiative focused on addressing diversity representation in the arts on Wikipedia.

Akosua Adoma Owusu is a Ghanaian-American filmmaker and producer. Her films explore the colliding identities of black immigrants in America through multiple forms ranging from cinematic essays to experimental narratives to reconstructed Black popular media. Interpreting the notion of "double consciousness," coined by sociologist and civil rights activist W. E. B. Du Bois, Owusu aims to create a third cinematic space or consciousness. In her work, feminism, queerness, and African identities interact in African, white American, and black American cultural spaces.
Constance Coleman Richardson (1905–2002) was an American painter best known for her American Scene landscapes and interplay of light on figures, evocative of Edward Hopper. She attended Vassar College and Pennsylvania Academy of the Fine Arts and was married to art historian and museum director Edgar Preston Richardson from 1931 until his death in 1985.
References
- ↑ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2012-04-26. Retrieved 2011-12-17.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ↑ "Frederick Cummings, 57, Dealer, Art Historian and Museum Chief". The New York Times. November 5, 1990. Retrieved August 22, 2022.
- ↑ "Seattle Art Museum records - Special Collections, UW Libraries". Archived from the original on 2014-07-13. Retrieved 2011-12-17.
- ↑ "Friends of African and African American Art — the Detroit Institute of Arts Auxiliary". Archived from the original on 2011-11-09. Retrieved 2011-12-17.
- ↑ "FLAG History". Archived from the original on 2011-09-01. Retrieved 2011-12-17.
- ↑ "Willis F. Woods letters, 1947-1956 | Archives of American Art, Smithsonian Institution". Aaa.si.edu. Retrieved 2018-12-12.