Related Research Articles
The GATOR mine system is a United States military system of air-dropped anti-tank and anti-personnel mines developed in the 1980s to be compatible with existing cluster dispensers. It is used with two dispenser systems—the Navy 230 kg (500 lb) CBU-78/B and the Air Force 450 kg (1,000 lb) CBU-89/B. Additionally the mines are used with the land- and helicopter-based Volcano mine system.
The GBU-10 Paveway II is an American Paveway-series laser-guided bomb, based on the Mk 84 general-purpose bomb, but with laser seeking capabilities and wings for guidance. Introduced into service c. 1976, it is used today by USAF, US Navy, US Marine Corps, Royal Australian Air Force and various NATO air forces.

The GBU-12 Paveway II is an American aerial laser-guided bomb, based on the Mk 82 500-pound (227 kg) general-purpose bomb, but with the addition of a nose-mounted laser seeker and fins for guidance. A member of the Paveway series of weapons, Paveway II entered into service c. 1976. It is currently in service with the U.S. Air Force, U.S. Navy, U.S. Marine Corps, and various other air forces.
The Mark 84 or BLU-117 is a 2,000 pound American general-purpose bomb. It is the largest of the Mark 80 series of weapons. Entering service during the Vietnam War, it became a commonly used US heavy unguided bomb to be dropped. At the time, it was the third largest bomb by weight in the US inventory behind the 15,000-pound (6,800 kg) BLU-82 "Daisy Cutter" and the 3,000-pound (1,400 kg) M118 "demolition" bomb. It is currently sixth in size due to the addition of the 5,000 lb (2,300 kg) GBU-28 in 1991, the 22,600 lb (10,300 kg) GBU-43/B Massive Ordnance Air Blast bomb (MOAB) in 2003, and the 30,000 lb (14,000 kg) Massive Ordnance Penetrator.
The Joint Direct Attack Munition (JDAM) is a guidance kit that converts unguided bombs, or "dumb bombs", into all-weather precision-guided munitions. JDAM-equipped bombs are guided by an integrated inertial guidance system coupled to a Global Positioning System (GPS) receiver, giving them a published range of up to 15 nautical miles (28 km). JDAM-equipped bombs range from 500 to 2,000 pounds. The JDAM's guidance system was jointly developed by the United States Air Force and United States Navy, hence the "joint" in JDAM. When installed on a bomb, the JDAM kit is given a GBU identifier, superseding the Mark 80 or BLU nomenclature of the bomb to which it is attached.

Paveway is a series of laser-guided bombs (LGBs).

The CBU-97 Sensor Fuzed Weapon is a United States Air Force 1,000-pound (450 kg)-class freefall Cluster Bomb Unit. It was developed and produced by Textron Defense Systems. A CBU-97 used in conjunction with the Wind Corrected Munitions Dispenser guidance tail kit is converted to a precision-guided weapon, and the combination is designated CBU-105.

The "SPICE" is an Israeli-developed, EO/GPS- guidance kit used for converting air-droppable unguided bombs into precision-guided bombs.

A guided bomb is a precision-guided munition designed to achieve a smaller circular error probable (CEP).

The Armement Air-Sol Modulaire, commonly called AASM or HAMMER, is a French, all-weather, smart air-to-surface stand off weapon developed by Safran Electronics & Defense. Meant for both close air support and deep strike missions, the AASM is highly modular.
The GBU-44/B Viper Strike glide bomb was a GPS-aided laser-guided variant of the Northrop Grumman Brilliant Anti-Tank (BAT) munition which originally had a combination acoustic and infrared homing seeker. The system was initially intended for use from UAVs, and it was also integrated with the Lockheed AC-130 gunship, giving that aircraft a precision stand-off capability. The Viper Strike design is now owned by MBDA.

The XM395 Precision Guided Mortar Munition (PGMM) is a 120 mm guided mortar round developed by Alliant Techsystems.
The CBU-87 Combined Effects Munition (CEM) is a cluster bomb used by the United States Air Force, developed by Aerojet General/Honeywell and introduced in 1986 to replace the earlier cluster bombs used in the Vietnam War. CBU stands for Cluster Bomb Unit. When the CBU-87 is used in conjunction with the Wind Corrected Munitions Dispenser guidance tail kit, it becomes much more accurate, and is designated CBU-103.

The HOPE and HOSBO are a family of precision-guided munitions, currently under development by Diehl Defence for the German Luftwaffe. Diehl BGT was expected to reach production readiness in 2010, although neither the weapon nor the integration has been ordered so far. German officials have announced that HOPE has greater penetration capability than a USAF GBU-28 munition.
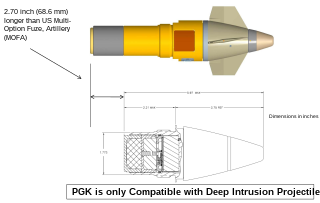
The M1156 Precision Guidance Kit (PGK), formerly XM1156, is a U.S. Army-designed precision guidance system to turn existing 155 mm artillery shells into smart weapons. The prime contractor was Alliant Techsystems – later merging with Orbital Sciences Corporation to form Orbital ATK, in turn being taken over by Northrop Grumman and renamed Northrop Grumman Innovation Systems – and the industry team includes Interstate Electronics Corporation. By April 2018, more than 25,000 PGKs had been produced.
The CBU-107 Passive Attack Weapon (PAW) is an air-dropped guided bomb containing metal penetrator rods of various sizes. It was designed to attack targets where an explosive effect may be undesirable, such as fuel storage tanks or chemical weapon stockpiles in civilian areas.

LS is an abbreviation for a family of Chinese built precision-guided munitions (PGM) named Thunder Stone Precision Guided Bomb developed by Luoyang Electro-Optics Technology Development Centre (EOTDC), a subsidiary of China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation (CASC). Alternatively, the LS PGB is also referred to by its gliding capability, as Thunder Stone Gliding Guided Bomb, or LS GGB. The guidance design of LS PGB is also adopted for another family of Chinese PGM, the YZ series, such as YZ-102 series. These PGMs are referred to in China as precision guided bombs (PGB).

A precision-guided munition is a guided munition intended to precisely hit a specific target, to minimize collateral damage and increase lethality against intended targets. During the First Gulf War guided munitions accounted for only 9% of weapons fired, but accounted for 75% of all successful hits. Despite guided weapons generally being used on more difficult targets, they were still 35 times more likely to destroy their targets per weapon dropped.

The GBU-39/B Small Diameter Bomb (SDB) is a 250-pound (110 kg) precision-guided glide bomb that is intended to provide aircraft with the ability to carry a higher number of more accurate bombs. Most US Air Force aircraft will be able to carry a pack of four SDBs in place of a single 2,000-pound (910 kg) bomb. It first entered service in 2006. The Ground Launched Small Diameter Bomb (GLSDB) was later developed to enable the SDB to be launched from a variety of ground launchers and configurations.

The Umbani is a precision-guided bomb kit manufactured by Denel Dynamics in South Africa. It consists of a number of modules fitted to NATO standard Mk81, Mk82 or Mk83 low drag free-fall bombs to convert them into guided glide bombs.
References
- ↑ Pike, John. "Wind Corrected Munition Dispenser (WCMD) - Smart Weapons". www.globalsecurity.org.
- ↑ "Lockheed Martin WCMD (Wind Corrected Munitions Dispenser) - Designation Systems".
- ↑ "USAF terminates WCMD-ER contract".