A mulch is a layer of material applied to the surface of soil. Reasons for applying mulch include conservation of soil moisture, improving fertility and health of the soil, reducing weed growth and enhancing the visual appeal of the area.

Stucco or render is a construction material made of aggregates, a binder, and water. Stucco is applied wet and hardens to a very dense solid. It is used as a decorative coating for walls and ceilings, external building siding, and as a sculptural and artistic material in architecture. Stucco may be used to cover less visually appealing construction materials, such as metal, concrete, cinder block, or clay brick and adobe.

Siding or wall cladding is the protective material attached to the exterior side of a wall of a house or other building. Along with the roof, it forms the first line of defense against the elements, most importantly sun, rain/snow, heat and cold, thus creating a stable, more comfortable environment on the interior side. The siding material and style also can enhance or detract from the building's beauty. There is a wide and expanding variety of materials to side with, both natural and artificial, each with its own benefits and drawbacks. Masonry walls as such do not require siding, but any wall can be sided. Walls that are internally framed, whether with wood, or steel I-beams, however, must always be sided.

Home repair involves the diagnosis and resolution of problems in a home, and is related to home maintenance to avoid such problems. Many types of repairs are "do it yourself" (DIY) projects, while others may be so complicated, time-consuming or risky as to suggest the assistance of a qualified handyman, property manager, contractor/builder, or other professionals. Repair is not necessarily the same as home improvement, although many improvements can result from repairs or maintenance. Often the costs of larger repairs will justify the alternative of investment in full-scale improvements. It may make just as much sense to upgrade a home system as to repair it or incur ever-more-frequent and expensive maintenance for an inefficient, obsolete or dying system. For a DIY project, it is also useful to establish limits on how much time and money you're willing to invest before deciding a repair is overwhelming and discouraging, and less likely to ever be completed.

Vinyl siding is plastic exterior siding for houses and small apartment buildings, used for decoration and weatherproofing, imitating wood clapboard, board and batten or shakes, and used instead of other materials such as aluminum or fiber cement siding. It is an engineered product, manufactured primarily from polyvinyl chloride (PVC) resin. In the UK and New Zealand a similar material is known as uPVC weatherboarding.

Fiber cement siding is a building material used to cover the exterior of a building in both commercial and domestic applications. Fiber cement is a composite material made of cement reinforced with cellulose fibers. Originally, asbestos was used as the reinforcing material but, due to safety concerns, that was replaced by cellulose in the 1980s. Fiber cement board may come pre-painted or pre-stained or can be done so after its installation.

A window shutter is a solid and stable window covering usually consisting of a frame of vertical stiles and horizontal rails. Set within this frame can be louvers, solid panels, fabric, glass and almost any other item that can be mounted within a frame. Shutters may be employed for a variety of reasons, including controlling the amount of sunlight that enters a room, to provide privacy, security, to protect against weather or unwanted intrusion or damage and to enhance the aesthetics of a building.

Roof shingles are a roof covering consisting of individual overlapping elements. These elements are typically flat, rectangular shapes laid in courses from the bottom edge of the roof up, with each successive course overlapping the joints below. Shingles are held by the roof rafters and are made of various materials such as wood, slate, flagstone, metal, plastic, and composite materials such as fibre cement and asphalt shingles. Ceramic roof tiles, which still dominate in Europe and some parts of Asia, are still usually called tiles. Roof shingles may deteriorate faster and need to repel more water than wall shingles. They are a very common roofing material in the United States.

Exterior insulation and finish system (EIFS) is a general class of non-load bearing building cladding systems that provides exterior walls with an insulated, water-resistant, finished surface in an integrated composite material system. In Europe, systems similar to EIFS are known as External Wall Insulation System (EWIS) and External Thermal Insulation Cladding System (ETICS).

A vapor barrier is any material used for damp proofing, typically a plastic or foil sheet, that resists diffusion of moisture through the wall, floor, ceiling, or roof assemblies of buildings to prevent interstitial condensation and of packaging. Technically, many of these materials are only vapor retarders as they have varying degrees of permeability.

Flashing refers to thin pieces of impervious material installed to prevent the passage of water into a structure from a joint or as part of a weather resistant barrier system. In modern buildings, flashing is intended to decrease water penetration at objects such as chimneys, vent pipes, walls, windows and door openings to make buildings more durable and to reduce indoor mold problems. Metal flashing materials include lead, aluminium, copper, stainless steel, zinc alloy, and other materials.
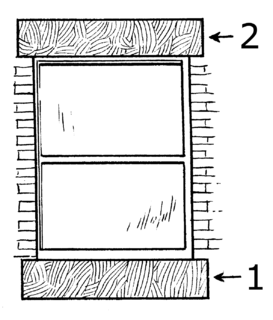
A window sill is the horizontal structure or surface at the bottom of a window. Window sills serve to structurally support and hold the window in place.
Weatherstripping is the process of sealing openings such as doors, windows, and trunks from the elements. The term can also refer to the materials used to carry out such sealing processes. The goal of weatherstripping is to prevent rain and water from entering entirely or partially and accomplishes this by either returning or rerouting water. A secondary goal of weatherstripping is to keep interior air in, thus saving energy on heating and air conditioning.

Rigid panel insulation, also referred to as continuous insulation, can be made from foam plastics such as polyurethane (PUR), polyisocyanurate (PIR), and polystyrene, or from fibrous materials such as fiberglass, rock and slag wool. Rigid panel continuous insulation is often used to provide a thermal break in the building envelope, thus reducing thermal bridging.

A rainscreen is an exterior wall detail where the siding stands off from the moisture-resistant surface of an air/water barrier applied to the sheathing to create a capillary break and to allow drainage and evaporation. The rainscreen is the cladding or siding itself but the term rainscreen implies a system of building. Ideally the rainscreen prevents the wall air/water barrier from getting wet but because of cladding attachments and penetrations water is likely to reach this point, and hence materials are selected to be moisture tolerant and integrated with flashing. In some cases a rainscreen wall is called a pressure-equalized rainscreen wall where the ventilation openings are large enough for the air pressure to nearly equalize on both sides of the rain screen, but this name has been criticized as being redundant and is only useful to scientists and engineers.

Cladding is the application of one material over another to provide a skin or layer. In construction, cladding is used to provide a degree of thermal insulation and weather resistance, and to improve the appearance of buildings. Cladding can be made of any of a wide range of materials including wood, metal, brick, vinyl, and composite materials that can include aluminium, wood, blends of cement and recycled polystyrene, wheat/rice straw fibres. Rainscreen cladding is a form of weather cladding designed to protect against the elements, but also offers thermal insulation. The cladding does not itself need to be waterproof, merely a control element: it may serve only to direct water or wind safely away in order to control run-off and prevent its infiltration into the building structure. Cladding may also be a control element for noise, either entering or escaping. Cladding can become a fire risk by design or material.

Roofline is used to describe the fascia, soffits, bargeboards, antefixes and cladding that forms the frontage immediately below the roof and the eaves of many homes and buildings. These are traditionally made from wood, but can be made of a variety of different materials, including plastic, such as polyvinyl chloride.
Interstitial condensation can create structural dampening that occurs when moist air penetrates inside the hidden space within an enclosed wall, roof or floor cavity structure. When that moisture laden air reaches a layer inside the interstitial structure that is at dew point temperature, it condenses into liquid water on that surface. The moisture laden air can penetrate into hidden interstitial wall cavity through the exterior in a warm/humid outdoor period, and from inside the building during warm/humid indoor periods. Groundwater soaking the basement foundation walls from wet soil is common. This can result from a high water table or from improperly drained rainwater runoff soaking into the ground next to the basement walls. Moisture saturated basement walls will add moisture directly into basement interstitial spaces leading to interstitial condensation with cool basement temperatures.

Millwork building materials are historically any woodmill-produced products for building construction. Stock profiled and patterned millwork building components fabricated by milling at a planing mill can usually be installed with minimal alteration. Today, millwork also encompasses items that are made using alternatives to wood, including synthetics, plastics, and wood-adhesive composites.

Hybrid wood or wood hybrid systems (WHS) is a multilayer composite material, composed on the surface of a skin made of composite wood (WPC) adhering to an underneath structural core, in general aluminum. Invented in Japan in 2008, this technological evolution is based on wood composite technology which was conceived in 1972 by Sadao Nishibori and patented in 1983 to substitute threatened exotic wood species. WHS are not fibre-reinforced plastic (FRP).
















