Related Research Articles

Queen Anne's War (1702–1713) was the second in a series of French and Indian Wars fought in North America involving the colonial empires of Great Britain, France, and Spain; it took place during the reign of Anne, Queen of Great Britain. In the United States, it is regarded as a standalone conflict under this name. Elsewhere it is usually viewed as the American theater of the War of the Spanish Succession. It is also known as the Third Indian War. In France it was known as the Second Intercolonial War.
New France was the territory colonized by France in North America, beginning with the exploration of the Gulf of Saint Lawrence by Jacques Cartier in 1534 and ending with the cession of New France to Great Britain and Spain in 1763 under the Treaty of Paris.

King William's War was the North American theater of the Nine Years' War (1688–1697), also known as the War of the Grand Alliance or the War of the League of Augsburg. It was the first of six colonial wars fought between New France and New England along with their respective Native allies before France ceded its remaining mainland territories in North America east of the Mississippi River in 1763.
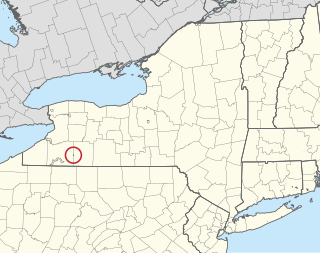
Oil Springs Reservation or Oil Spring Reservation is an Indian reservation of the federally recognized Seneca Nation that is located in southwestern New York, United States. As of the 2010 census, the Indian reservation had one resident; in 2005 no tribal members had lived on the property. The reservation covers about one square mile (2.6 km2), divided between the present-day counties of Allegany and Cattaraugus. The reservation is northwest of the village of Cuba. It is bordered by the Town of Cuba and the Town of Ischua.
The Beaver Wars, also known as the Iroquois Wars or the French and Iroquois Wars were a series of conflicts fought intermittently during the 17th century in North America throughout the Saint Lawrence River valley in Canada and the Great Lakes region which pitted the Iroquois against the Hurons, northern Algonquians and their French allies. As a result of this conflict, the Iroquois destroyed several confederacies and tribes through warfare: the Hurons or Wendat, Erie, Neutral, Wenro, Petun, Susquehannock, Mohican and northern Algonquins whom they defeated and dispersed, some fleeing to neighbouring peoples and others assimilated, routed, or killed.

The Great Peace of Montreal was a peace treaty between New France and 39 First Nations of North America that ended the Beaver Wars. It was signed on August 4, 1701, by Louis-Hector de Callière, governor of New France, and 1300 representatives of 39 Indigenous nations.
The Seneca ( SEN-ik-ə; are a group of Indigenous Iroquoian-speaking people who historically lived south of Lake Ontario, one of the five Great Lakes in North America. Their nation was the farthest to the west within the Six Nations or Iroquois League in New York before the American Revolution. For this reason, they are called “The Keepers of the Western Door.”

The Treaty of Easton was a colonial agreement in North America signed in October 1758 during the French and Indian War between British colonials and the chiefs of 13 Native American nations, representing tribes of the Iroquois, Lenape (Delaware), and Shawnee. Negotiations over more than a week were concluded on October 26, 1758, at a ceremony held in Easton, Pennsylvania between the British colonial governors of the provinces of Pennsylvania and New Jersey, and representatives of 13 Indian nations, including the Iroquois, who sent chiefs of three of their nations to ensure their continued domination of their Ohio Country region; the eastern and western Lenape (Delaware), represented by two chiefs and headmen; Shawnee and others. More than 500 Native Americans attended the outdoor ceremony, after lengthy negotiations to bring peace to the regions of Pennsylvania, New Jersey and the Ohio Country.
The Covenant Chain was a series of alliances and treaties developed during the seventeenth century, primarily between the Iroquois Confederacy (Haudenosaunee) and the British colonies of North America, with other Native American tribes added. First met in the New York area at a time of violence and social instability for the colonies and Native Americans, the English and Iroquois councils and subsequent treaties were based on supporting peace and stability to preserve trade. They addressed issues of colonial settlement, and tried to suppress violence between the colonists and Indian tribes, as well as among the tribes, from New England to the Colony of Virginia.

The Two Row Wampum Treaty, also known as Guswenta or Kaswentha and as the Tawagonshi Agreement of 1613 or the Tawagonshi Treaty, is a mutual treaty agreement, made in 1613 between representatives of the Five Nations of the Haudenosaunee and representatives of the Dutch government in what is now upstate New York. The agreement is considered by the Haudenosaunee to be the basis of all of their subsequent treaties with European and North American governments, and the citizens of those nations, including the Covenant Chain treaty with the British in 1677 and the Treaty of Canandaigua with the United States in 1794.

Richard Coote, 1st Earl of Bellomont, known as The Lord Coote between 1683–89, was an Irish nobleman and colonial administrator who represented Droitwich in the English Parliament from 1688 to 1695. He was a prominent Williamite, supporting William III and Mary II during the Glorious Revolution.
William Tailer was a military officer and politician in the Province of Massachusetts Bay. Born into the wealthy and influential Stoughton family, he twice married into other politically powerful families. He served as lieutenant governor of the province from 1711 until 1716, and again in the early 1730s. During each of these times he was briefly acting governor. He was a political opponent of Governor Joseph Dudley, and was a supporter of a land bank proposal intended to address the province's currency problems. During his first tenure as acting governor he authorized the erection of Boston Light, the earliest lighthouse in what is now the United States.
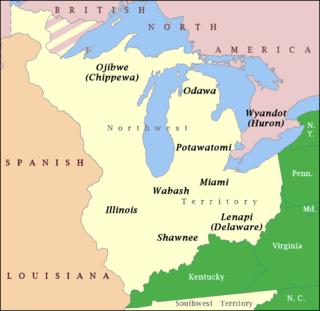
The Northwestern Confederacy, or Northwestern Indian Confederacy, was a loose confederacy of Native Americans in the Great Lakes region of the United States created after the American Revolutionary War. Formally, the confederacy referred to itself as the United Indian Nations, at their Confederate Council. It was known infrequently as the Miami Confederacy since many contemporaneous federal officials overestimated the influence and numerical strength of the Miami tribes based on the size of their principal city, Kekionga.

The Treaty of Fort Stanwix was a treaty finalized on October 22, 1784, between the United States and Native Americans from the six nations of the Iroquois League. It was signed at Fort Stanwix, in present-day Rome, New York, and was the first of several treaties between Native Americans and the United States after the American victory in the Revolutionary War.
The Iroquois, also known as the Five Nations or the Six Nations and by the endonym Haudenosaunee, are an Iroquoian-speaking confederacy of Native Americans and First Nations peoples in northeast North America and Upstate New York. They were known during the colonial years to the French as the "Iroquois League", and later as the "Iroquois Confederacy". The English called them the "Five Nations", including the Mohawk, Oneida, Onondaga, Cayuga, and Seneca. After 1722, the Iroquoian-speaking Tuscarora from the southeast were accepted into the confederacy, which became known as the Six Nations.

Teedyuscung was known as "King of the Delawares". He worked to establish a permanent Lenape (Delaware) home in eastern Pennsylvania in the Lehigh, Susquehanna, and Delaware River valleys. Teedyuscung participated in the Treaty of Easton, which resulted in the surrender of Lenape claims to all lands in Pennsylvania. Following the treaty, the Lenape were forced to live under the control of the Iroquois in the Wyoming Valley near modern-day Wilkes-Barre. Teedyuscung was murdered by arsonists in the night of April 19, 1763. This marked the beginning of the end of the Lenape presence in Pennsylvania. Teedyuscung's son Chief Bull conducted a raid on the Wyoming Valley that was part of a greater Indian uprising. As a result, the Lenape were forced to move west of the Appalachian Mountains by the Royal Proclamation of 1763.
Canassatego was a leader of the Onondaga nation who became a prominent diplomat and spokesman of the Iroquois Confederacy in the 1740s. He was involved in several controversial land sales to colonial British officials. He is now best known for a speech he gave at the 1744 Treaty of Lancaster, where he recommended that the British colonies emulate the Iroquois by forming a confederacy. He was reportedly assassinated, perhaps by sympathizers or agents of New France.
The Treaty of Washington (1831) was a treaty between the Menominee and the United States Government. The treaty was initially made and signed on February 8, 1831 in Washington, D.C. In the treaty, the Menominee ceded about 2,500,000 acres of their land in Wisconsin primarily adjacent to Lake Michigan. During the ratification of the treaty in June 1832, the United States Senate modified the treaty to provide additional land for the Stockbridge-Munsee tribe. The Menominee Tribe did not agree to the changes, and the treaty was renegotiated on October 27, 1832 to resolve the differences. These two treaties are commonly referred to singularly as the Treaty of Washington.

Kondiaronk, known as Le Rat, was Chief of the Native American Wendat people at Michilimackinac in New France. As a result of an Iroquois attack and dispersal of the Hurons in 1649, the latter settled in Michilimackinac. The Michilimackinac area is the strait between Lakes Huron and Michigan in the present-day United States.
Dekanisora was an Onondaga chief and orator. Holding a position on the Iroquois Grand Council, he attempted to maintain peace between the Iroquois and the French and English, and to maintain independence from both. Cadwallader Colden described Dekanisora as one of the world's best speakers.
References
- ↑ Fenton, William Nelson (1998). The Great Law and the Longhouse: A Political History of the Iroquois Confederacy. University of Oklahoma Press. p. 423. ISBN 978-0-8061-3003-3.
- ↑ Salinger, Sharon V. (4 August 2004). Taverns and Drinking in Early America. JHU Press. p. 37. ISBN 978-0-8018-7899-2.