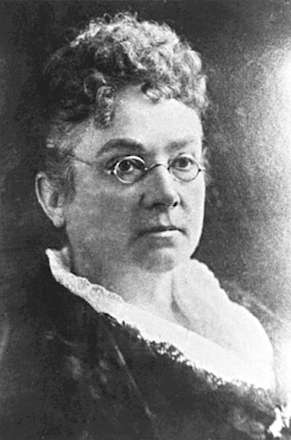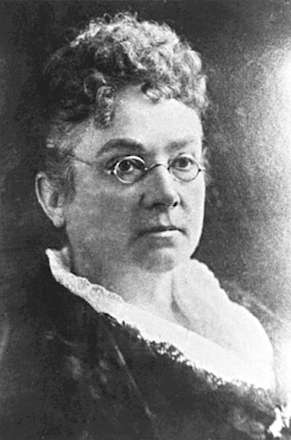
Emily Howard Stowe was a Canadian physician who was the first female physician to practise in Canada, the second licensed female physician in Canada and an activist for women's rights and suffrage. Stowe helped found the women's suffrage movement in Canada and campaigned for the country's first medical college for women.

New York Medical College is a private medical school in Valhalla, New York. Founded in 1860, it is a member of the Touro University System.

The Flexner Report is a book-length landmark report of medical education in the United States and Canada, written by Abraham Flexner and published in 1910 under the aegis of the Carnegie Foundation. Flexner not only described the state of medical education in North America, but he also gave detailed descriptions of the medical schools that were operating at the time. He provided both criticisms and recommendations for improvements of medical education in the United States.

Matilda Evans, M.D., also known as Matilda Arabella Evans was the first African-American woman licensed to practice medicine in South Carolina and an advocate for improved health care for African Americans, particularly children.

Rebecca Lee Crumpler, born Rebecca Davis,, was an American physician, nurse and author. After studying at the New England Female Medical College, in 1864 she became the first African American woman to become a doctor of medicine in the United States. Crumpler was also one of the first female physician authors in the nineteenth century. In 1883, she published A Book of Medical Discourses. The book has two parts that cover the prevention and cure of infantile bowel complaints, and the life and growth of human beings. Dedicated to nurses and mothers, it focuses on maternal and pediatric medical care and was among the first publications written by an African American on the subject of medicine.
Washington University School of Medicine (WUSM) is the medical school of Washington University in St. Louis, and located in the Central West End neighborhood of St. Louis, Missouri. Founded in 1891, the School of Medicine shares a campus with Barnes-Jewish Hospital, St. Louis Children's Hospital, and the Alvin J. Siteman Cancer Center. It has consistently ranked among the top medical schools in the United States in terms of the number and amount of research grants/funding awarded by the National Institutes of Health, in addition to other measures.
The London School of Medicine for Women (LSMW) established in 1874 was the first medical school in Britain to train women as doctors. The patrons, vice-presidents, and members of the committee that supported and helped found the London School of Medicine for Women wanted to provide educated women with the necessary facilities for learning and practicing midwifery and other branches of medicine while also promoting their future employment in the fields of midwifery and other fields of treatment for women and children.

The Edinburgh School of Medicine for Women was founded by Sophia Jex-Blake in Edinburgh, Scotland, in October 1886, with support from the National Association for Promoting the Medical Education of Women. Sophia Jex-Blake was appointed as both the Director and the Dean of the School. The first class of women to study at the Edinburgh School of Medicine for Women consisted of eight students, the youngest of whom was nineteen years of age. Throughout its twelve years in operation, the school struggled to find financial funding to remain open. A rival institution, the Edinburgh College of Medicine for Women, set up by Elsie Inglis with the help of her father John Inglis, attracted several students of Jex-Blake, including Martha Cadell and Grace Cadell. St Mungo's College and Queen Margaret College in Glasgow also accepted women medical students and when the Scottish universities began to do so the Edinburgh School of Medicine could no longer compete. The school closed in 1898. Over the twelve years of its operation, the Edinburgh School of Medicine provided education to approximately eighty female students. Of those eighty students, thirty-three completed the full course of medical training at the Edinburgh School while many others chose to finish their education at outside institutions.
Drexel University College of Medicine is the medical school of Drexel University, a private research university in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. The medical school represents the consolidation of two medical schools: Hahnemann Medical College, originally founded as the nation's first college of homeopathy, and the Woman's Medical College of Pennsylvania, the first U.S. medical school for women, which became the Medical College of Pennsylvania when it admitted men in 1970; these institutions merged in 1993, became affiliated with Drexel University College of Medicine in 1998, and were fully absorbed into the university in 2002. With one of the nation's largest enrollments for a private medical school, Drexel University College of Medicine is the second most applied-to medical school in the United States. It is ranked no. 83 in research by U.S. News & World Report.

Martha George Rogers Ripley was an American physician, suffragist, and professor of medicine. Founder of the Maternity Hospital in Minneapolis, Minnesota, Ripley was one of the most outspoken activists for disadvantaged female rights. A prominent leader in the American Woman Suffrage Association, Ripley also served six years as president of the Minnesota Woman Suffrage Association.
A.T. Still University (ATSU) is a private medical school based in Kirksville, Missouri, with a second campus in Arizona and third campus in Santa Maria, California. It was founded in 1892 by Andrew Taylor Still and was the world's first osteopathic medical school. It is accredited by the Higher Learning Commission. ATSU includes three campuses on 200 acres with seven schools and colleges.
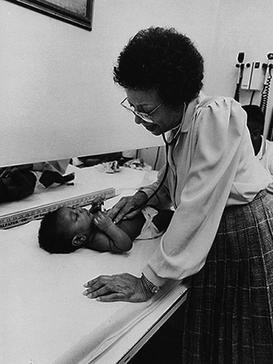
Helen Elizabeth Nash was a pediatrician known for breaking racial and gender barriers in the medical field. She began her career at the Homer G. Phillips Hospital, and later worked at the Saint Louis Children’s Hospital. She started her own private practice and was a faculty member at the Washington University School of Medicine. Her earliest work included decreasing infant mortality in Homer G. Phillips Hospital. Her private practice was notable for educating teens on proper sexual health. Additionally, she was one of the first medical doctors to address patient health as care for the patient and their support systems.

Clemence Sophia Lozier was an American physician who founded the New York Medical College and Hospital for Women. Dr. Lozier was also a noted feminist and activist, and served as president of the New York City Suffrage League and the National Women's Suffrage Association.

Mary Hancock McLean was a physician and missionary. Born to Elijah McLean, a physician, and Mary Stafford, she enjoyed a privileged childhood with academic opportunities uncommon for girls of her time period. After graduating from the University of Michigan Medical School, she became the first woman to hold an official position at the St. Louis Female Hospital and the first woman admitted to the St. Louis Medical Society.
Barbara Ross-Lee, D.O. is an American physician, academic, and the first African-American woman to serve as dean of a U.S. medical school; she is also known as the sister of Diana Ross along with being the aunt of actress Tracee Ellis Ross, and singer-songwriters Rhonda Ross Kendrick and Evan Ross. She majored in biology and chemistry at Wayne State University, graduating in 1965. Then, in 1969, she entered Michigan State University's College of Osteopathic Medicine. Ross-Lee then went on to open her own private family practice, teach as a professor, and hold other positions within the medical community. In 1993, she was elected as the first woman dean of a medical school, at Ohio University's Heritage College of Osteopathic Medicine. She has earned several awards and honors for her work and accomplishments.

Hannah Tyler Wilcox was an American physician.

Susanna Way Dodds was an American physician, hydrotherapist and natural hygiene proponent.

The standard entry-to-practice degree in modern evidence-based medicine in India is the Bachelor of Medicine and Bachelor of Surgery (MBBS). Alternative systems of Medicine in India are Ayurveda (BAMS), Unani (BUMS), Siddha(BSMS), Homeopathy (BHMS). M.B.B.S. a credential earned upon completion of a five-and-a-half-year undergraduate program. The curriculum is divided into one year of preclinical studies in general science subjects and three and a half years of paraclinical and clinical studies, followed by a one-year clinical internship. Before beginning the internship, students are required to pass several examinations, the final one of which is conducted in two parts. Postgraduate education in medical specialties typically takes 3 additional years of study after the MBBS and concludes with the award of a Master of Surgery or Doctor of Medicine(MD). Postgraduate diplomas in medical specialities may also be awarded upon the completion of two-year training programs. After that a person can further get a degree in superspeciality in his or her respective branch after successful completion of 3 years of superspeciality in a medical college.

Cleora Augusta Stevens Seaman was an American physician based in Cleveland, Ohio.

Hahnemann Medical College of the Pacific was an American homeopathic medical school in San Francisco, California. It was established in 1881 as Hahnemann Medical College, with the first graduating class in 1884. During the period of 1888–1902, it was known as Hahnemann Hospital College of San Francisco. Its last name change, 1902–1915, was to Hahnemann Medical College of the Pacific.