
At the beginning of 1914 the British Army had a reported strength of 710,000 men including reserves, of which around 80,000 were regular troops ready for war. By the end of the First World War almost 1 in 4 of the total male population of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland had joined up, over five million men. Of these men, 2.67 million joined as Volunteers and 2.77 million as conscripts. Monthly recruiting rates for the army varied dramatically.
The Conscription Crisis of 1944 was a political and military crisis following the introduction of forced military service for men in Canada during World War II. It was similar to the Conscription Crisis of 1917, but was not as politically damaging.

The First Australian Imperial Force was the main expeditionary force of the Australian Army during World War I. It was formed on 15 August 1914, following Britain's declaration of war on Germany, initially with a strength of one infantry division and one light horse brigade. The infantry division subsequently fought at Gallipoli between April and December 1915, being reinforced by a second division which was later raised, as well as three light horse brigades. After being evacuated to Egypt the AIF was expanded to five infantry divisions, which were committed to the fighting in France and Belgium along the Western Front in March 1916. A sixth infantry division was partially raised in 1917 in the United Kingdom, but was broken up and used as reinforcements following heavy casualties on the Western Front. Meanwhile, two mounted divisions remained in the Middle East to fight against Turkish forces in the Sinai and Palestine.
Conscription in Australia, or mandatory military service also known as national service, has a controversial history dating back to the first years of nationhood. Australia currently only has provision for conscription during times of war.

Military service is service by an individual or group in an army or other militia, whether as a chosen job (volunteer) or as a result of an involuntary draft (conscription).

Conscription in the United States, commonly known as the draft, has been employed by the federal government of the United States in five conflicts: the American Revolution, the American Civil War, World War I, World War II, and the Cold War. The third incarnation of the draft came into being in 1940 through the Selective Training and Service Act. It was the country's first peacetime draft. From 1940 until 1973, during both peacetime and periods of conflict, men were drafted to fill vacancies in the United States Armed Forces that could not be filled through voluntary means. The draft came to an end when the United States Armed Forces moved to an all-volunteer military force. However, the Selective Service System remains in place as a contingency plan; all male citizens between the ages of 18 and 25 are required to register so that a draft can be readily resumed if needed. United States Federal Law also provides for the compulsory conscription of men between the ages of 17 and 45 and certain women for militia service pursuant to Article I, Section 8 of the United States Constitution and 10 U.S. Code § 246.
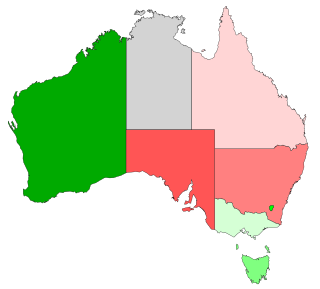
The 1916 Australian plebiscite was held on 28 October 1916. It was the first non-binding Australian plebiscite, and contained one question concerning military service. This plebiscite was held due to Prime Minister Billy Hughes' desire to conscript young Australian men for overseas service during World War I. It was conducted under the Military Service Referendum Act 1916.

The 1917 Australian plebiscite was held on 20 December 1917. It contained just the one question.

The British Army came into being with the unification of the Kingdoms of England and Scotland into the Kingdom of Great Britain in 1707. The new British Army incorporated Regiments that had already existed in England and Scotland. The Army has traditionally relied on volunteer recruits, the only exceptions to this being during the latter part of the First World War until 1919, and then again during the Second World War when conscription was brought in during the war and stayed until 1960.
Compulsory military training (CMT), a form of conscription, was practised for males in New Zealand between 1909 and 1972. Prior to and after this period military training in New Zealand has been voluntary.
The End Conscription Campaign was an anti-apartheid organisation allied to the United Democratic Front (UDF) and composed of conscientious objectors and their supporters in South Africa. It was formed in 1983 to oppose the conscription of all white South African men into military service in the South African Defence Force.

Opposition to World War I included socialist, anarchist, syndicalist, and Marxist groups on the left, as well as Christian pacifists, Canadian and Irish nationalists, women's groups, intellectuals, and rural folk. Women across the spectrum were much less supportive than men.
Conscription in the United Kingdom has existed for two periods in modern times. The first was from 1916 to 1920, the second from 1939 to 1960, with the last conscripted soldiers leaving the service in 1963. Known as Military Service from 1916 to 1920, the system of conscription from 1939 to 1960 was called National Service, but between 1939 and 1948, it was often referred to as "war service" in documents relating to National Insurance and pension provision.
During the second half of World War One, the First Australian Imperial Force experienced a shortage of men as the number of men volunteering to fight overseas declined and the casualty rate increased. At the time, military service within the Commonwealth of Australia and its territories was compulsory for Australian men, but that requirement did not extend to conflict outside of Australia. In 1916, Prime Minister Billy Hughes called a plebiscite to determine public support for extending conscription to include military service outside the Commonwealth for the duration of the war. The referendum, held on 28 October 1916, narrowly rejected the proposal. A second plebiscite, held a year later on 20 December 1917, also failed to gain a majority.
The Committee to Oppose the Conscription of Women (COCW), later renamed the Women’s Committee to Oppose Conscription (WCOC), was founded in 1943 in the United States by Mildred S. Olmsted. The committee was created to combat legislation that would draft nurses into the American armed forces. The organization was also active in combating the Austin-Wadsworth Bill, or the National Service Act, which would make it compulsory for men and women to work in war industry jobs as needed during World War II.

Women in the Second World War took on many different roles during the War, including as combatants and workers on the home front. The Second World War involved global conflict on an unprecedented scale; the absolute urgency of mobilizing the entire population made the expansion of the role of women inevitable, although the particular roles varied from country to country. Millions of women of various ages died as a result of the war.

The Queensland Recruiting Committee was a volunteer organisation in Queensland, Australia, which urged Queensland men to enlist for military service during World War I. It operated from May 1915 to December 1916, when it was replaced by an Australian Government recruitment organisation, the Queensland State Recruiting Committee.

On 9 July 1917, a disturbance broke out at the Brisbane School of Arts, when a meeting of the Women's Compulsory Service Petition League was interrupted by activists from the Women's Peace Army, with the confrontation degenerating into violence and mayhem.
Margaret Sturge Thorp, also known as "The Peace Angel", was a peace activist and labour activist active in Australia in the 20th century. A Quaker, her religious beliefs guided her to a life of advocating for a variety of pacifist and feminist causes.











