
Coppicing is a traditional method of woodland management which exploits the capacity of many species of trees to put out new shoots from their stump or roots if cut down. In a coppiced wood, which is called a copse, young tree stems are repeatedly cut down to near ground level, resulting in a stool. New growth emerges, and after a number of years, the coppiced tree is harvested, and the cycle begins anew. Pollarding is a similar process carried out at a higher level on the tree in order to prevent grazing animals from eating new shoots. Daisugi, is a similar Japanese technique.

Samsø is a Danish island in the Kattegat 15 kilometers (9.3 mi) off the Jutland Peninsula. Samsø is located in Samsø municipality. The community has 3,724 inhabitants (2017) called Samsings and is 114 km² in area. Due to its central location, the island was used during the Viking Age as a meeting place. The etymology of the island's name is unknown.

Arboriculture is the cultivation, management, and study of individual trees, shrubs, vines, and other perennial woody plants. The science of arboriculture studies how these plants grow and respond to cultural practices and to their environment. The practice of arboriculture includes cultural techniques such as selection, planting, training, fertilization, pest and pathogen control, pruning, shaping, and removal.

An arboretum in a general sense is a botanical collection composed exclusively of trees of a variety of species. Originally mostly created as a section in a larger garden or park for specimens of mostly non-local species, many modern arboreta are in botanical gardens as living collections of woody plants and is intended at least in part for scientific study.

Mount Auburn Cemetery, located in Cambridge, Massachusetts, is the first rural or garden cemetery in the United States. It is the burial site of many prominent Boston Brahmins, and is a National Historic Landmark.

Utsjoki is a municipality in Finland, the northernmost in the country. It is in Lapland and borders Norway as well as the municipality of Inari. The municipality was founded in 1876. It has a population of 1,178 (31 December 2021) and covers an area of 5,372.00 square kilometres (2,074.14 sq mi) of which 227.51 km2 (87.84 sq mi) is water. The population density is 0.23 inhabitants per square kilometre (0.60/sq mi).

Picea sitchensis, the Sitka spruce, is a large, coniferous, evergreen tree growing to almost 100 meters (330 ft) tall, with a trunk diameter at breast height that can exceed 5 m (16 ft). It is by far the largest species of spruce and the fifth-largest conifer in the world, and the third-tallest conifer species. The Sitka spruce is one of the few species documented to exceed 90 m (300 ft) in height. Its name is derived from the community of Sitka in southeast Alaska, where it is prevalent. Its range hugs the western coast of Canada and the US, continuing south into northernmost California.

Skogskyrkogården is a cemetery located in the Gamla Enskede district south of central Stockholm, Sweden. Its design, by Gunnar Asplund and Sigurd Lewerentz, reflects the development of architecture from Nordic Classicism to mature functionalism.

Abney Park cemetery is one of the "Magnificent Seven" cemeteries in London, England.

Erik Gunnar Asplund was a Swedish architect, mostly known as a key representative of Nordic Classicism of the 1920s, and during the last decade of his life as a major proponent of the modernist style which made its breakthrough in Sweden at the Stockholm International Exhibition (1930). Asplund was professor of architecture at the Royal Institute of Technology from 1931. His appointment was marked by a lecture, later published under the title "Our architectonic concept of space." The Woodland Crematorium at Stockholm South Cemetery (1935-1940) is considered his finest work and one of the masterpieces of modern architecture.

Vestre Cemetery is located in a large park setting in the Kongens Enghave district of Copenhagen, Denmark. With its 54 hectares it is the largest cemetery in Denmark.

Stabbursdalen National Park is a national park in North Norway. It contains the northernmost pine forest in the world. It is located in Porsanger Municipality in Finnmark county, Norway. The park surrounds the Stabburselva river and its surrounding valley, just west of the large Porsangerfjorden. A small corner of the park extends into neighboring Kvalsund Municipality.

Muchalls Castle stands overlooking the North Sea in the countryside of Kincardine and Mearns, Aberdeenshire, Scotland. The lower course is a well-preserved Romanesque, double-groined 13th-century tower house structure, built by the Frasers of Muchalls. Upon this structure, the 17th-century castle was begun by Alexander Burnett of Leys and completed by his son, Sir Thomas Burnett, 1st Baronet, in 1627. The Burnetts of Leys built the remaining four-storey present-day castle.
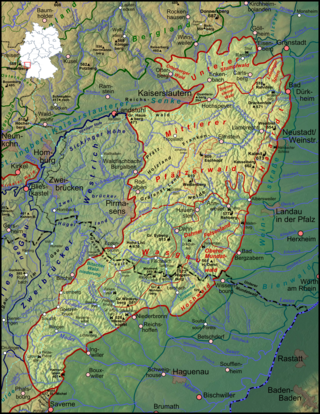
The Palatinate Forest, sometimes also called the Palatine Forest, is a low-mountain region in southwestern Germany, located in the Palatinate in the state of Rhineland-Palatinate. The forest is a designated nature park covering 1,771 km2 and its highest elevation is the Kalmit.

Hans Grässel was a German architect. Grässel studied and performed almost his entire career in Munich, and as the council architect of the city he created a series of cemeteries of which Munich Waldfriedhof, opened in 1907, is well known for being the first woodland cemetery. Grässel also wrote a pamphlet on cemetery design, Über Friedhofanlagen und Grabdenkmale (1913). In 1914, he was given the order Pour le Mérite.

The Munich Waldfriedhof is one of 29 cemeteries of Munich in Bavaria, Germany. It is one of the larger and more famous burial sites of the city, known for its park-like design and tombs of notable personalities. The Waldfriedhof is considered the first woodland cemetery.

A rural cemetery or garden cemetery is a style of cemetery that became popular in the United States and in the mid-19th century due to the overcrowding and health concerns of urban cemeteries. They were typically built one to five miles outside of the city, far enough to be separated from the city, but close enough for visitors. They often contain elaborate monuments, memorials, and mausoleums in a landscaped park-like setting.

A veteran tree is a tree of a great cultural, landscape or nature conservation value due its great age, size or condition.

A dehesa is a multifunctional, agrosylvopastoral system and cultural landscape of southern and central Spain and southern Portugal; in Portugal, it is known as a montado. Its name comes from the Latin 'defensa' (fenced) referring to land that was fenced, and usually destined for pasture. Dehesas may be private or communal property. Used primarily for grazing, they produce a variety of products, including non-timber forest products such as wild game, mushrooms, honey, cork, and firewood. They are also used to raise the Spanish fighting bull and the Iberian pig. The main tree component is oaks, usually holm and cork. Other oaks, including melojo and quejigo, may be used to form dehesa, the species utilized depending on geographical location and elevation. Dehesa is an anthropogenic system that provides not only a variety of foods, but also wildlife habitat for endangered species such as the Spanish imperial eagle.

Skjoldhøjkilen is a recreational and natural site, in the district of Brabrand in the western part of Aarhus in Denmark. It stretches westwards from Hasle Hills, like a wavy green strip of meadows, small lakes and woodlands. It is 3.5 km long and just as Hasle Hills, it is administered by the self-governing institution 'Hasle Bakker'.




















