Related Research Articles

In female human anatomy, Skene's glands or the Skene glands are glands located around the lower end of the urethra. The glands are surrounded by tissue that swells with blood during sexual arousal, and secrete a fluid from openings near the urethra, particularly during orgasm.

The Bartholin's glands are two pea sized compound alveolar glands located slightly posterior and to the left and right of the opening of the vagina. They secrete mucus to lubricate the vagina.

A cyst, also traditionally known from Old English as a wen, is a closed sac, having a distinct envelope and division compared with the nearby tissue. Hence, it is a cluster of cells that have grouped together to form a sac ; however, the distinguishing aspect of a cyst is that the cells forming the "shell" of such a sac are distinctly abnormal when compared with all surrounding cells for that given location. A cyst may contain air, fluids, or semi-solid material. A collection of pus is called an abscess, not a cyst. Once formed, a cyst may resolve on its own. When a cyst fails to resolve, it may need to be removed surgically, but that would depend upon its type and location.

A bile duct is any of a number of long tube-like structures that carry bile, and is present in most vertebrates.

In urinary catheterization a latex, polyurethane, or silicone tube known as a urinary catheter is inserted into the bladder through the urethra to allow urine to drain from the bladder for collection. It may also be used to inject liquids used for treatment or diagnosis of bladder conditions. A clinician, often a nurse, usually performs the procedure, but self-catheterization is also possible. A catheter may be in place for long periods of time or removed after each use.

The seminal vesicles are a pair of convoluted tubular glands that lie behind the urinary bladder of male mammals. They secrete fluid that partly composes the semen.
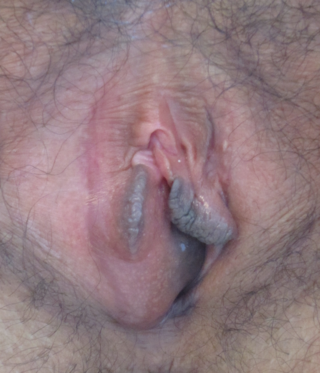
A Bartholin's cyst occurs when a Bartholin's gland within the labia becomes blocked. Small cysts may result in minimal or no symptoms. Larger cysts may result in swelling on one side of the vagina, as well as pain during sex or walking. If the cyst becomes infected, an abscess can occur, which is typically red and very painful. If there are no symptoms, no treatment is needed. Bartholin's cysts affect about 2% of women at some point in their life. They most commonly occur during childbearing years.

Caspar Bartholin the Younger, was a Danish anatomist who first described the "Bartholin's gland" in the 17th century. The discovery of the Bartholin's gland is sometimes mistakenly credited to his grandfather.

Adenoid cystic carcinoma is a rare type of cancer that can exist in many different body sites. This tumor most often occurs in the salivary glands, but it can also be found in many anatomic sites, including the breast, lacrimal gland, lung, brain, bartholin gland, trachea, and the paranasal sinuses.

A milium, also called a milk spot or an oil seed, is a clog of the eccrine sweat gland. It is a keratin-filled cyst that can appear just under the epidermis or on the roof of the mouth. Milia are commonly associated with newborn babies, but can appear on people of all ages. They are usually found around the nose and eyes, and sometimes on the genitalia, often mistaken by those affected as warts or other sexually transmitted diseases. Milia can also be confused with stubborn whiteheads.

Pseudocysts are like cysts, but lack epithelial or endothelial cells. Initial management consists of general supportive care. Symptoms and complications caused by pseudocysts require surgery. Computed tomography (CT) scans are used for initial imaging of cysts, and endoscopic ultrasounds are used in differentiating between cysts and pseudocysts. Endoscopic drainage is a popular and effective method of treating pseudocysts.

Oral mucocele is a condition caused by two related phenomena - mucus extravasation phenomenon and mucous retention cyst.

A ranula is a mucus extravasation cyst involving a sublingual gland and is a type of mucocele found on the floor of the mouth. Ranulae present as a swelling of connective tissue consisting of collected mucin from a ruptured salivary gland caused by local trauma. If small and asymptomatic further treatment may not be needed, otherwise minor oral surgery may be indicated.

Percutaneous transhepatic cholangiography, percutaneous hepatic cholangiogram (PTHC) is a radiological technique used to visualize the anatomy of the biliary tract. A contrast medium is injected into a bile duct in the liver, after which X-rays are taken. It allows access to the biliary tree in cases where endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography has been unsuccessful. Initially reported in 1937, the procedure became popular in 1952.

Marsupialization is the surgical technique of cutting a slit into an abscess or cyst and suturing the edges of the slit to form a continuous surface from the exterior surface to the interior surface of the cyst or abscess. Sutured in this fashion, the site remains open and can drain freely. This technique is used to treat a cyst or abscess when a single draining would not be effective and complete removal of the surrounding structure would not be desirable. The technique is often applied to Gartner's duct cysts, pancreatic cysts, pilonidal cysts, and Bartholin's cysts.
Bartholin is a Danish family name.

A Rathke's cleft cyst is a benign growth on the pituitary gland in the brain, specifically a mucin-filled cyst in the posterior portion of the anterior pituitary gland. It occurs when the Rathke's pouch does not develop properly and ranges in size from 2 to 40 mm in diameter.

Bartholin gland carcinoma is a type of cancer of the vulva arising in the Bartholin gland. It typically presents with a painless mass at one side of the vaginal opening in a female of middle-age and older, and can appear similar to a Bartholin cyst. The mass may be big or small, may be deep under skin or appear nearer the surface with overlying ulceration. Average age at presentation is 53-years.

Vaginal cysts are uncommon benign cysts that develop in the vaginal wall. The type of epithelial tissue lining a cyst is used to classify these growths. They can be congenital. They can present in childhood and adulthood. The most common type is the squamous inclusion cyst. It develops within vaginal tissue present at the site of an episiotomy or other vaginal surgical sites. In most instances they do not cause symptoms and present with few or no complications. A vaginal cyst can develop on the surface of the vaginal epithelium or in deeper layers. Often, they are found by the woman herself and as an incidental finding during a routine pelvic examination. Vaginal cysts can mimic other structures that protrude from the vagina such as a rectocele and cystocele. Some cysts can be distinguished visually but most will need a biopsy to determine the type. Vaginal cysts can vary in size and can grow as large as 7 cm. Other cysts can be present on the vaginal wall though mostly these can be differentiated. Vaginal cysts can often be palpated (felt) by a clinician. Vaginal cysts are one type of vaginal mass, others include cancers and tumors. The prevalence of vaginal cysts is uncertain since many go unreported but it is estimated that 1 out of 200 women have a vaginal cyst. Vaginal cysts may initially be discovered during pregnancy and childbirth. These are then treated to provide an unobstructed delivery of the infant. Growths that originate from the urethra and other tissue can present as cysts of the vagina.
Vulvar tumors are those neoplasms of the vulva. Vulvar and vaginal neoplasms make up a small percentage (3%) of female genital cancers. They can be benign or malignant. Vulvar neoplasms are divided into cystic or solid lesions and other mixed types. Vulvar cancers are those malignant neoplasms that originate from vulvar epithelium, while vulvar sarcomas develop from non-epithelial cells such as bone, cartilage, fat, muscle, blood vessels, or other connective or supportive tissue. Epithelial and mesenchymal tissue are the origin of vulvar tumors.
References
- ↑ Chen, Katherine T. (2019). "Bartholin gland cyst and abscess: Word catheter placement". UpToDate. Retrieved 22 June 2020.
- ↑ Baskett, Thomas F. (2019). "Samuel Buford Word". Eponyms and Names in Obstetrics and Gynaecology. Cambridge University Press. pp. 456–457. ISBN 978-1-108-42170-6.