Related Research Articles

A barrister is a type of lawyer in common law jurisdictions. Barristers mostly specialize in courtroom advocacy and litigation. Their tasks include arguing cases in courts and tribunals, drafting legal pleadings, researching the law and giving legal opinions.

A lawyer is a person who is qualified to offer advice about the law, draft legal documents, or represent individuals in legal matters.

In the European Union, competition law promotes the maintenance of competition within the European Single Market by regulating anti-competitive conduct by companies to ensure that they do not create cartels and monopolies that would damage the interests of society.
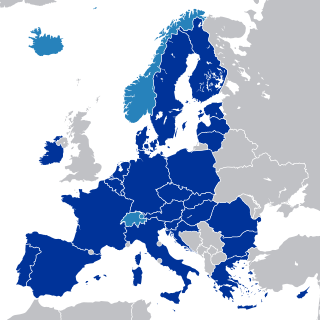
The European single market, also known as the European internal market or the European common market, is the single market comprising mainly the 27 member states of the European Union (EU). With certain exceptions, it also comprises Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway, and Switzerland. The single market seeks to guarantee the free movement of goods, capital, services, and people, known collectively as the "four freedoms". This is achieved through common rules and standards that all participating states are legally committed to follow.
The EFTA Court is a supranational judicial body responsible for the three EFTA members who are also members of the European Economic Area (EEA): Iceland, Liechtenstein and Norway.
Flaminio Costa v ENEL (1964) Case 6/64 was a landmark decision of the European Court of Justice which established the primacy of European Union law over the laws of its member states.

The Freedom to Provide Services or sometimes referred to as free movement of services along with the Freedom of Establishment form the core of the European Union's functioning. With the free movement of workers, citizens, goods and capital, they constitute fundamental rights that give companies and citizens the right to provide services without restrictions in any member country of the EU regardless of nationality and jurisdiction.
Article 101 of the Treaty on the Functioning of the European Union prohibits cartels and other agreements that could disrupt free competition in the European Economic Area's internal market.
Van Gend en Loos v Nederlandse Administratie der Belastingen (1963) Case 26/62 was a landmark case of the European Court of Justice which established that provisions of the Treaty Establishing the European Economic Community were capable of creating legal rights which could be enforced by both natural and legal persons before the courts of the Community's member states. This is now called the principle of direct effect. The case is acknowledged as being one of the most important, and possibly the most famous development of European Union law.
Bates v. State Bar of Arizona, 433 U.S. 350 (1977), was a United States Supreme Court case in which the Court upheld the right of lawyers to advertise their services. In holding that lawyer advertising was commercial speech entitled to protection under the First Amendment, the Court upset the tradition against advertising by lawyers, rejecting it as an antiquated rule of etiquette.

The Legal Services Board is an independent body responsible for overseeing the regulation of lawyers in England and Wales. It is a non-departmental public body sponsored by the Ministry of Justice, created through the Legal Services Act of 2007.

International Transport Workers Federation v Viking Line ABP (2007) C-438/05 is an EU law case of the European Court of Justice, in which it was held that there is a positive right to strike, but the exercise of that right could infringe a business's freedom of establishment under the Treaty on the Functioning of the European Union article 49. Often called The Rosella case or the Viking case, it is relevant to all labour law within the European Union. The decision has been criticised for the Court's inarticulate line of reasoning, and its disregard of fundamental human rights.

The general principles of European Union law are general principles of law which are applied by the European Court of Justice and the national courts of the member states when determining the lawfulness of legislative and administrative measures within the European Union. General principles of European Union law may be derived from common legal principles in the various EU member states, or general principles found in international law or European Union law. General principles of law should be distinguished from rules of law as principles are more general and open-ended in the sense that they need to be honed to be applied to specific cases with correct results.

Meca Medina and Majcen v Commission (2006) C-519/04 P was a landmark judgement in the European Court of Justice that established primacy of EU law over sports federations. The ruling concerned David Meca-Medina and Igor Majcen, long distance swimmers from Spain and Slovenia and their failed drugs test. The case was wide-reaching and important because it established the scope and nature that individual laws by sporting regulators, league operators and individual associations in Europe could impose their own rules and if they were in direct conflict with EU treaties, acquis or judgements by the European Courts of Justice.

O2 (Germany) GmbH & Co OHG v Commission (2006) T-328/03 is an EU competition law case, concerning the requirements for a restriction of competition to be found under TFEU article 101.

Josemansv Burgemeester van Maastricht is a European Union law case from 2010, concerning cannabis and the free movement of services in the European Union. The Second Chamber of the Court of Justice of the European Union pronounced its ruling on 16 December 2010.
Alpine Investments BV v Minister van Financiën (1995) C-384/93 is an EU law case, concerning the free movement of services in the European Union.

Omega Spielhallen und Automatenaufstellungs-GmbH v Oberbürgermeisterin der Bundesstadt Bonn (2004) C-36/02 is an EU law case, concerning the freedom to provide services and the free movement of goods in the European Union.

Ker-Optika bt v ÀNTSZ Dél-dunántúli Regionális Intézete [2010] ECR, Case C-108/09 is an EU law case concerning a conflict of law between Hungarian national legislation and European Union law. The Hungarian legislation regarding the online sale of contact lenses was considered with regards to whether it was necessary for the protection of public health, and it was concluded that this could have been done by less restrictive measures. Despite the internal measure in this case being categorised as a selling arrangement, which would generally be determined by the discrimination test established in Keck, the Court went on to use a market access test, as per Italian Trailers. Thus, this case is crucial in the recent development of the tests for determining measures equaling equivalent effect.