Related Research Articles

Richard was an English prince who was King of the Romans from 1257 until his death in 1272. He was the second son of John, King of England, and Isabella, Countess of Angoulême. Richard was nominal Count of Poitou from 1225 to 1243, and he also held the title Earl of Cornwall since 1225. He was one of the wealthiest men in Europe and joined the Barons' Crusade, where he achieved success as a negotiator for the release of prisoners and assisted with the building of the citadel in Ascalon.

Richard de Clare, 5th Earl of Hertford, 6th Earl of Gloucester, 2nd Lord of Glamorgan, 8th Lord of Clare was the son of Gilbert de Clare, 4th Earl of Hertford, and Isabel Marshal. He was also a powerful Marcher Lord in Wales and inherited the Lordship of Glamorgan upon the death of his father. He played a prominent role in the constitutional crisis of 1258–1263.

Dibden is a small village in Hampshire, England, which dates from the Middle Ages. It is dominated by the nearby settlements of Hythe and Dibden Purlieu. It is in the civil parish of Hythe and Dibden. It lies on the eastern edge of the New Forest in a valley, which runs into Southampton Water.

Aldringham is a village in the Blything Hundred of Suffolk, England. The village is located 1 mile south of Leiston and 3 miles northwest of Aldeburgh close to the North Sea coast. The parish includes the coastal village of Thorpeness. The mid-2005 population estimate for Aldringham cum Thorpe parish was 730.

Quarr Abbey is a monastery between the villages of Binstead and Fishbourne on the Isle of Wight in southern England. The name is pronounced as "Kwor". It belongs to the Catholic Order of St Benedict.

Nuneham Courtenay is a village and civil parish about 5 miles (8 km) SSE of Oxford. It occupies several miles close to the east bank of the River Thames.

de Lacy is the surname of an old Norman family which originated from Lassy, Calvados. The family took part in the Norman Conquest of England and the later Norman invasion of Ireland. The name is first recorded for Hugh de Lacy (1020–1085). His sons, Walter and Ilbert, left Normandy and travelled to England with William the Conqueror. The awards of land by the Conqueror to the de Lacy sons led to two distinct branches of the family: the northern branch, centred on Blackburnshire and west Yorkshire was held by Ilbert's descendants; the southern branch of Marcher Lords, centred on Herefordshire and Shropshire, was held by Walter's descendants.
The Lord of the Isle of Wight was a feudal title, at times hereditary and at others by royal appointment in the Kingdom of England, before the development of an extensive peerage system.

Seacourt is a deserted medieval village (DMV) in the civil parish of Wytham, in the Vale of White Horse district, in Oxfordshire, England, near the city of Oxford.The site is now mostly beneath the Oxford Western By-pass (A34), about 0.3 miles (0.48 km) south of the Seacourt/Hinksey Stream crossing.

Isabel de Forz was the eldest daughter of Baldwin de Redvers, 6th Earl of Devon (1217–1245). On the death of her brother Baldwin de Redvers, 7th Earl of Devon, in 1262, without children, she inherited suo jure the earldom and also the feudal barony of Plympton in Devon, and the lordship of the Isle of Wight. After the early death of her husband and her brother, before she was thirty years old, she inherited their estates and became one of the richest women in England, living mainly in Carisbrooke Castle on the Isle of Wight, which she held from the king as tenant-in-chief.

Ial or Yale was a commote of medieval Wales within the cantref of Maelor in the Kingdom of Powys. When the Kingdom was divided in 1160, Maelor became part of the Princely realm of Powys Fadog, and belonged to the Royal House of Mathrafal. Yale eventually merged with another commote and became the Lordship of Bromfield and Yale, later a royal lordship under the Tudors and Stuarts.
Sir Gilbert Denys of Siston, Gloucestershire, was a soldier, and later an administrator. He was knighted by January 1385, and was twice knight of the shire for Gloucestershire constituency, in 1390 and 1395 and served as Sheriff of Gloucestershire 1393-4. He founded the family which provided more Sheriffs of Gloucestershire than any other.

Arreton Manor is a manor house in Arreton, Isle of Wight, England. Its history is traced to 872 AD to the time of King Alfred the Great and his parents. It was left by King Alfred by his will to his youngest son Aethelweard. Once owned by William the Conqueror, as mentioned in the Domesday Book in 1086, in the 12th century it became part of Quarr Abbey and was used by the monks for over 400 years. In 1525, it was leased to the Leigh family. The manor was rebuilt between 1595 and 1612. Built in Jacobean style, it is in the shape of a "H".
Bigbury Manor is a small manor house on the Isle of Wight within the Newchurch parish. It is a small holding to the north of Apse Heath, was confirmed to Quarr Abbey by Isabel de Fortibus, and remained in the possession of the abbey until the Dissolution of the monasteries, when it passed to the Crown. It was granted in 1610 to Lionel Cranfield. In 1631, Basil Nicoll and others obtained a grant of the messuage or grange of Bidborowe.
The Manor of Dyrham was a former manorial estate in the parish of Dyrham in South Gloucestershire, England.
The feudal barony of Berry Pomeroy was one of eight feudal baronies in Devonshire, England, which existed during the mediaeval era. It had its caput at the manor of Berry Pomeroy, 20 miles south of the City of Exeter and 2 miles east of the town of Totnes, where was situated Totnes Castle, the caput of the feudal barony of Totnes. The exact location of the 11th-century baron's residence is unclear; perhaps it was next to the parish church on the site of the former rectory known as Berry House, as it is now believed that the nearby ruined Berry Pomeroy Castle was not built until the 15th century.
Eversley Manor is a manor in Eversley, Hampshire, England. Mentioned in the Domesday Book, in 1669, it was purchased by Sir Andrew Henley of Bramshill House, who then ran it.
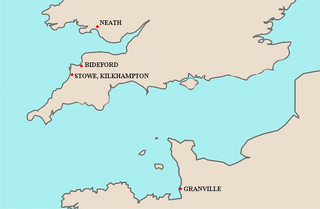
Sir Richard de Grenville was one of the Twelve Knights of Glamorgan who served under Robert FitzHamon, in the conquest of Glamorgan in Wales. He obtained from FitzHamon the lordship of Neath in which he built Neath Castle and in 1129 founded Neath Abbey. He is by tradition the founder and ancestor of the prominent Westcountry Grenville family of Stowe in the parish of Kilkhampton in Cornwall and of Bideford in Devon, the later head of which family was John Granville, 1st Earl of Bath (1628–1701). The surname of his supposed descendants the Westcountry Grenville family was spelled by tradition "Grenville" until 1661 when it was altered to "Granville".

Milton Abbot is a village, parish, and former manor in Devon, 6 miles (9.7 km) north-west of Tavistock, Devon, and 6 miles (9.7 km) south-east of Launceston, Cornwall.
References
This article includes text incorporated from William Page's "A History of the County of Hampshire: Volume 5 (1912)", a publication now in the public domain