Extensible Markup Language (XML) is a markup language that defines a set of rules for encoding documents in a format that is both human-readable and machine-readable. The World Wide Web Consortium's XML 1.0 Specification of 1998 and several other related specifications—all of them free open standards—define XML.

The Geography Markup Language (GML) is the XML grammar defined by the Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC) to express geographical features. GML serves as a modeling language for geographic systems as well as an open interchange format for geographic transactions on the Internet. Key to GML's utility is its ability to integrate all forms of geographic information, including not only conventional "vector" or discrete objects, but coverages and sensor data.
The International Press Telecommunications Council (IPTC), based in London, United Kingdom, is a consortium of the world's major news agencies, other news providers and news industry vendors and acts as the global standards body of the news media.
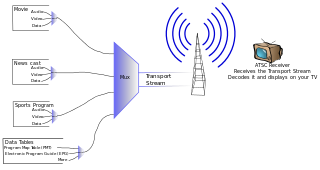
The Program and System Information Protocol (PSIP) is the MPEG and privately defined program-specific information originally defined by General Instrument for the DigiCipher 2 system and later extended for the ATSC digital television system for carrying metadata about each channel in the broadcast MPEG transport stream of a television station and for publishing information about television programs so that viewers can select what to watch by title and description. Its FM radio equivalent is Radio Data System (RDS).
The Global Justice XML Data Model is a data reference model for the exchange of information within the justice and public safety communities. The Global JXDM is a product of the Global Justice Information Sharing Initiative's (Global) Infrastructure and Standards Working Group (ISWG), and was developed by the Global ISWG's XML Structure Task Force (XSTF).

Learning Object Metadata is a data model, usually encoded in XML, used to describe a learning object and similar digital resources used to support learning. The purpose of learning object metadata is to support the reusability of learning objects, to aid discoverability, and to facilitate their interoperability, usually in the context of online learning management systems (LMS).
The National Information Exchange Model (NIEM) is an XML-based information exchange framework from the United States. NIEM represents a collaborative partnership of agencies and organizations across all levels of government and with private industry. The purpose of this partnership is to effectively and efficiently share critical information at key decision points throughout the whole of the justice, public safety, emergency and disaster management, intelligence, and homeland security enterprise. NIEM is designed to develop, disseminate, and support enterprise-wide information exchange standards and processes that will enable jurisdictions to automate information sharing.
Catalogue Service for the Web (CSW), sometimes seen as Catalogue Service - Web, is a standard for exposing a catalogue of geospatial records in XML on the Internet. The catalogue is made up of records that describe geospatial data, geospatial services, and related resources.
SensorML is an approved Open Geospatial Consortium standard. SensorML provides standard models and an XML encoding for describing sensors and measurement processes. SensorML can be used to describe a wide range of sensors, including both dynamic and stationary platforms and both in-situ and remote sensors.
Technical Report 069 (TR-069) is a technical specification of the Broadband Forum that defines an application layer protocol for remote management of customer-premises equipment (CPE) connected to an Internet Protocol (IP) network. TR-069 uses the CPE WAN Management Protocol (CWMP) which provides support functions for auto-configuration, software or firmware image management, software module management, status and performance managements, and diagnostics.
Entity–attribute–value model (EAV) is a data model to encode, in a space-efficient manner, entities where the number of attributes that can be used to describe them is potentially vast, but the number that will actually apply to a given entity is relatively modest. Such entities correspond to the mathematical notion of a sparse matrix.
The Open Packaging Conventions (OPC) is a container-file technology initially created by Microsoft to store a combination of XML and non-XML files that together form a single entity such as an Open XML Paper Specification (OpenXPS) document. OPC-based file formats combine the advantages of leaving the independent file entities embedded in the document intact and resulting in much smaller files compared to normal use of XML.
Observations and Measurements (O&M) is an international standard which defines a conceptual schema encoding for observations, and for features involved in sampling when making observations. While the O&M standard was developed in the context of geographic information systems, the model is derived from generic patterns proposed by Fowler and Odell, and is not limited to spatial information. O&M is one of the core standards in the OGC Sensor Web Enablement suite, providing the response model for Sensor Observation Service (SOS).

EPUB is an e-book file format that uses the ".epub" file extension. The term is short for electronic publication and is sometimes styled ePub. EPUB is supported by many e-readers, and compatible software is available for most smartphones, tablets, and computers. EPUB is a technical standard published by the International Digital Publishing Forum (IDPF). It became an official standard of the IDPF in September 2007, superseding the older Open eBook standard.
The Office Open XML file formats are a set of file formats that can be used to represent electronic office documents. There are formats for word processing documents, spreadsheets and presentations as well as specific formats for material such as mathematical formulae, graphics, bibliographies etc.
Bus monitoring is a term used in flight testing when capturing data from avionics buses and networks in data acquisition telemetry systems. Commonly monitored avionics buses include
The Sensor Observation Service (SOS) is a web service to query real-time sensor data and sensor data time series and is part of the Sensor Web. The offered sensor data comprises of sensors themselves, which are encoded in the Sensor Model Language (SensorML), and the measured values in the Observations and Measurements encoding format. The web service as well as both file formats are open standards and specifications of the same name defined by the Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC).
The Quake Markup Language (QuakeML) is a flexible, extensible and modular XML representation of seismological data which is intended to cover a broad range of fields of application in modern seismology.



