
Papua New Guinea, officially the Independent State of Papua New Guinea, is a country in Oceania that comprises the eastern half of the island of New Guinea and its offshore islands in Melanesia. Its capital, located along its southeastern coast, is Port Moresby. It is the world's third largest island country with an area of 462,840 km2 (178,700 sq mi).
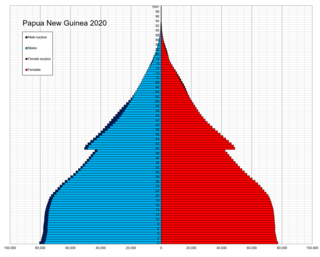
The indigenous population of Papua New Guinea is one of the most heterogeneous in the world. Papua New Guinea has several thousand separate communities, most with only a few hundred people. Divided by language, customs, and tradition, some of these communities have engaged in endemic warfare with their neighbors for centuries. It is the second most populous nation in Oceania.

A cargo cult is an indigenist millenarian belief system in which adherents perform rituals which they believe will cause a more technologically advanced society to deliver goods. These cults were first described in Melanesia in the wake of contact with allied military forces during the Second World War.

The music of Papua New Guinea has a long history.

A slit drum or slit gong is a hollow percussion instrument. In spite of the name, it is not a true drum but an idiophone, usually carved or constructed from bamboo or wood into a box with one or more slits in the top. Most slit drums have one slit, though two and three slits occur. If the resultant tongues are different width or thicknesses, the drum will produce two different pitches. It is used throughout Africa, Southeast Asia, and Oceania. In Africa such drums, strategically situated for optimal acoustic transmission, have been used for long-distance communication.

Morobe Province is a province on the northern coast of Papua New Guinea. The provincial capital and largest city is Lae. The province covers 33,705 km², with a population of 674,810, and since the division of Southern Highlands Province in May 2012 it is the most populous province. It includes the Huon Peninsula, the Markham River, and delta, and coastal territories along the Huon Gulf. The province has nine administrative districts. At least 101 languages are spoken, including Kâte and Yabem language. English and Tok Pisin are common languages in the urban areas, and in some areas pidgin forms of German are mixed with the native language.
The family of North Huon Gulf languages is a subgroup of the Huon Gulf languages of Papua New Guinea.

The koteka, horim, penis gourd, and Armor Condom is a penis sheath traditionally worn by native male inhabitants of some ethnic groups in New Guinea to cover their penis. They are normally made from a dried-out gourd, Lagenaria siceraria, although unrelated species such as pitcher-plant Nepenthes mirabilis, are also used. They are held in place by a small loop of fiber attached to the base of the koteka and placed around the scrotum. A secondary loop placed around the chest or abdomen is attached to the main body of the koteka.
The Tolai are the indigenous people of the Gazelle Peninsula and the Duke of York Islands of East New Britain in the New Guinea Islands region of Papua New Guinea. They are ethnically close kin to the peoples of adjacent New Ireland and tribes like the Tanga people and are thought to have migrated to the Gazelle Peninsula in relatively recent times, displacing the Baining people who were driven westwards.

The Huli are an indigenous people who live in the Hela Province of Papua New Guinea. They speak primarily Huli and Tok Pisin; many also speak some of the surrounding languages, and some also speak English. They are one of the largest cultural groups in Papua New Guinea, numbering over 250,000 people.

Islam in Papua New Guinea is a minority religion, with over 5,000 followers. The majority of the Muslims are Sunni, while a small number are Ahmadiyya. Majority of Muslims in Papua New Guinea are indigenous Papua New Guineans.
The Papuans are one of four major cultural groups of Papua New Guinea. The majority of the population lives in rural areas. In isolated areas there still remains a handful of the giant communal structures that previously housed the whole male population, with a circling cluster of huts for the women. The Papuan people are Melanesian people composed of at least 240 different peoples, each with its own language and culture. Sago is the staple food of the Papuan supplemented with hunting, fishing and small gardens.
Yabem, or Jabêm, is an Austronesian language of Papua New Guinea.

Marind or Marind-Anim are people living in South New Guinea.
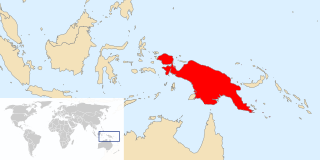
New Guinea is the world's second-largest island, and with an area of 785,753 km2 (303,381 sq mi), the largest island in the Southern Hemisphere. Located in Melanesia in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, it is separated by the 150 km wide Torres Strait from Australia. Numerous smaller islands are located to the west and east. The eastern half of the island is the major land mass of the independent state of Papua New Guinea. The western half, known as Western New Guinea or West Papua, forms a part of Indonesia and is organized as the provinces of Papua and West Papua.
The Urapmin people are an ethnic group numbering about 375 people in the Telefomin District of the West Sepik Province of Papua New Guinea. One of the Min peoples who inhabit this area, the Urapmin share the common Min practices of hunter-gatherer subsistence, taro cultivation, and formerly, an elaborate secret cult available only to initiated men.
The Etoro, or Edolo, are a tribe and ethnic group of Papua New Guinea. Their territory comprises the southern slopes of Mt. Sisa, along the southern edge of the central mountain range of New Guinea, near the Papuan Plateau. They are well known among anthropologists because of ritual acts practiced between the young boys and men of the tribe. The Etoro believe that young males must ingest the semen of their elders to achieve adult male status and to properly mature and grow strong.

Kundu is a pidgin name in Papua New Guinea for an hourglass shaped drum used to accompany formal occasions, religious ceremonies and for celebrations. This drum is emblematic of Papua New Guinea and it appears on the country's coat of arms.
Yabim-Mape Rural LLG is a local-level government (LLG) of Morobe Province, Papua New Guinea.

The tifa, tiwa or tiva is a single-headed goblet drum used throughout the Maluku Islands of Eastern Indonesia, where it is traditionally the "dominant instrument" in Maluku province music. The term tifa has been used outside of the Maluku Islands, including on the island of Java and on the island of New Guinea, in Indonesia's Papua province.













