
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is the national public health agency of the United States. It is a United States federal agency, under the Department of Health and Human Services, and is headquartered in Atlanta, Georgia.

The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health is the United States federal agency responsible for conducting research and making recommendations for the prevention of work-related injury and illness. NIOSH is part of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) within the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Despite its name, it is not part of the National Institutes of Health. Its current director is John Howard.

The DPT vaccine or DTP vaccine is a class of combination vaccines against three infectious diseases in humans: diphtheria, pertussis, and tetanus. The vaccine components include diphtheria and tetanus toxoids and either killed whole cells of the bacterium that causes pertussis or pertussis antigens. The whole cells or antigens will be depicted as either "DTwP" or "DTaP", where the lower-case "w" indicates whole-cell inactivated pertussis and the lower-case "a" indicates pertussis antigens.

An occupational hazard is a hazard experienced in the workplace. Occupational hazards can encompass many types of hazards, including chemical hazards, biological hazards (biohazards), psychosocial hazards, and physical hazards. In the United States, the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) conduct workplace investigations and research addressing workplace health and safety hazards resulting in guidelines. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) establishes enforceable standards to prevent workplace injuries and illnesses. In the EU a similar role is taken by EU-OSHA.
Injury prevention is an effort to prevent or reduce the severity of bodily injuries caused by external mechanisms, such as accidents, before they occur. Injury prevention is a component of safety and public health, and its goal is to improve the health of the population by preventing injuries and hence improving quality of life. Among laypersons, the term "accidental injury" is often used. However, "accidental" implies the causes of injuries are random in nature. Researchers prefer the term "unintentional injury" to refer to injuries that are nonvolitional but often preventable. Data from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control show that unintentional injuries are a significant public health concern: they are by far the leading cause of death from ages 1 through 44. During these years, unintentional injuries account for more deaths than the next three leading causes of death combined. Unintentional injuries also account for the top ten sources of nonfatal emergency room visits for persons up to age 9 and nine of the top ten sources of nonfatal emergency room visits for persons over the age of 9.
The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention's National Center for Injury Prevention and Control's mission is to provide leadership in preventing and controlling injuries, i.e., reducing the incidence, severity, and adverse outcomes of injury, the leading cause of death for those aged 1 – 44. A 1985 National Research Council report entitled Injury in America recommended that United States Congress establish a new program at the CDC to address the problem of injury. Initially the program was supported with funds from the United States Department of Transportation. In 1990 Congress passed the Injury Control Act which authorized the program within the CDC, and in 1992, the CDC formally established the Center. The Center has three branches: the Division of Acute Care, Rehabilitation Research, and Disability Prevention; the Division of Unintentional Injury Prevention; and the Division of Violence Prevention.

Measles vaccine protects against becoming infected with measles. Nearly all of those who do not develop immunity after a single dose develop it after a second dose. When rates of vaccination within a population are greater than 92%, outbreaks of measles typically no longer occur; however, they may occur again if rates of vaccination decrease. The vaccine's effectiveness lasts many years. It is unclear if it becomes less effective over time. The vaccine may also protect against measles if given within a couple of days after exposure to measles.
The Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention is an independent agency of the National Health Commission, based in Changping District, Beijing, China.

The Vaccines for Children Program (VFC) is a federally funded program in the United States providing no-cost vaccines to children who lack health insurance or who otherwise cannot afford the cost of the vaccination. The VFC program was created by the Omnibus Budget Reconciliation Act of 1993 and is required to be a new entitlement of each state's Medicaid plan under section 1928 of the Social Security Act. The program was officially implemented in October 1994 and serves eligible children in all U.S. states, as well as the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico, the U.S. Virgin Islands, American Samoa, Guam, and the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands.
Tetanus vaccine, also known as tetanus toxoid (TT), is a toxoid vaccine used to prevent tetanus. During childhood, five doses are recommended, with a sixth given during adolescence.

David L. Katz is an American physician. He was the founding director of the Yale-Griffin Prevention Research Center that was founded at Griffin Hospital in Derby, Connecticut in 1998.

Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency, formerly Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, is an organization under the South Korean Ministry of Welfare and Health that is responsible for an organ transplant and advancement of public health by managing prevention, survey, quarantine, trial, and research on infectious diseases, chronic and rare illnesses and injuries. It was founded in December 2003 and is located in Osong Health Technology Administration Complex in Cheongju. The organization is led by the vice-ministerial-level Commissioner of KDCA.
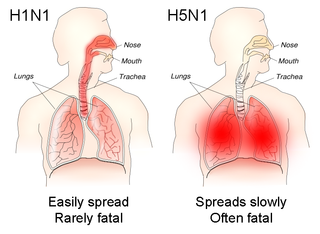
US influenza statistics by flu season. From the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention page called "Disease Burden of Flu": "Each year CDC estimates the burden of influenza in the U.S. CDC uses modeling to estimate the number of flu illnesses, medical visits, hospitalizations, and deaths related to flu that occurred in a given season. The methods used to calculate these estimates are described on CDC’s webpage, How CDC Estimates the Burden of Seasonal Flu in the U.S."
Kathleen A. Ethier is an American social psychologist and public health official with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). In 2016, she was appointed the Director of CDC's Division of Adolescent and School Health in the National Center for HIV/AIDS, Viral Hepatitis, STD, and TB Prevention. As of 2020, Ethier is also head of the CDC's community mitigation task force for the COVID-19 pandemic.

Jeffrey P. Koplan is an American physician and epidemiologist who is the Vice President for Global Health at Emory University. He established and became the first Director of the Emory Global Health Institute from 2006 to 2013. Koplan was the director of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention from 1998 to 2002; he had previously worked at the CDC for more than twenty years, looking into HIV-contaminated blood, as well as the Bhopal disaster. During his tenure as Director, he fought syphilis, and supervised the investigation into the 2001 anthrax attacks; before leaving the agency in March 2002.

The Africa Centres for Disease Control and Prevention is a public health agency of the African Union to support the public health initiatives of member states and strengthen the capacity of their health institutions to deal with disease threats. The Africa CDC ideas was proposed by the government of Ethiopia in 2013 during TB/HIV special submit in Abuja Nigeria. From 2013 to 2016 the modalities and statue of Africa CDC were developed and the specialized agency was officially launched in January 2017.

Rochelle Paula Walensky is an American physician-scientist who is the director of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the administrator of the Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry. Prior to her appointment at the CDC, she was the Chief of the Division of Infectious Diseases at Massachusetts General Hospital and a professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School. Walensky is an expert on HIV/AIDS.

The term variant of concern (VOC) for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 is a category used for variants of the virus where mutations in their spike protein receptor binding domain (RBD) substantially increase binding affinity in RBD-hACE2 complex, while also being linked to rapid spread in human populations.













