Related Research Articles

The Amazon rainforest, also called Amazon jungle or Amazonia, is a moist broadleaf tropical rainforest in the Amazon biome that covers most of the Amazon basin of South America. This basin encompasses 7,000,000 km2 (2,700,000 sq mi), of which 5,500,000 km2 (2,100,000 sq mi) are covered by the rainforest. This region includes territory belonging to nine nations and 3,344 formally acknowledged indigenous territories.
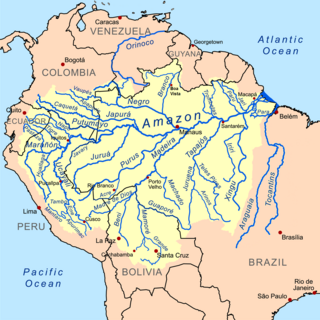
The Amazon basin is the part of South America drained by the Amazon River and its tributaries. The Amazon drainage basin covers an area of about 7,000,000 km2 (2,700,000 sq mi), or about 35.5 percent of the South American continent. It is located in the countries of Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, Guyana, Peru, Suriname, and Venezuela, as well as the territory of French Guiana.

A blackwater river is a type of river with a slow-moving channel flowing through forested swamps or wetlands. Most major blackwater rivers are in the Amazon Basin and the Southern United States. The term is used in fluvial studies, geology, geography, ecology, and biology. Not all dark rivers are blackwater in that technical sense. Some rivers in temperate regions, which drain or flow through areas of dark black loam, are simply black due to the color of the soil; these rivers are black mud rivers. There are also black mud estuaries.

The Amazonian manatee is a species of manatee that lives in the Amazon Basin in Brazil, Peru, Colombia and Ecuador. It has thin, wrinkled brownish or gray colored skin, with fine hairs scattered over its body and a white chest patch. It is the smallest of the three extant species of manatee.

Terra preta is a type of very dark, fertile anthropogenic soil (anthrosol) found in the Amazon Basin. It is also known as "Amazonian dark earth" or "Indian black earth". In Portuguese its full name is terra preta do índio or terra preta de índio. Terra mulata is lighter or brownish in color.

Eleotridae is a family of fish commonly known as sleeper gobies, with about 34 genera and 180 species. Most species are found in the tropical Indo-Pacific region, but there are also species in subtropical and temperate regions, warmer parts of the Americas and near the Atlantic coast in Africa. While many eleotrids pass through a planktonic stage in the sea and some spend their entire lives in the sea; as adults, the majority live in freshwater streams and brackish water. One of its genera, Caecieleotris, is troglobitic. They are especially important as predators in the freshwater stream ecosystems on oceanic islands such as New Zealand and Hawaii that otherwise lack the predatory fish families typical of nearby continents, such as catfish. Anatomically, they are similar to the gobies (Gobiidae), though unlike the majority of gobies, they do not have a pelvic sucker.

The Peruvian spider monkey, also known as the black-faced black spider monkey, is a species of spider monkey that lives in Peru, as well as in Brazil and in Bolivia. At 60 centimetres long, they are relatively large among species of monkey, and their strong, prehensile tails can be up to 1 m (3 ft) long. Unlike many species of monkey, they have only a vestigial thumb, an adaptation which enables them to travel using brachiation. Peruvian spider monkeys live in groups of 20–30 individuals, but these groups are rarely all together simultaneously. The size and dynamics of the resulting subgroups vary with food availability and sociobehavioral activity. They prefer to eat fleshy fruit, but will change their diet in response to scarcity of ripe fruit. Individuals of this species also eat small animals, insects and leaves based on availability. Females separate from the band to give birth, typically in the fall. These females inhabit a group of core areas where resources are abundant in certain seasons. Typically, males exhibit ranging over longer distances than females, with movement of individuals enhancing the fluidity of subgroup size. Peruvian spider monkey are independent at about 10 months, with a lifespan of about 20 years.

Ilex guayusa is a species of tree of the holly genus, native to the Amazon Rainforest. One of four known caffeinated holly trees, the leaves of the guayusa tree are harvested fresh and brewed like a tea for their stimulative effects.

The ocellate river stingray, also known as the peacock-eye stingray or black river stingray, is a species of freshwater stingray in the family Potamotrygonidae. It was the first species to be described in the family and is also the most widespread, ranging throughout much of the Río de la Plata, Amazon, Mearim and Orinoco basins in tropical and subtropical South America. It is sometimes kept in aquaria.

The Manu parrotlet or Amazonian parrotlet is a species of parrotlet native to the western Amazon basin, from southern Peru to northwest Bolivia. It is found in lowland forests near bamboo and rivers.
Pimelodina flavipinnis is the only species of the genus Pimelodina of the family Pimelodidae of catfish.
Aguarunichthys is a genus of long-whiskered catfishes native to South America.

Hemiodontichthys is a monotypic genus of the family Loricariidae of catfish. Its only species is Hemiodontichthys acipenserinus.

The smooth-sided toad or spotted toad, formerly known as Bufo guttatus, is a species of toad in the family Bufonidae. It is found in the Amazonian Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, and Venezuela, as well as the Guianas. Specimens from southern Peru, Bolivia, and Brazil might represent Rhaebo ecuadorensis described in 2012.

The Amazon River frog is a species of frog in the family Ranidae that occurs in the northern and Amazonian South America east of the Andes, with scattered records from northeastern Brazil. In Spanish, it is known as rana verde verdadera. Its natural habitats are tropical rainforests near permanent waterbodies. It is not considered threatened by the International Union for Conservation of Nature. It is highly appreciated as food by the Ye’kwana of southeastern Venezuela.

The black-and-white antbird is a species of bird in the family Thamnophilidae. It is monotypic within the genus Myrmochanes. It is found in Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, and Peru. Its natural habitats are subtropical or tropical moist lowland forests and subtropical or tropical moist shrubland.

Acanthicus adonis, the adonis pleco or polka dot lyre-tail pleco, is a large species of armored catfish. It was originally described from the lower Tocantins River in Brazil, but individuals resembling the species have also been recorded from Amazonian Peru. The species is occasionally seen in the aquarium trade, but its massive adult size and territorially aggressive behavior means that a very large tank is required. These fish are opportunistic omnivores.

Ranitomeya amazonica is a poison dart frog in the genus Ranitomeya. It was first described by Rainer Schulte in 1999 as Dendrobates amazonicus when he separated it from Dendrobates ventrimaculatus, primarily on the basis of call characteristics. The validity of the species has been debated, but further studies, also including genetic data, support its validity.

A clearwater river is classified based on its chemistry, sediments and water colour. Clearwater rivers have a low conductivity, relatively low levels of dissolved solids, typically have a neutral to slightly acidic pH and are very clear with a greenish colour. Clearwater rivers often have fast-flowing sections.
Hypostomus pantherinus is a species of catfish in the family Loricariidae. It is native to South America, where it occurs in the Madeira River basin in Brazil. The species reaches at least 4.8 cm in standard length and is believed to be a facultative air-breather. Although originally described by Rudolf Kner in 1854 based on a single specimen from the Guaporé River basin in Brazil, Hypostomus pantherinus was redescribed in 2021 and its range was found to also include Bolivia.
References
- ↑ Fleck, David W.; Harder, John D. (1995). "Ecology of Marsupials in Two Amazonian Rain Forests in Northeastern Peru". Journal of Mammalogy. 76 (3): 809–818. doi:10.2307/1382749. JSTOR 1382749.
- ↑ Brown, Jason L.; Schulte, Rainer; Summers, Kyle (17 March 2006). "A new species of Dendrobates (Anura: Dendrobatidae) from the Amazonian lowlands in Perú". Zootaxa. 1152 (1): 45. doi:10.11646/zootaxa.1152.1.2.