
A calendar is a system of organizing days. This is done by giving names to periods of time, typically days, weeks, months and years. A date is the designation of a single and specific day within such a system. A calendar is also a physical record of such a system. A calendar can also mean a list of planned events, such as a court calendar, or a partly or fully chronological list of documents, such as a calendar of wills.

A year is the time taken for astronomical objects to complete one orbit. For example, a year on Earth is the time taken for Earth to revolve around the Sun. Generally, a year is taken to mean a calendar year, but the word is also used for periods loosely associated with the calendar or astronomical year, such as the seasonal year, the fiscal year, the academic year, etc. The term can also be used in reference to any long period or cycle, such as the Great Year.

Inventory or stock refers to the goods and materials that a business holds for the ultimate goal of resale, production or utilisation.
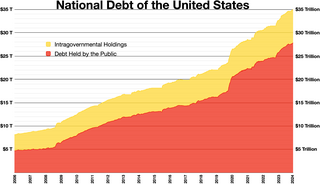
The national debt of the United States is the total national debt owed by the federal government of the United States to Treasury security holders. The national debt at any point in time is the face value of the then-outstanding Treasury securities that have been issued by the Treasury and other federal agencies. The terms "national deficit" and "national surplus" usually refer to the federal government budget balance from year to year, not the cumulative amount of debt. In a deficit year the national debt increases as the government needs to borrow funds to finance the deficit, while in a surplus year the debt decreases as more money is received than spent, enabling the government to reduce the debt by buying back some Treasury securities. In general, government debt increases as a result of government spending and decreases from tax or other receipts, both of which fluctuate during the course of a fiscal year. There are two components of gross national debt:
Stock valuation is the method of calculating theoretical values of companies and their stocks. The main use of these methods is to predict future market prices, or more generally, potential market prices, and thus to profit from price movement – stocks that are judged undervalued are bought, while stocks that are judged overvalued are sold, in the expectation that undervalued stocks will overall rise in value, while overvalued stocks will generally decrease in value. A target price is a price at which an analyst believes a stock to be fairly valued relative to its projected and historical earnings.
Financial analysis refers to an assessment of the viability, stability, and profitability of a business, sub-business or project.
Trailing twelve months (TTM) is a measurement of a company's financial performance used in finance. It is measured by using the income statements from a company's reports, to calculate the income for the twelve-month period immediately prior to the date of the report. This figure is calculated by analysts because quarterly and interim reports often show only income from the preceding 3, 6 or 9 months, not a full year; because they do not represent a full year, such data can be skewed by seasonal trading patterns, such as higher sales over Christmas, giving a less accurate picture of a company's fiscal health.

The term annual percentage rate of charge (APR), corresponding sometimes to a nominal APR and sometimes to an effective APR (EAPR), is the interest rate for a whole year (annualized), rather than just a monthly fee/rate, as applied on a loan, mortgage loan, credit card, etc. It is a finance charge expressed as an annual rate. Those terms have formal, legal definitions in some countries or legal jurisdictions, but in the United States:
Year-to-date (YTD) refers to the period starting from the beginning of the current year and continuing up to the present day.
A Form 10-K is an annual report required by the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), that gives a comprehensive summary of a company's financial performance. Although similarly named, the annual report on Form 10-K is distinct from the often glossy "annual report to shareholders", which a company must send to its shareholders when it holds an annual meeting to elect directors. The 10-K includes information such as company history, organizational structure, executive compensation, equity, subsidiaries, and audited financial statements, among other information.
In finance, return is a profit on an investment. It comprises any change in value of the investment, and/or cash flows which the investor receives from that investment over a specified time period, such as interest payments, coupons, cash dividends and stock dividends. It may be measured either in absolute terms or as a percentage of the amount invested. The latter is also called the holding period return.
A fiscal year is used in government accounting, which varies between countries, and for budget purposes. It is also used for financial reporting by businesses and other organizations. Laws in many jurisdictions require company financial reports to be prepared and published on an annual basis but generally with the reporting period not aligning with the calendar year. Taxation laws generally require accounting records to be maintained and taxes calculated on an annual basis, which usually corresponds to the fiscal year used for government purposes. The calculation of tax on an annual basis is especially relevant for direct taxes, such as income tax. Many annual government fees—such as council tax and license fees, are also levied on a fiscal year basis, but others are charged on an anniversary basis.
Same-store sales is a business term that refers to the difference in revenue generated by a retail chain's existing outlets over a certain period, compared to an identical period in the past, usually in the previous year. By comparing sales data from existing outlets that is, by excluding new outlets or outlets which have since closed, the comparison is like-to-like, and avoids comparing fundamentally incomparable data. This financial and operational metric is expressed as a percentage.
The 4–4–5 calendar is a method of managing accounting periods, and is a common calendar structure for some industries such as retail and manufacturing. It divides a year into four quarters of 13 weeks, each grouped into two 4-week "months" and one 5-week "month". The longer "month" may be set as the first (5–4–4), second (4–5–4), or third (4–4–5) unit.
Month-to-date (MTD) is a period starting at the beginning of the current calendar month and ending on either the current date or the last business day before the current date. Month-to-date is used in many contexts, mainly for recording results of an activity in the time between a date and the beginning of the current month.
Quarter-to-date (QTD) is a period starting at the beginning of the current quarter and ending at the current date. Quarter-to-date is used in many contexts, mainly for recording results of an activity in the time between a date and the beginning of either the calendar or fiscal quarter.
An accounting period, in bookkeeping, is the period with reference to which management accounts and financial statements are prepared.
Taxes in Germany are levied at various government levels: the federal government, the 16 states (Länder), and numerous municipalities (Städte/Gemeinden). The structured tax system has evolved significantly, since the reunification of Germany in 1990 and the integration within the European Union, which has influenced tax policies. Today, income tax and Value-Added Tax (VAT) are the primary sources of tax revenue. These taxes reflect Germany's commitment to a balanced approach between direct and indirect taxation, essential for funding extensive social welfare programs and public infrastructure. The modern German tax system accentuate on fairness and efficiency, adapting to global economic trends and domestic fiscal needs.
Flux Analysis is an accounting process used to identify and explain changes in financial statements over a specific period. It involves comparing financial data—such as account balances or line items—from one period to another, highlighting significant variances, and determining the reasons behind those changes. This method helps organizations understand the financial trends, operational impacts, and potential anomalies in their accounts, enabling better decision-making and financial planning.




