
Rabbi Binyamin "Benny" Elon was an Israeli Orthodox rabbi and politician who served as a member of the Knesset for Moledet and the National Union between 1996 and 2009. A ninth-generation Jerusalemite, Elon lived in Beit El, an Israeli settlement in the West Bank, for over twenty years, and was married to author and journalist Emuna Elon. They had six children. His father, Menachem Elon, was the former Deputy Chief Justice of Israel. His brother, disgraced Rabbi Mordechai Elon, has been a prominent controversial figure in the Religious Zionist Movement.

Pisgat Ze'ev is an Israeli settlement in East Jerusalem and the largest residential neighborhood in Jerusalem with a population of over 50,000. Pisgat Ze'ev was established by Israel as one of the city's five Ring Neighborhoods on land effectively annexed after the 1967 Six-Day War.

Beit El or Beth El is an Israeli settlement and local council located in the Binyamin Region of the West Bank. The Orthodox Jewish town was settled in 1977–78 by the ultranationalist group Gush Emunim. It is located in the hills north of Jerusalem, east of the Palestinian city of al-Bireh, adjacent to Ramallah. In September 1997, Beit El was awarded local council status. The head of the local council is Shai Alon. In 2022 its population was 6,108.
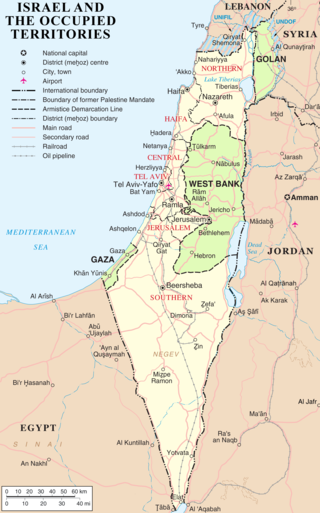
Israel has occupied the Golan Heights of Syria and the Palestinian territories since the Six-Day War of 1967. It has previously occupied the Sinai Peninsula of Egypt and southern Lebanon as well. Prior to 1967, control of the Palestinian territories was split between Egypt and Jordan, which occupied the Gaza Strip and the West Bank, respectively. The Israeli occupation of the Palestinian territories and the Golan Heights, where Israel has transferred parts of its population and built large settlements, is the longest military occupation in modern history.

Mercaz HaRav is a national-religious yeshiva in Jerusalem, founded in 1924 by Ashkenazi Chief Rabbi Abraham Isaac Kook. Located in the city's Kiryat Moshe neighborhood, it has become the most prominent religious-Zionist yeshiva in the world and synonymous with Rabbi Kook's teachings. Many Religious Zionist educators and leaders have studied at Mercaz HaRav.

The 97th Netzah Yehuda Battalion, previously known as Nahal Haredi is a battalion in the Kfir Brigade of the Israel Defense Forces. The purpose of the unit is to allow Haredi Jewish men to serve as combat soldiers in the Israeli military by creating an atmosphere conducive to their religious convictions in the strict observance of Halakha. The battalion has been accused of human rights violations against Palestinians, including killing unarmed civilians, killing suspects in custody, sexual assault and torture.
The Jewish Underground, or in abbreviated form, simply Makhteret, was a radical right-wing fundamentalist organization considered terrorist by Israel, formed by prominent members of the Israeli political movement Gush Emunim that existed from 1979 to 1984. Two issues catalyzed the establishment of the underground: One was the signing of the Camp David Accords, which led to the Egypt–Israel peace treaty in 1979, and which the movement, opposed to the peace process, wished to block, viewing it as the first step in the establishment of a Palestinian state in the West Bank. A second element was the settlement project, which, in bringing two distinct ethnic communities into closer proximity, led to an uptick in hostilities that brought about a growing emphasis on the existential threat in both communities. The Jewish Underground developed two operational objectives: One consisted of a plot to blow up the Dome of the Rock, while the other branch concentrated on both avenging acts of Palestinian violence against settlers and of establishing a punitive deterrence. Some understood the terrorist acts as a means of inducing Palestinians to flee their homeland, based on the 1948 and 1967 experience, and parallels are drawn to the Terror Against Terror movement, which had a similar aim. Robert Friedman stated that the Makhteret was "the most violent anti-Arab terrorist organization since the birth of Israel".

Hemdat is a community Israeli settlement in the West Bank located near the Palestinian hamlet of Khirbet Makhoul, in the Jordan River Valley on a plain at an altitude of 178 metres along the Allon Road in the municipal jurisdiction of the Bik'at HaYarden Regional Council. Other Israeli settlements in the area are Ro'i and Beka'ot. The closest city, Beit Shean, is a thirty-minute drive north of Hemdat. In 2022 it had a population of 361.

Uri Yehuda Ariel is an Israeli politician who formerly served as a member of the Knesset for The Jewish Home, and as Minister of Agriculture and Rural Development.
David Wilder is an American leader of Israeli settlers and the spokesman for The Committee of The Jewish Community of Hebron.
The Zionist Freedom Alliance (ZFA) is a Zionist movement that advocates Israel's moral, legal and historic rights for the Jewish people to the entire Land of Israel, which they consider to include the territory captured during the 1967 Six-Day War. It was established in 1999 by Magshimey Herut activists in response to what they perceived to be growing anti-Israel sentiment among young people throughout the world. ZFA claims that their narrative has not been presented since before the start of the Oslo peace process and that this has resulted in the world's ignorance of Israel's claim to all territory between the Mediterranean Sea and Jordan River. ZFA views Zionism as a revolutionary struggle and itself as the voice of Jewish national liberation. Its members are both religious and non-religious Jews.

Alon Shvut is an Israeli settlement in the West Bank, established in June 1970 over lands confiscated from the nearby Palestinian town of Khirbet Beit Zakariyyah. It is part of the Etzion bloc of the West Bank, administered by the Gush Etzion Regional Council, and neighbors the Israeli settlements of Kfar Etzion, Rosh Tzurim, Neve Daniel, Elazar, Bat Ayin, Migdal Oz, and Efrat. In 2022, its population was 3,046.

Mateh Yehuda Regional Council is a regional council in the Jerusalem District of Israel. In 2024 it was home to 51,125 people.

Beit HaArava is an Israeli settlement and kibbutz in the West Bank. Located near the Dead Sea and Jericho at the eponymous Beit HaArava Junction, the intersection of Highway 1 and Highway 90, it falls under the jurisdiction of Megilot Regional Council. In 2022 it had a population of 508.

Beit HaShalom, or the Rajabi House, also known as Beit HaMeriva, is a four-story apartment building located in the H-2 Area of Hebron, in the West Bank.

Beit Hagai, also Hagai, is an Israeli settlement organized as a community settlement located in the southern Hebron Hills in the West Bank. The settlement population was 460 in 2004, according to a classified government document published by the Haaretz newspaper, and lies within the municipal jurisdiction of the Har Hevron Regional Council. The religious Jewish community's name, Haggai, is an acronym of the given names Hanan Krauthammer, Gershon Klein, and Yaakov Zimmerman, three Nir Yeshiva students murdered in the 1980 Hebron terrorist attack. The community rabbi for Beit Hagai is Rabbi Moshe Eliezer Rabinovich (HaLevy). In 2022 it had a population of 725. The international community considers Israeli settlements in the West Bank illegal under international law, but the Israeli government disputes this.

Ras al-Amud is a Palestinian neighborhood in East Jerusalem, located southeast of the Old City of Jerusalem, overlooking the Palestinian neighborhoods of Silwan to the south and Abu Dis and al-Eizariya to the east, and bordering the Jewish neighborhood of Ma'ale HaZeitim to the north, which overlooks the Temple Mount. There were about 11,922 Arabs living in the neighborhood in 2003.
Od Yosef Chai, also known as Od Yosef Hai is a yeshiva situated in the West Bank settlement of Yitzhar. Od Yosef Chai includes several related institutions; a yeshiva high school, a yeshiva gedola, a kollel and the publishing house that released "The King's Torah", and other materials.
Hebrew Universalism is a religious, cultural, and political philosophy that synthesizes aspects of secular Jewish nationalism, Haredi non-Zionism, and Jewish humanism. It was initially formulated by the first Ashkenazi Chief Rabbi of British Mandatory Palestine, Abraham Isaac Kook, as a means of unifying Jewish civilization.

The VISION movement is a Hebrew Universalist political movement founded by American-born Israeli rabbi, West Bank settler, and Jewish Defense League veteran, Yehuda HaKohen.














